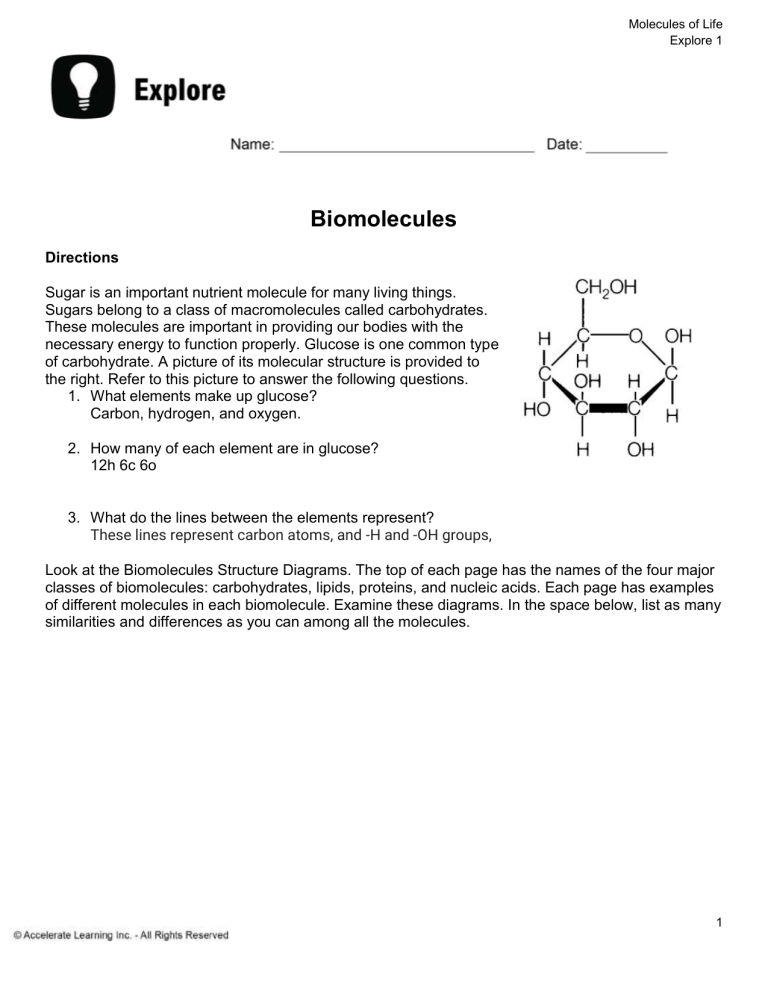
Molecules of Life Explore 1 Biomolecules Directions Sugar is an important nutrient molecule for many living things. Sugars belong to a class of macromolecules called carbohydrates. These molecules are important in providing our bodies with the necessary energy to function properly. Glucose is one common type of carbohydrate. A picture of its molecular structure is provided to the right. Refer to this picture to answer the following questions. 1. What elements make up glucose? Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. 2. How many of each element are in glucose? 12h 6c 6o 3. What do the lines between the elements represent? These lines represent carbon atoms, and -H and -OH groups, Look at the Biomolecules Structure Diagrams. The top of each page has the names of the four major classes of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Each page has examples of different molecules in each biomolecule. Examine these diagrams. In the space below, list as many similarities and differences as you can among all the molecules. 1 Molecules of Life Explore 1 Similarities Differences Glucose sucrose and cellulose are all made up They are shaped differently. of Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Carbon. Proteins and nucleic acid have nitrogen Cholesterol, Saturated fatty acid, and unsaturated fatty acid are all made up of the same elements. Methionine has sulfur Nucleic acids have phosphorus All of the biomolecules have “H” and “O” Most of them seem to have “H” “O” and “C” Glucose is a common monosaccharide, which is a base unit, or monomer, of all carbohydrate molecules. Glucose is a very important monosaccharide, because it is the type of sugar used by the body for energy. Look at the glucose molecule and compare it with the rest of the biomolecules. 4. Is glucose more or less complex than the rest of the biomolecules? Explain. It looks more simple than other biomolecules. It is a monosaccharide so there is only one structure. 5. Look at sucrose, a disaccharide, and cellulose, a polysaccharide, on the carbohydrate page. How do you think these two molecules were formed? It looks like two glucose units bonded 2 Molecules of Life Explore 1 together for the disaccharide and three for the polysaccharide. 6. Look at DNA, a polymer, and nucleotide, a monomer, on the nucleic acid page. There are sugar molecules within these structures. How many sugar molecules are in DNA and the nucleotide? The basic building block of DNA (nucleotide) contains one sugar molecule and there are four nucleotides in DNA. 7. Look at all the molecules on the carbohydrate and lipid pages. What is a specific similarity and difference between the lipid and carbohydrate molecules? They all contain Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen. They are all shaped differently, the carbohydrates are single and bonded sugar molecules. 8. Look at the molecules on the protein page. How do you think glucose could be used to synthesize these molecules? It looks like the proteins have nitrogen so if you added nitrogen to the glucose, all of the elements of protein would be present. 9. If an animal does not consume glucose, how is the body still able to obtain the energy needed for cell processes? The body could synthesize glucose from other carbohydrates. 3




