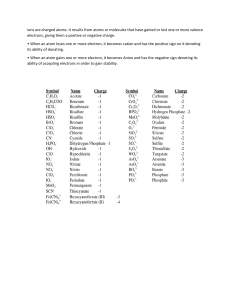
1 Chapter-2 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical bonding: The force by which two (or more) atoms are held together to form a stable molecule. Chemical bond Why do atoms participate in chemical bonding ? Reason: The elements with unstable electronic configuration participate in chemical bonding to attain stable electronic configuration. How do the atoms form chemical bonds and attain stable electronic configuration? Ans: The atoms having unstable electronic configuration lose or gain electrons or share electrons with other atoms to attain stability. What is stable electronic configuration? If an element has 8 electrons in its valence shell (outer most orbit) or completely filled valence shell then it is said to have stable electronic configuration. e.g : Noble gases posses stable electronic configuration. Noble gas Electronic configuration K L M N Helium 2 Neon 2 8 Argon 2 8 8 Krypton 2 8 18 8 Since the noble gases have stable electronic configuration they do not participate in chemical bonding hence they are inert. Helium has duplet configuration i.e. 2 electrons in valence shell Noble gases other than Helium have octet configuration i.e. 8 valence electrons. “The elements with unstable electronic configuration tend to attain the stable electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas by either electron transfer or sharing electrons”- Octet rule Stable electronic configuration (stability) is attained by an in the following ways: i) By electron transfer between two atoms- Electrovalent bond ii) By the mutual sharing of electrons between the atoms- Covalent bond ICSE CHEMISTRY for Class X www.icsechemistry16.blogspot.com https://icsechemistry16.blogspot.com 2 Electrovalent bond (or) Ionic bond: The transfer of electron/s between the atoms with a higher difference in their electronegativity values leads to the formation of Electrovalent bond. Covalent bond : The mutual sharing of electrons between the atoms whose electronegativity difference is negligible results in a Covalent bond. Electrovalent bond (or) Ionic bond :The electrostatic force of attraction which binds two or more oppositely charged ions formed by the transfer of electron/s from the metal atom to the non metal atom. Electrovalent compound: The compounds formed as a result of the transfer electrons. Electrovalency: The number of electrons lost or gained by an atom of an element to attain stability. The electrovalent bond is possible between a metal and a non metal. The metal atom atom loses electron/s to nonmetal atom so that the metal and the nonmetal attain stable electronic configuration. As the metal loses electron/s it is oxidized and forms a cation (positive ion). Oxidation: Na – e- Na+ Mg – 2e- Mg2+ The non metal atom accepts electron/s and it is reduced to form an anion (negative ion). Reduction: Cl2 – 2e- 2ClO2 – 4e- 2O2Formation of Electrovalent (Ionic) Compounds: Example 1 Sodium chloride ( NaCl): Sodium is a metal with electronic configuration 2,8,1 – has one valence electron. Chlorine is a non metal with electronic configuration 2,8,7 – has 7 valence electrons. Sodium has to lose one electron from its valence shell to attain the electronic configuration of its nearest noble gas (Neon) i.e. 2, 8. Chlorine has gain one electron for the electronic configuration of its nearest noble gas (Argon) i.e 2,8,8 Hence Sodium loses its one electron from the valence shell to the chlorine atom. Representation of Sodium Chloride using electron dot structures ICSE CHEMISTRY for Class X www.icsechemistry16.blogspot.com https://icsechemistry16.blogspot.com 3 Example 2 Magnesium Oxide (MgO) Mg – electronic configuration is 2, 8, 2- it loses 2 electrons O – electronic configuration is 2,6 – it has to gain two electrons. One Magnesium atom donates two electrons to the Oxygen atom. Example 3 Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2) Mg – 2,8,2 – Mg atom has to lose 2 electrons and Cl – 2,8,7 – each Chlorine atom requires one more electron to get the stable electronic configuration. Hence Mg atom donates one electron to each chlorine atom. Covalent bond: The bond formed by the mutual sharing of electron pairs between the given pairs of atoms (of same