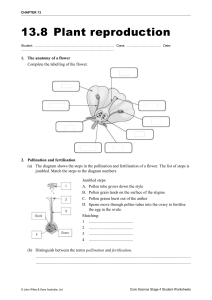
Science Home Explanations Biology Botany Your library Create Free trial Study sets, textbooks, ... chapter 38 bio - flowers questions Leave the first rating 10 studiers recently IN-CLASS Live STUDY 11) Meiosis occurs within all of the following flower parts except the Flashcards A) ovule. B) style. Learn C) megasporangium. D) anther. Write E) ovary. Spell Test Click card to see definition 👆 Previous ← Next → Match Flip 11/52 Gravity Space Created by Kierra_Johnson12 Terms in this set (52) 1)The products of meiosis in A) spores plants are always which of the following? A) spores B) eggs C) sperm D) seeds E) both B and C 2) Which of the following is the A) sporophyte-meiosis-gametophyte-gametes- correct sequence during fertilization-diploid zygote alternation of generations in a flowering plant? A) sporophyte-meiosisgametophyte-gametesfertilization-diploid zygote B) sporophyte-mitosisgametophyte -meiosissporophyte C) haploid gametophyte gametes-meiosis-fertilizationdiploid sporophyte D) sporophyte-spores-meiosisgametophyte-gametes E) haploid sporophyte -sporesfertilization-diploid gametophyte 3) Which of the following is true B) Meiosis occurs in sporophytes to produce spores. in plants? A) Meiosis occurs in gametophytes to produce gametes. B) Meiosis occurs in sporophytes to produce spores. C) The gametophyte is the dominant generation in flowering plants. D) Plants exist continually as either sporophytes or gametophytes. E) Male game tophytes and female gametophytes have the same structure. 4) All of the following are D) a small (reduced) sporophyte. features of angiosperms except A) a triploid endosperm. B) an ovary that becomes a fruit. C) animal pollination. D) a small (reduced) sporophyte. E) double fertilization. 5)Based on studies of plant E) receptacle evolution, which flower part is not a modified leaf? A) stamen B) carpel C) petal D) sepal E) receptacle 6)All of the following floral C) sepal. parts are directly involved in pollination or fertilization except the A) stigma. B) anther. C) sepal. D) carpel. E) style. 7)A mutation in which of the E) either C or D following floral parts would have the greatest impact on C) stamen pollination? D) carpel A) sepal B) petal C) stamen D) carpel E) either C or D 8)A mutation in which of the E) either C or D following floral parts would have the greatest potential C) stamen impact on fertilization? D) carpel A) sepal B) petal C) stamen D) carpel E) either C or D 9) Which of the following is the D) sepals-petals-stamens-carpels correct order of floral organs from the outside to the inside of a complete flower? A) petals-sepals-stamenscarpels B) sepals-stamens-petalscarpels C) spores-gametes-zygote embryo D) sepals-petals-stamenscarpels E) male gametophyte -female gametophyte-sepals-petals 10) All of the following are B) photosynthesis. primary functions of flowers except A) pollen production. B) photosynthesis. C) meiosis. D) egg production. E) sexual reproduction. 11) Meiosis occurs within all of B) style. the following flower parts except the A) ovule. B) style. C) megasporangium. D) anther. E) ovary. 12) A perfect flower is fertile, E) It has both stamens and carpels. but may be either complete or incomplete. Which of the following correctly describes a perfect flower? A) It has no sepals. B) It has fused carpels. C) It is on a dioecious plant. D) It has no endosperm. E) It has both stamens and carpels. 13) Carpellate flowers E) develop into fruits. A) are perfect. B) are complete. C) produce pollen. D) are found only on dioecious plants. E) develop into fruits. 14) Which of the following A) dioecious types of plants is not able to self-pollinate? A) dioecious B) monoecious C) complete D) wind-pollinated E) insect-pollinated 15) In flowering plants, pollen is A) anther. released from the A) anther. B) stigma. C) carpel. D) filament. E) pollen tube. 16) In the life cycle of an D) microsporocyte angiosperm, which of the following stages is diploid? A) megaspore B) generative nucleus of a pollen grain C) polar nuclei of the embryo sac D) microsporocyte E) both megaspore and polar nuclei 17) Where does meiosis occur E) megasporocyte and microsporocyte in flowering plants? A) megasporocyte B) microsporocyte C) endosperm D) pollen tube E) megasporocyte and microsporocyte 18) Which of the following is a C) meiosis-pollination-nuclear fusion-formation of correct sequence of processes embryo and endosperm that takes place when a flowering plant reproduces? A) meiosis-fertilizationovulation-germination B) fertilization-meiosis-nuclear fusion-formation of embryo and endosperm C) meiosis-pollination-nuclear fusion-formation of embryo and endosperm D) growth of pollen tube pollination-germinationfertilization E) meiosis-mitosis-nuclear fusion-pollen 19) Which of these is incorrectly A) anthergametophyte paired with its life-cycle generation? A) anthergametophyte B) pollengametophyte C) embryo sac gametophyte D) stamensporophyte E) embryosporophyte 20) Which of the following is