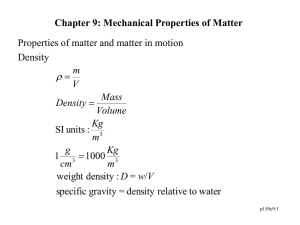
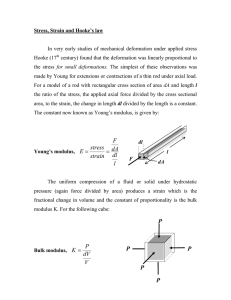
1. Annealing point – It is the temperature at which n = 10.35P and internal stresses can be relieved in about 15 mins. 2. Brittle fracture – Ceramics and glass undergo a fracture when subjected to a tensile test and don’t undergo plastic deformation. 3. Chemically strengthened glass – when the silicate network in silica glass undergoes stress periodically it produces strong glass. 4. Cold working – plastic deformation occurring well before one half times the melting point 5. Creep – can be defined as plastic deformation occurring at high temperature over constant load and over a large period of time. The creep curve explains that plastic deformation occurs with relation to time. 6. Critical Resolved sheer stress – when the tow value is big enough to cause a slip by dislocation motion, then it is called that. (Applied force is needed to cause this deformation) . 7. Critical shear stress – is one order of magnitude less than bulk shear modulus. Theoretical stress level for shearing a crystal in the absence of dislocations. 8. Cross linking – joining of adjacent, linear polymeric molecules by chemical bonding. 9. Dislocation climb – a mechanism for creep deformation, in which the dislocation moves to an adjacent slip plane by diffusion. 10. Ductility – Deformability 11. Dynamic modulus of elasticity – parameter representing the stiffness of a material under an oscillating load. 12. Elastomer – a polymer with a rubbery plateau in the elasticity vs temperature graph 13. Engineering strain – increase in sample length under a load divided by sample length without any stress 14. Engineering stress – load on a material divided by original sample area. 15. Flexural modulus – stiffness of a material as measured in bending. 16. Flexural strength – failure stress on a material as measured in bending. 17. Gage length – Region of minimum cross-sectional area in a mechanical test specimen. 18. Glass transition temperature – The temperature above which the glass becomes a supercooled liquid and also a range below it where it is a rigid solid. 19. Griffith crack model - Prediction of stress intensification at the tip of a crack in a brittle material. 20. Hooke’s Law – is the linear relation between stress and strain during elastic deformation. 21. Lower yield point – the onset of plastic deformation in a low carbon steel 22. Melting range – temperature range at which the viscosity of glass is b/w 50 and 500 p. 23. Modulus of elasticity – slope of the stress strain curve in the elastic region 24. In bending – failure stress of a material as measured in bending 25. Modulus of rigidity – Elastic modulus under pure shear loading 26. Plastic deformation – permanent deformation associated with distortions and reformation of atomic bonds through chemical bonding. 27. Poisson’s ratio – Mechanical Property indicating the contraction perpendicular to extension caused by tensile stress. 28. Relaxation time – the time taken for the stress on a polymer to go below the initial applied stress 29. Residual stress – the stress remaining with a structural material after all the applied loads are removed. 30. Resolved shear stress – stress operating on a slip system. 31. Rockwell hardness – common mechanical parameter 32. Shear Modulus – Elastic modulus under pure shear loading 33. Shear strain – elastic displacement caused by pure shear loading. 34. Shear stress – load per unit area 35. Slip system – a combination of families of crystallographic planes and directions that correspond to dislocation motion 36. Softening point - Temperature at which glass has a viscosity of 10^7 P, corresponding to the lower end of the working point 37. Softening temperatures – the temp at which the material in a heat expansion experiment can no longer support the weight of length monitoring probe 38. Solution hardening – Fortification of a material associated with restriction of plastic deformation due to solid solution formation 39. Specific strength – strength per unit density 40. Strain hardening – the strengthening of a metal alloy by deformation 41. Strain hardening exponent – the slop of a log -log true stress vs true strain plot between plastic deformation and the onset of necking 42. Stress relaxation – mechanical phenomena where stress reduces exponentially with time under a constant strain 43. Tempered glass – heat treatment that serves to place the exterior surface in a residual compressive state 44. Tensile strength – the maximum stress experienced by a material during a tensile test 45. Toughness = total area under stress strain curve, upper yield point – distinct break from the elastic region in the stress strain curve for a low carbon steel 46. Upper yield point – mechanical behavior involving both solid like and fluid like behavior 47. Working range – temp range at which glass products are formed 10^4-8 48. Slope of stress strain curve in the elastic region – young’s modulus. Formula sheet