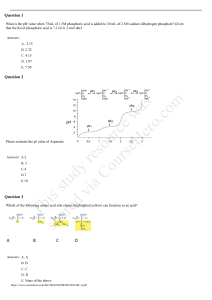
Case Study – PB is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m P.B., a 64-year-old housewife and grandmother, is admitted to the emergency department by ambulance with burns sustained when her gas furnace exploded when she was relighting a pilot light. She is awake and oriented but very agitated and frightened and cannot remember the accident. She is having severe pain in her face and upper chest. She also is shivering and complains of being cold, and her voice is raspy. Her hair and eyebrows are singed, and she has mixed areas of red, fluid-filled vesicles and waxy, white skin involving her face, anterior neck, all of her right arm, dorsal aspect of her left arm, and anterior chest and abdomen. Her heart rate is 132 beats/min, respiratory rate is 36 breaths/min, and a thigh blood pressure is 110/52 mm Hg. P.B.'s past medical history is positive for a myocardial infarction at age 50 with resultant chronic heart failure. Her current medications are as follows: quinapril (Accupril) 20 mg daily, furosemide (Lasix) 20 mg daily, and pravastatin (Pravachol) 40 mg daily. 1. As you initiate care for P.B., activities during this emergent phase should be prioritized. Sequence the activities according to priority with the corresponding interventions Administer IV morphine. Administer IV fluids.3 Administer 100% humidified O2. 1. Administer tetanus prophylaxis. Establish an IV access. 2. Initiate appropriate wound care. Insert an indwelling urinary catheter. Prepare for nasotracheal or endotracheal intubation. sh Th Estimate body surface area burned. This study source was downloaded by 100000778630909 from CourseHero.com on 12-09-2021 08:02:23 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/68519557/Case-Study-PB-Student-worksheet-doc/ 2. In the emergency department you carefully assess and observe P.B. Which finding would be most concerning? Edema in upper airway, 3. Fluid replacement is initiated for P.B. using the Parkland formula. She reports that she weighs about 120 lb. To monitor and evaluate her fluid replacement, you review the formula for estimating the rate of fluid replacement. (Know mun browder & rule of nines) is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m A. Using the Rule of Nines chart, you estimate the extent of deep partial-thickness and full-thickness burns as _36__%. B. You calculate that P.B. should receive about _3827______ ml of fluid in the first 8 hours after the time of injury. 3900. (491 ml/hr) 4. As fluid therapy is being initiated for P.B., you monitor her condition closely. You prioritize assessment for which complication during this period? Pulmonary edema. 5. P.B. rapidly develops edema in burned as well as nonburned areas. You realize that her edema Is r/t burned shock. Hypovolemic shock sh Th 6. After starting fluid replacement via a central subclavian catheter, the physician intubates P.B. with an orotracheal endotube. She is transferred to the burn unit where an arterial line and nasogastric tube are placed. Her face burns will be treated with the open method while the rest of her burns will be treated with impregnated sterile gauze dressings. Select all the appropriate interventions you would plan for P.B. during this emergent phase of her burns. There are ten correct answers. Daily wt, v/s, I/O, pain, keep pt warm, mental status changes, This study source was downloaded by 100000778630909 from CourseHero.com on 12-09-2021 08:02:23 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/68519557/Case-Study-PB-Student-worksheet-doc/ 7. During the emergent phase when P.B. is intubated, she becomes very agitated and anxious, groping around with her arms. You may alleviate her distress by: is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Tell her this is temporary and develop a form of communication with her & use non verbal communication. 8. Twenty-four hours after P.B.'s admission to the burn unit, eschar begins to develop over her burned areas. You monitor the radial pulse in her right arm, recognizing that an escharotomy may be indicated to prevent Compartment syndrome 9. P.B. has had serial laboratory tests for the past 3 days to determine adequacy of fluid replacement and the onset of the acute phase of the burn injury. Match the correct laboratory findings to the phase of burn injury. Emergent or Acute Phase. Hgb, Laboratory Findings Hct 40% Th Urine-specific gravity 1.038- emergent sh Serum K+ 6.1 mEq/L (6.1 mmol/L)- emergent Serum K+ 3.6 mEq/L (3.6 mmol/L)- acute Urine-specific gravity 1.018- acute This study source was downloaded by 100000778630909 from CourseHero.com on 12-09-2021 08:02:23 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/68519557/Case-Study-PB-Student-worksheet-doc/ Hct 54%- emergent Serum Na+ 145 mEq/L (145 mmol/L)- acute Hb 10.7 g/dl (107 g/L)- emergent Serum albumin 3.6 g/dl (36 g/L)- emergent Serum Na+ 130 mEq/L (130 mmol/L)- emergent is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m 10. Because of the location of P.B.'s burns and the treatment required, she is taken to the operating room for surgical debridement of her wounds. The majority of her chest and arm burns are deep partial-thickness burns, and about 30% of the burns on her face and abdomen are full-thickness burns. The physician applies sheet autografts from her thighs to the areas of full-thickness burns. Following the application of the grafts, which statement by P.B. indicates the need for further patient teaching? a. “I am glad that these skin grafts will help to minimize scar formation." b. "I hope to see lots of clots under the skin grafts to prevent me from bleeding too much." c. "It is so nice to know that the surgeon scraped all the dead burnt tissue off of me." d. "It will be nice to have freedom from pain with this new skin graft." Th 11. In the acute phase of burn management, P.B. is at risk for stress-related complications. You carefully monitor her for signs and symptoms of __gastric__(Curling’s)_______ulcer and an increase in serum_glucose___levels. sh 12. You are working with a nursing assistant. Which nursing activity included in the care plan is best delegated to nursing assistive personnel (NAP) (select all that apply)? a. Empty and record P.B.'s hourly urine output. b. Reapply sequential compression devices following P.B.'s bath. c. Assess P.B.'s pain relief following administration of morphine. This study source was downloaded by 100000778630909 from CourseHero.com on 12-09-2021 08:02:23 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/68519557/Case-Study-PB-Student-worksheet-doc/ d. Administer subcutaneous insulin based on P.B.'s capillary blood glucose reading. 13. P.B.'s endotracheal tube is removed as her edema subsides, but she is withdrawn and refuses to participate in self-care. She tells you that she would rather die than look like she does. An appropriate approach for you to use in helping P.B. with her grieving is to a. encourage her to talk about her fears regarding her disfigurement and loss of function. b. assure her that as the wounds heal, she will have little or no scarring and deformity. is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m c. encourage her family to visit frequently and tell her that her appearance isn't important. sh Th d. explain that if she doesn't perform the prescribed exercises and activities, contractures will develop that will limit her function even more. This study source was downloaded by 100000778630909 from CourseHero.com on 12-09-2021 08:02:23 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/68519557/Case-Study-PB-Student-worksheet-doc/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)