E) microsporocyte-meiosis-microspores -mitosis- the correct sequence of events two haploid cells per pollen grain in a pollen sac? A) sporangiameiosistwo haploid cellsmeiosistwo pollen grains per cell B) pollen grainmeiosistwo generative cells two tube cells per pollen grain C) two haploid cellsmeiosisgenerative celltube cell-fertilizationpollen grain D) pollen grainmitosismicrosporesmeiosis generative cell plus tube cell E) microsporocyte-meiosismicrospores -mitosis-two haploid cells per pollen grain 21) Which of the following B) A megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis. occurs in an angiosperm ovule? A) An antheridium forms from the megasporophyte. B) A megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis. C) The egg nucleus is usually diploid. D) A pollen tube emerges to accept pollen after pollination. E) The endosperm surrounds the megaspore mother cell. 22) Where and by which C) mitosis in male gametophytes process are sperm produced in plants? A) meiosis in pollen grains B) meiosis in anthers C) mitosis in male gametophytes D) mitosis in the micropyle E) mitosis in the embryo sac 23) In which of the following B) embryo sac female gametophyte pairs are the two terms equivalent? A) ovule egg B) embryo sac female gametophyte C) endospermmale gametophyte D) seedzygote E) microsporepollen grain 24) Which of the following is C) pollen grain the male gametophyte of a flowering plant? A) ovule B) microsporocyte C) pollen grain D) embryo sac E) stamen 25) In flowering plants, a C) two sperm nuclei and one tube cell nucleus. mature male gametophyte contains A) two haploid gametes and a diploid pollen grain. B) a generative cell and a tube cell. C) two sperm nuclei and one tube cell nucleus. D) two haploid microspores. E) a haploid nucleus and a diploid pollen wall. 26) Within the female A) three antipodal cells, two polar nuclei, one egg, gametophyte, three mitotic and two synergids. divisions of the megaspore produce A) three antipodal cells, two polar nuclei, one egg, and two synergids. B) the triple fusion nucleus. C) three pollen grains. D) two antipodal cells, two polar nuclei, two eggs, and two synergids. E) a tube nucleus, a generative cell, and a sperm cell. 27) The largest cell(s) of the D) central cell. typical angiosperm embryo sac is (are) the A) egg cell. B) antipodals. C) synergids. D) central cell. E) microsporocyte. 28) In modern agriculture, what C) introduction of genes into a plant that prevent its does "terminator technology" seeds from maturing refer to? A) introduction of bacterial genes that release insect toxins into plants B) introduction of male sterility genes into plants to prevent selfing C) introduction of genes into a plant that prevent its seeds from maturing D) Bt genes produced in maize pollen E) selection of resistant clones following mutator treatment of seeds 29) Flowers are made of C) leaves. modified A) roots. B) stems. C) leaves. D) ovules. E) shoots. 30) Which of these is unique to D) double fertilization flowering plants? A) a dominant sporophyte generation B) an embryo surrounded by nutritive tissue C) haploid gametophytes D) double fertilization E) pollen production 31) What is the relationship D) Pollination brings gametophytes together so that between pollination and fertilization can occur. fertilization in flowering plants? A) Fertilization precedes pollination. B) Pollination easily occurs between plants of different species. C) Pollen is formed within megasporangia so that male and female gametes are near each other. D) Pollination brings gametophytes together so that fertilization can occur. E) If fertilization occurs, pollination is unnecessary. 32) Recent research has shown B) the rejection of self cells. that pollination requires that carpels recognize pollen grains as "self or nonself." For selfincompatibility, the system requires A) rejection of nonself cells. B) the rejection of self cells. C) carpel incompatibility with the egg cells. D) that the flowers be incomplete. E) the union of genetically identical sperm and egg cells. 33) In plants, which of the A) genetic variation following could be an advantage of sexual reproduction as opposed to asexual reproduction? A) genetic variation B) mitosis C) stable populations D) rapid population increase E) greater longevity 34) Which of the following is E) It produces clones. true about vegetative reproduction? A) It involves both meiosis and mitosis to produce haploid and diploid cells. B) It produces vegetables. C) It involves meiosis only. D) It can lead to genetically altered forms of the species. E) It produces clones. 