or different kind) of non metals. Covalent compound (molecule) : The compounds (molecules) formed as a result of mutual sharing of electrons between the atoms are called covalent compounds. Covalency: The number of electron pairs that an atom shares with other atom/s to get stable electronic configuration. The element which has 7 valence electrons (i.e. short of one electron for octet configuration) contributes one electron and shares one pair of electron with other atom. Cl - 2,8,7 Cl - 2,8,7 Chlorine molecule single covalent bond The element having 6 valence electrons (short of 2 electrons) contributes 2 electrons hence shares two pairs of electrons. ICSE CHEMISTRY for Class X www.icsechemistry16.blogspot.com https://icsechemistry16.blogspot.com 4 Oxygen 2,6 Oxygen molecule Double bond Similarly the element with 5 valence electrons contributes 3 electrons and shares three pairs of electrons. Nitrogen 2,5 Oxygen 2,6 Nitrogen 2,5 Nitrogen molecule Formation of Hydrogen molecule Formation of Methane molecule (CH4) Triple bond Formation of Carbon tetra chloride molecule (CCl4) ICSE CHEMISTRY for Class X www.icsechemistry16.blogspot.com https://icsechemistry16.blogspot.com 5 Formation of Water molecule: - Two single bonds - Two lone pairs Formation of Ammonia molecule - Three single bonds - One lone pair Lone pair: The pair of electrons which is not involved in any bond formation. Co-ordinate covalent bond (or) Dative bond: The bond formed by the sharing of electron pair between two atoms where one atom contributes both the electron. Example 1 : Formation of Hydronium ion [H3O+]: represents the co-ordinate covalent bond between Oxygen atom and Hydrogen where both the electrons coming from Oxygen atom but being shared by Oxygen and Hydrogen. This is due to the lone pair effect of Oxygen atom in water molecule. Hydromium ion : 1-dative bond and 2 covalent bonds. Example 2: Formation of Ammonium ion [NH4+]: Ammonium ion : 1- dative bond and 3- covalent bonds. ICSE CHEMISTRY for Class X www.icsechemistry16.blogspot.com https://icsechemistry16.blogspot.com 6 Polar covalent and non polar molecules Polar molecules 1. Due to the electronegativity difference between the atoms the electrons are distributed unequally which leads to charge separation. 2. Example: HCl, H2O , NH3 etc. Non-polar molecules 1. There is no charge separation since the electron pair is equally distributed between the atoms. 2. Example: H2, Cl2, O2, N2, CCl4, CH4 etc Charge separation in Hydrogen chloride molecule: In HCl molecule Chlorine is more electronegative than Hydrogen so the electron pair is more strongly attracted by Chlorine atom due this a slight negative charge is developed on Chlorine and a slight positive charge on Hydrogen atom. Hence it becomes a polar compound. Comparison between Ionic compounds and Covalent compounds: Ionic compounds Covalent compounds 1. As the ions in ionic compounds are 1. In these compounds the molecules are held by the strong electrostatic force of have weak Vander waal’s forces so attraction they : they: Exist in solid state Exist as soft solids, liquids and gases. Are non volatile Are non- volatile Have high boiling and melting points Have low boiling and melting points. 2. These compounds undergo 2. Polar covalent compounds undergo dissociation and become free in their ionization in their aqueous solutions molten or aqueous solution form hence and produce free ions so they conduct they conduct electricity. electricity in aqueous solutions. They are non conductors in Non-polar compounds do not solid state because the ions are undergo ionization so they are not free. non-conductors. e.g. CCl4 3. These can be electrolysed in their 3. Polar covalent compounds can be molten state or aqueous solutions. electrolysed in their aqueous solutions. 4. Soluble in water. 4. Polar compounds are soluble in polar solvents like water. Non polar compounds are soluble in non polar solvents like Benzene 5. Reactions between ionic compounds 5. Covalent compounds undergo slow take place rapidly in their solutions reactions because they have to break since they produce free ions easily. the bonds and form new bonds. ICSE CHEMISTRY for Class X www.icsechemistry16.blogspot.com https://icsechemistry16.blogspot.com