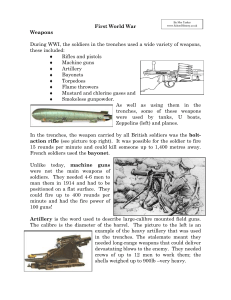
Military History Terms General Terms artillery: cannons and large guns casualties: the total number of killed, wounded, captured, and missing soldiers in a battle/conflict cavalry: soldiers on horseback cease-fire agreement: an agreement to stop fighting, but it is not a peace treaty, the two sides are still at war Conventional Warfare: A form of warfare that is conducted by regular, uniformed and national military units and uses ordinary (not nuclear) military weapons and battlefield tactics. flank: the side or edge of a military formation Guerilla Warfare: A form of fighting carried on through hit-and-run raids, ambushes, and other surprise attacks by soldiers who don't wear uniforms and hide by blending in with the local population infantry: soldiers who fight on foot World War I Terms Arms Race: a competition between nations to have the most powerful weapons barrage: a focused artillery bombardment over a wide area belligerent: a country engaged in war blockade: the use of troops or ships to prevent commercial traffic from entering or leaving a city or region commercial vessels: ships used for trade that transport products to make a profit contraband: illegal traffic, smuggled goods front: an area of conflict between opposing armies International Law: rules of conduct agreed upon by all nations, of one nation to another, both in peace & war1 mobilize: prepare military forces for war munitions: military weapons, ammunition, and equipment neutral: not favoring either side in a dispute No Man's Land: area between trenches shells: an explosive artillery projectile or bomb stalemate: a deadlock in which neither side is able to defeat the other Trench Warfare: Fighting with trenches, mines, and barbed wire. Horrible living conditions, great slaughter, minimal/no gains, stalemate. Unrestricted Submarine Warfare: the use of submarines to sink without warning any ship (including neutral ships and unarmed passenger liners) found in an enemy's waters World War II Terms beachhead: first position on a beach secured by an invading force & used to land further troops & supplies Blitzkrieg: "Lighting war," fast-moving attack to quickly breakthrough enemy lines & overwhelm defenders bomber: a plane used to drop bombs embargo: an official ban on trade or other commercial activity with a particular country escort zone: an area in which commercial ships are protected by military vessels from submarine attack fighter: a plane that attacks other aircraft and/or protects bombers fire raid: a bombing attack designed to burn down large portions of a city indemnity: a payment for damage or loss Island Hopping: a strategy that involves selectively attacking specific enemy-held islands & bypassing others paratrooper: a soldier who is trained to jump out of a plane using a parachute theater: a large geographic area in which military operations are coordinated Unconditional Surrender: giving up to an enemy without any demands or requests 1 Taken from a speech given by former U.S. President William Howard Taft at Union College, Schenectady, N.Y., on 13 June 1917.