35) Which of the following is a C) Making cuttings of ornamental plants is a form of true statement about clonal fragmentation. reproduction in plants? A) Clones of plants do not occur naturally. B) Cloning, although achieved in animals, has not been demonstrated in plants. C) Making cuttings of ornamental plants is a form of fragmentation. D) Reproduction of plants by cloning may be either sexual or asexual. E) Viable seeds can result from sexual reproduction only. 36) The integuments of an C) form a seed coat ovule function to do what? A) protect against animal predation B) ensure double fertilization C) form a seed coat D) both A and B E) both A and C 37) A fruit includes E) both A and B A) one or more seeds. B) the ovary wall. C) fleshy cells rich in sugars. D) brightly colored pigments to attract animal dispersers. E) both A and B 38) A fruit is a (an) A) mature ovary. A) mature ovary. B) mature ovule. C) seed plus its integuments. D) fused carpel. E) enlarged embryo sac. 39) Which of the following B) imbibition conditions is needed by almost all seeds to break dormancy? A) exposure to light B) imbibition C) abrasion of the seed coat D) exposure to cold E) covering of fertile soil 40) What is typically the result C) Both a diploid embryo and triploid endosperm of double fertilization in are formed. angiosperms? A) The endospe rm develops into a diploid nutrient tissue. B) A triploid zygote is formed. C) Both a diploid embryo and triploid endosperm are formed. D) Two embryos develop in every seed. E) The fertilized antipodal cells develop into the seed coat. 41) Which of the following D) It develops from the fertilized egg. statements regarding the endosperm is false? A) Its nutrients may be absorbed by the cotyledons in the seeds of eudicots. B) It develops from a triploid cell. C) Its nutrients are digested by enzymes in monocot seeds following hydration. D) It develops from the fertilized egg. E) It is rich in nutrients, which it provides to the embryo. 42) In angiosperms, products E) proembryo and the cotyledons. of the terminal cell become the A) suspensor. B) proembryo. C) cotyledons. D) suspensor and the proembryo. E) proembryo and the cotyledons. 43) Which of the following B) It forms the suspensor that anchors the embryo. statements is correct about the basal cell in a zygote? A) It develops into the root of the embryo. B) It forms the suspensor that anchors the embryo. C) It results directly from the fertilization of the polar nuclei by a sperm nucleus. D) It divides and initiates the two cotyledons. E) It forms the proembryo. 44) What is the embryonic root D) radicle called? A) plumule B) hypocotyl C) epicotyl D) radicle E) shoot 45) A plant that has small, D) wind-pollinate green petals is most likely to be A) bee -pollinated. B) bird-pollinated. C) bat-pollinated. D) wind-pollinate 46) Pollen grain is to ________ as A) male gametophyte; embryo sac ________ is to female gametophyte. A) male gametophyte; embryo sac B) embryo sac; ovule C) ovule; sporophyte D) anther; seed E) petal; sepal 47) A seed develops from C) an ovule. A) an ovum. B) a pollen grain. C) an ovule. D) an ovary. E) an embryo. 48) Fruits develop from D) ovaries. A) microsporangia. B) receptacles. C) fertilized eggs. D) ovaries. E) ovules. 49)The first step in the C) imbibition of water. germination of a seed is usually A) pollination. B) fertilization. C) imbibition of water. D) hydrolysis of starch and other food reserves. E) emergence of the radicle. 50) When seeds germinate, the A) obtain a dependable water supply. radicle emerges before the shoot. This allows the seedling to quickly A) obtain a dependable water supply. B) mobilize stored carbohydrates. C) protect the emerging coleoptile. D) avoid etiolation. E) initiate photosynt hesis. 51) Regardless of where in the E) graft varietal Burgundy grape scions onto native world a vineyard is located, in (Californian) root stocks. order for the winery to produce a Burgundy, it must use varietal grapes that originated in Burgundy, France. The most effective way for a new California grower to plant a vineyard to produce Burgundy is to A) plant seeds obtained from French varietal Burgundy grapes. B) transplant varietal Burgundy plants from France. C) root cuttings of varietal Burgundy grapes from France. D) cross French Burgundy grapes with native American grapes. E) graft varietal Burgundy grape scions onto native (Californian) root stocks. 52) The most immediate D) increasing crop yield. potential benefits of introducing genetically modified crops include A) increasing the amount of land suitable for agriculture. B) overcoming genetic incompatibility. C) increasing the frequency of self-pollination. D) increasing crop yield. E) both B and C Recommended textbook explanations Biology Nelson Science Perspectives 10 1st Edition Kenneth R. Miller, Levine 1st Edition Christy C. Hayhoe, Doug Hayhoe, Jeff Major, ... 2,470 explanations 1,359 explanations Science Fusion Texas, Grade5: New Energy for... Biology 1st Edition Stephen Nowicki HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT 478 explanations 1,895 explanations 1/6 Subjects Features Help About Language Arts and Humanities Quizlet Live Help Center Company English (USA) Languages Quizlet Checkpoint Honor Code Blog Math Quizlet Learn Community Guidelines Press Science Explanations Teachers Careers Social Science Flashcards Advertise Other Mobile Privacy Upgrades Ad and Cookie Policy Terms © 2022 Quizlet Inc. Profi