G8-Q3-WK-5-6-Determine-the-number-of-protons-neutrons-and-electrons-of-an-atom-for-students-revised
advertisement

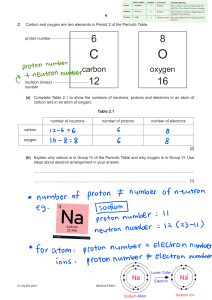
SCIENCE 8 Protons, Neutrons and Electrons Quarter 3 Week 5-6 Most Essential Learning Competency: Determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom S8MT-IIIe-f-10 Department of Education • Republic of the Philippines Science– Grade 8 Alternative Delivery Mode Quarter 3 – Week 5-6: Protons, Neutrons and Electrons First Edition, 2021 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this book are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Published by the Department of Education Secretary: Undersecretary: Assistant Secretary: Author: Veronica P. Ventura and Reyneth Renan Matta Editor: Rebecca M. Roxas, EPS-Science Reviewer: Rogelio A. Yag-at – HT VI Management and Development Team School Division Superintendent: Maria Magdalena M. Lim, CESO V Chief Education Supervisor: Aida H. Rondilla CID Education Program Supervisor: CID – LRMDS Librarian II: Lady Hannah C. Gillo CID – LRMDS PDO II: Albert James P. Macaraeg HOW TO USE THIS MODULE Before starting the module, I wa nt yo u to set aside other tasks that will disturb yo u while enjoying the lessons. Read the simple instructions below to successfully e njoy the objectives of this kit. Have fun! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Follow carefully all the contents and instructions indica ted in every page of this module. Write on yo ur notebook the concepts about the lessons. Writing enha nces learning that is important to develop and keep in mind. Perform all the provided activities in the module. Let your facilitator/guardian assess your a ns wers using the answer key card. Analyze conceptually the post-test and apply what yo u ha ve learned. PARTS OF THE MODULE • • • • • • • • Expectations – These are what yo u will be able to know after completing the lessons in the module. Pre-test – This will measure your prior knowledge and the concepts to be mastered througho ut the lesson. Looking Back to Your Lesson - This section will measure what learnings and skills you understood from the previous lesson. Brief Introduction – This section will give you an overview of the lesson. Activities – This is a set of activities that you will perform with a partner. Remember – This section summarizes the concepts and applications of the lessons. Check your understanding – It will verify how you learned from the lesson. Post-test – This will measure how m uc h yo u have learned from the entire module. WEEEK 5: PROTONS, NEUTRONS AND ELECTRONS EXPECTATIONS In this lesson, you will gain deeper understanding of protons, neutrons and electrons. Specifically, this module will help you to: Determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom; Describe the identity of a substance according to its atomic structure; and Calculate the atomic number and atomic mass of an atom. PRE-TEST Directions: Multiple Choice. Read the statements below then choose the letter of the BEST answer. 1. The smallest particle of an element is called a/an ________. a. proton b. neutron c. electron d. atom 2. It is a subatomic particle found within the nucleus and is positively charged. a. proton b. neutron c. electron d. atom 3. It is a subatomic particle found outside the nucleus and is negatively charged. a. proton b. neutron c. electron d. atom 4. It is a subatomic particle found within the nucleus and has no charge. a. proton b. neutron c. electron d. atom 5. The proton, neutron and electron is collectively called _________. a. subatomic particles b. subatomic parts c. subatomic structure d. subatomic charges LOOKING BACK TO YOUR LESSON PARTS OF THE ATOM The nucleus of an atom contains the protons and neutrons while the electrons are located outside the nucleus in the electron cloud and are found orbiting the atom in an orbital. The structure of an atom https://otrasteel.blogspot.com/2017/07/31-label-parts-of-atom.ht ml The charges of protons, neutrons and electrons of an atom varies. Protons are positively charged and is symbolized as p+ , neutrons have no charge and is symbolized as no and electrons are negatively charged and is symbolized as e- . This will be discussed further as we go along the module. BRIEF INTRODUCTION The atom is the smallest particle of an eleme nt. Protons, neutrons and electrons make-up the composition of atoms. Collectively, they are called subatomic particles. Using the periodic table of elements, the subatomic particles in a given atom can be computed. The Periodic Table of Elements Retrieved at https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/periodic -table/ PROTONS To determine the number of protons of an atom, locate the atomic number of a given element on the periodic table. The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons in the nucleus gives the identity of an element. No. of Proton = Atomic Number Take the Helium element as an example, the atomic number of Helium (He) is 2. Therefore, the number of protons found in the nucleus of Helium is also 2. Helium Retrieved from Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. All rights reserved. ELECTRONS The number of electrons is determined using the atomic number. