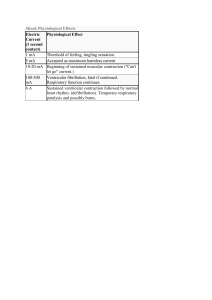
MEDICAL NOTES: - 3 MOST IMPORTANT ORGANS OF THE HUMAN BODY: - 1. BRAIN 2. HEART 3. LUNGS MYOCARDIUM (the heart itself, which contracts) THE 2 ATRIA THE 2 VENTRICLES CONDUCTION SYSTEM The MAIN job of pumping blood is in VENTRICLES BRAIN: - - This organ is EXTREMELY vulnerable without OXYGEN, irreversible damage in it occurs within 5-7 minutes RESPIRATORY CENTER Gives commands to inhale and exhale and stopes when the brain begins to lack oxygen. In the absence of a patient’s breathing, resort to ARTIFICIAL RESPIRATION NOTE: - Even with non-functional atria a person can live LUNGS: - - Gas exchange occurs Through the thin walls of alviol and capillaries, oxygen enters the bloodstream, and carbon dioxide from the blood enters the lungs and exhale. Things that will affect this process: -Oxygen concentration -Airway state -Lung diseases -Blood pressure - HEART: - The cardiac conduction system is responsible for the generation and transmission of electrical signals that cause the heart to contract. The impulse is generated in the SINOATRIAL NODE, then spreads throughout the heart. First, the ATRIA contract, then the impulse is slightly delayed in AV NODE, then passes through PURKINJE FIBERS, which causes a reduction in ventricles. NOTE: - - - In case the sinoatreous node does not work, impulses are generated by an AV node or even Purkinje fibers. - Cells of the Cardiac Conduction System generate impulses at a certain intervals of time. Sinoatrial node has the HIGHEST generation frequency; AV node (60 pulses); Purkinje Fibers (40 pulses) per minute Since the frequency of the impulses of the SA node is greater, the impulses passing from it depolarize the remaining cells and prevent them from generating their impulses. PERICARDUM (heart bag) - - This study source was downloaded by 100000797520967 from CourseHero.com on 12-15-2021 23:16:20 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/86334660/444490967-Medical-Notesdocx/ - As soon as the SA node turns off, the AV node starts generating pulses with its own frequency. - - Multiple pulse sources occur in the atria The atria and ventricles contract independently. The heart continues to perform the pumping function NO THREAT TO LIFE ECG (ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY) CARDIAC ARREST - - - - - A way to monitor the heart’s impulses If you connect 2 electrodes to a person’s hands, then they will receive voltage from the impulses in the heart. It is possible to connect electrodes in different ways P – ATRIAL CONTRACTION QRS – VENTRICULAR CONTRACTION T- VENTRICULAR RELAXATION When the signal goes to the electrode, we see a positive voltage, when from – negative - - SINUS RHYTHM When the impulse comes out of the sinus node and the heart beats with the same frequency - - - These are conditions in which the heart does not perform the pumping function or performs very weakly. TYPES OF CARDIAC ARREST: VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (90% OF CASES) ASYSTOLE (7%) ELECTROMECHANICAL DISSOCIATION (A RARE CONDITION) VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION Is a chaotic contraction of ventricular regions, without real pericablation of the blood. May due to exhaustion of the heart resource due to ischemia. Multiple impulses circulate the ventricles and the heart does NOT work simultaneously. “HEART FAILURE” THE PATIENT IS DYING VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA Similar condition, usually the initial stage of fibrillation, while the ventricles still maintain some kind of rhythm. IT IS NECESSARY TO TAKE URGENT MEASURES ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Condition of the heart in which the atria contract very often and erratically. - This may occur due to various reasons, such as ISCHEMIA (lack of oxygen) of the heart This study source was downloaded by 100000797520967 from CourseHero.com on 12-15-2021 23:16:20 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/86334660/444490967-Medical-Notesdocx/ - ASYSTOLE A condition which there is no electrical activity in the heart On the ECG, we see a line The chances of saving a patient with asystole are much lower than a patient with ventricular fibrillation - - 1. To cope with ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, defribillation is NEEDED - NOTE: - - A defibrillator is a device that sends a strong impulse through the heart. Such impulse for a moment drowns out all the chaotic electrical activity and there is a chance that the heart will return to sinus rhythm - IF ECG – asystole or small wave ventricular fibrillation – defibrillation is prohibited and meaningless. First, it is necessary to raise the resource of the heart so that a large fibrillation appears and only then defibrillate - as soon as fibrillation and tachycardia of the ventricles began, it is necessary to start CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION (CPR) and immediately carry out defibrillation, use drugs. - Blood pressure is the pressure in the arteries. SYSTOLIC (at the time of contraction of the heart) DIASTOLIC (at the moment, between heartbeats) 120/80 IS CONSIDERED NORMAL But different people may be different. 2. - Arterial blood saturation (oxygenation) (Sp02) - Below 60% = loss of consciousness - With this value of Sp02, organs, first of all, the heart and brain slowly begins to die. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation consists of chest pressures for pumping blood, artificial lung ventilation, defibrillation, and drug administration. BLOOD VESSELS: 2 MAIN CHARACTERISTICS: This study source was downloaded by 100000797520967 from CourseHero.com on 12-15-2021 23:16:20 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/86334660/444490967-Medical-Notesdocx/ oxygen -NOTES: It is measured using a PULSOXIMETER attached to a finger or ear. Sp02blood is an estimate the amount - It- means saturationofwith oxygen of oxygen rate in the - The normal is blood 95-99% - Below 90% = problems NOTE: - with This study source was downloaded by 100000797520967 from CourseHero.com on 12-15-2021 23:16:20 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/86334660/444490967-Medical-Notesdocx/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)