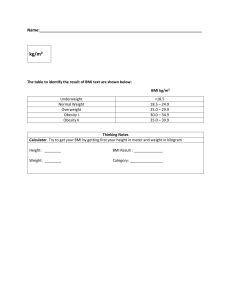
Subjective data: 89-year-old female patient came in due to lack of appetite as claimed by her daughter. Objective data:Patient was a known case of Hypertension and Hypothyroidism and is on maintenance medications namely Metropolol 12.5 mg per day and Synthroid 075mg per day.Patient had lost weight of 10lbs for the last 3 months. Patient was not carrdiorespiratoy distress as vital signs were normal. Patient was noted to have dry oral mucosa, bleeding gums and poor skin turgor. In summary,subjective data are data from the patient's point of view or known as symptoms including feelings, perceptions and concerns while objective data are observable and measurable signs obtained by the examiner through inspection and physical examination. 1. What two (2) nursing diagnoses can be derived from the problems list? a. Dehydration b. Iron Deficiency Anemia 1. What should be included in the plan of care? a.Urge the patient to drink prescribed amount of fluid. Oral fluid replacement is indicated for mild fluid deficit and is a cost-effective method for replacement treatment. Older patients have a decreased sense of thirst and may need ongoing reminders to drink. Being creative in slecting fluid sources (e.g., flavored gelatin, frozen juice bars, sports drink) can facilitate fluid replacement. Oral hydrating solutions (e.g., Rehydralyte) can be considered as needed. b. Aid the patient if he or she is unable to eat without assistance, and encourage the family or SO to assist with feedings, as necessary. Dehydrated patients may be weak and unable to meet prescribed intake independently. c. If patient can tolerate oral fluids, give what oral fluids patient prefers. Provide fluid and straw at bedside within easy reach. Provide fresh water and a straw. Most elderly patients may have reduced sense of thirst and may require continuing reminders to drink. The nursing interventions for a patient with iron deficiency anemia are: Administer prescribed medications, as ordered: · Administer IM or IV iron when oral iron is poorly absorbed. · Perform sensitivity testing of IM iron injection to avoid risk of anaphylaxis. · Advise patient to take iron supplements an hour before meals for maximum absorption; if gastric distress occurs, suggest taking the supplement with meals — resume to between-meals schedule if symptoms subside. · Inform patient that iron salts change stool to dark green or black. · Advise patient to take liquid forms of iron via a straw and rinse mouth with water. Reduce fatigue · Stress the importance of frequent rest periods. · Monitor hemoglobin, hematocrit, RBC count, and reticulocyte counts. · Educate energy-conservation techniques. · Encourage patient to continue iron therapy for a total therapy time (6 months to a year), even when fatigue is no longer present. Educate the patient and caregivers about iron deficiency anemia: · Explain the importance of the diagnostic procedures (such as complete blood count), bone marrow aspiration and a possible referral to a hematologist. · Explain the importance of iron replacement/supplementation. · Educate the client and the family regarding foods rich in iron (organ and other meats, leafy green vegetables, molasses, beans). 1. Calculate the patient's body mass index. BMI= weight/(height)² BMI=19.8 Normal 1. How many calories a day does this patient need to maintain her current weight? Explain your answer. The patient needs 1200kcal/day to maintain her current weight because she has a sedentary lifestyle which means only the amount of activity necessary to support independent living. 1. Discuss three (3) laboratory studies that would help determine the patient's nutritional status. Explain your answer. a. Electrolytes — especially sodium and potassium — and how well your kidneys are working. b. Urinalysis. Tests done on your urine can help show whether you're dehydrated and to what degree. c. Complete blood count (CBC) is a group of tests that evaluate the cells that circulate in blood, including red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets (PLTs). The CBC can evaluate your overall health and detect a variety of diseases and conditions, such as infections, and iron deficiency anemia. @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ 1. Develop a problems list from the objective and subjective data. Subjective: *Poor appetite as claimed by daughter. Rationale: The patient came to the office with her daughter who presented and expressed a concern that her