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the atomic number. Because the atom is neutral in charge, the positive and negative charges are equal to one another. No. of Electron = Atomic Number Using Helium as an example, the atomic number of Helium is 2, making the number of electrons of Helium 2 as well. NEUTRONS The number of neutrons is calculated by subtracting the number of protons found in the nucleus from the mass number. The mass number is usually located below the element symbol in the periodic table of elements. No. of Neutrons = Mass number – No. of protons or No. of Neutrons = Mass number – Atomic number ACTIVITIES Activity 1. Complete Me! Directions. Using the Periodic Table of Elements, determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom to complete the table below. Element Element Atomic Mass No. of No. of No. of Symbol Number Number Protons Neutrons Electrons Neon Ne Phosphorus P Sodium Na Pb Ytrium Argon 20 8 16 15 31 (no) 8 8 82 207 (e-) 15 24 Y Copper Boron 10 (p+) 13 11 50 39 35 29 82 89 29 B 5 11 5 5 C 6 12 6 6 18 40 22 Activity 2: Locate Me! A. Table Completion. Directions. Complete the table below. Sub-atomic Particle Symbol Charge Location in the Atom Proton Neutron Electron B. Fill in the blanks. Directions. Use your knowledge of the periodic table of elements to answer the following: 1. Give the number of protons in one atom of: Lithium Krypton Iron 2. Give the number of neutrons in one atom of: Vanadium Silicon ______ 3. Give the number of electrons in one atom of: Mercury Arsenic REMEMBER 1. The ATOMIC NUMBER is equal to the number of PROTONS and ELECTRONS in an atom. You can use the acronym A.P.E. as a guide to remember the concept. ATOMIC NUMBER = PROTON = ELECTRON 2. The number of NEUTRONS is computed by subtracting the number of PROTONS from the MASS NUMBER. NEUTRONS = MASS NUMBER - PROTONS CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING Directions: Fill in the blanks with the appropriate term to complete the statement below. Choose your answers from the word box. 4. The three particles of the atom and their respective charges are: a. b. c. 5. The atomic number tells you the number of in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of in a neutral atom of that element. The atomic number gives the “identity “of an element as well as its location on the Periodic Table. No two different elements will have the atomic number. WORD BOX: Same Protons Electrons Positive No Charge Protons Negative Electrons Neutrons POST TEST 1. An atom of an element is electrically neutral because the a. Number of protons equals the number of electrons b. Number of protons equals the number of neutrons c. Number of neutrons equals the number of electrons d. Number of atoms equals the number of electrons 2. The element Lithium has an atomic number of 3. It also has ____ number of protons: a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 3. There are the same number of these two particles in an atom a. protons and neutrons b. protons and electrons c. neutrons and electrons REFERENCES Nerd, Alicia. 2017. Label the Parts of an Atom. Retrieved at https://otrasteel.blogspot.com/2017/07/31-label-parts-ofatom.html on February 15, 2021 Encyclopedia Brittanica Inc. Helium. Retrieved at https://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=https%3A%2F%2Fcdn.britannica.com%2 F98%2F22398-050-BDC6E4E4%2Felement-helium-symbol-square-propertiessomeperiodic.jpg&imgrefurl=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.britannica.com%2Fscience%2Fh elium-chemical-element&tbnid=7MVeOkwNblGRoM&vet=12ahUKEwiunYPB9juAhVE6JQKHUlzC_wQMygIegUIARDhAQ..i&docid=WYJ0gcgO7QcJCM&w=16 00&h=1068&q=element&ved=2ahUKEwiunYPB9juAhVE6JQKHUlzC_wQMygIegUIARDhAQ Youngker, Andrew. 2018. How to Calculate Subatomic Particles Retrieved at https://sciencing.com/calculate-subatomic-particles-8221603.html on February 14, 2021 PubMed. National Library of Medicine. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Periodic Table of Elements. Retrieved at https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/periodic-table/ on February 14, 2021. Atomic Structure Worksheet. Atomic Structure Packet. Retrieved at https://www.washoeschools.net/cms/lib/NV01912265/Centricity/Domain/1130/Ato mic%20Structure%20Packet.doc