mother has not been eating well. Objective: * Weight reduction Rationale: Weight loss was indicated as evidenced by the differential and substantial decrease in weight of patient from 115 pounds to 105 pounds since the last visit which was three months ago. -Patient presented with Dehydration Rationale: Patient have poor skin turgor and dry oral mucus which is an indication of decrease in body fluid volume, fluid volume deficit or possible dehydration. -Body Weakness Rationale: Daughter shops for her mom as she no longer drives. She is eighty nine years old which raises her risk for decreased muscle strength which may lead to body weakness or ambulation difficulty. -Poor Appetite Rationale: Patient had been taking 0.75 mg of Synthroid every day. This medication is indicated for Hypothyroidism. One reason for loss of appetite in the elderly could be thyroid issues. In this case, the patient suffers from Hypothyroidism. Also -Loneliness or Depression Rationale: Based on research, the elderly are more prone to social isolation and depression. The lives alone and she also cooks her meals. This increases risk of her feeling depressed. 2. The following Nursing Diagnoses can be stipulated from this case: Imbalance Nutrition Activity Intolerance Fluid Volume Deficit 3. *Frequent assessment of patient weight should be done. Rationale: It will help us to have a baseline for caloric and nutrient requirement needed to be consumed by the patient, which then will guide us the necessary therapeutic nursing interventions to be given. * Assess patient's feelings and perspective of her diet. Rationale: We can provide nutritional plan for the patient based on her eating perspective. Patient's may have different perspective toward food type, preparation or handling. Health care personnel must be knowledgeable of these factors to improve patient's nutritional status. * Collaborate with a dietitian for complete nutritional assessment and to obtain medical suggestion or opinions to the nutritional status of the patient. Rationale: Collaboration with other health care professional is necessary to obtain more medical knowledge regarding the patient. It also facilitate our goals geared towards achievement of patient's holistic health status. * Provide good oral hygiene. Rationale: Patient already have gum bleeding and dentures loose, thus it is necessary to provide dental care always. It also help increase appetite and taste on food. * Patient lacks strength so we can schedule rest periods before meals. Rationale: Assistance of patient's activities of daily living may be done. Providing rest periods before meals may help regain patient's strength before the actual meal. 4 The patient’s BMI is 19.8 kg/m2 which is normal. To compute for body mass index you can use either International System of Units (SI) or the US customary system (USC). FORMULA using SI, Metric Unit: BMI = mass (kg) / height2 (m) Patient's Data: Weight: 105 lb Height: 5 feet, 1 inch *Convert first weight in pounds (lb) to kilograms (kg) and the height in feet and inch to meters (m) Weight in kilograms: 47.627kg Height in meters: 1.549m *Then proceed with the solution using the given formula: BMI = mass (kg) / height2 (m) BMI = 47.627 / 1.549 2 BMI = 47.627 / 2.399401 BMI = 19.8 kg / m2 * Patient's BMI is 19.8 kg/m2 which is normal. * Here is another method to solve for BMI FORMULA using USC Units: BMI = 703 × mass (lbs) / height2 (in) Patient's Data: Weight: 105 lb Height: 5 feet, 1 inch * Convert first the patient height in feet to inches. Height in inches: 61 inches *Then proceed with the solution using the given formula: BMI = 703 × mass (lbs) / height2 (in) BMI = 703 × 105 / 61 2 BMI = 703 × 105 / 3721 BMI = 73,815 / 3721 BMI = 19.8 kg / m2 Either of the two can be use as long as you have patient's data such as height and weight. Both formula will arrive with the same answer. 5. How many calories a day does this patient need to maintain her current weight? Based on research, active or sedentary women elderly are advised to have 1,600 to 2000 calories daily, or up to 2,600 if usually active. Patient 24-hour diet reveals approximately 1100-calorie intake only, which is below the normal calory intake for elderly. Additional 500 calories at least, should be consumed by the patient to maintain her current weight. Failure to do so may lead to further weight loss. 6. What laboratory studies would help determine the patient's nutritional status? * Albumin * Transferrin * Prealbumin * Retinol-binding protein