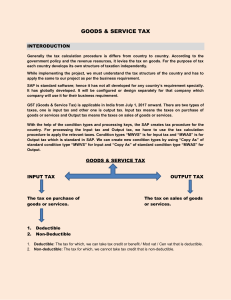
VC ERP Consulting Topics: Basics of ERP, SAP and Accounting Presented by Shivam Thakar Flow of Presentation Introduction of ERP Why ERP in Business? Introduction of SAP Business One Features and Functionalities of SAP Business One Process of Procurement Process of Sales Process of Manufacturing Introduction of GST Introduction of TDS Introduction of TCS Basics of Chart of Accounts What is ERP? • ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning • To manage and integrate the important parts of businesses • Focus on one business area , but work together by using same data to meet company’s needs • Finance, Accounting, Human Resources, Sales, Procurement, Logistic and Supply chain are components of ERP • Combines all data across departments into a single database that can be accessed by all employees Why ERP used in Business? • For expanding business, reduce costs and improve operations • Improves accuracy and productivity • Time saving • Help in planning , budget , forecast decisions • Quick access for employees • All branches of organisation at one database What is SAP Business one? • SAP Business One is ERP software • Designed for small and medium sized enterprise • Owned by German company SAP SE • Aims to automate key business function like finance, human resources and operations • Available in Microsoft Windows based product • Now available in mobile and tablets which are iOS and Android supported Features of SAP Business One: • Financial • Sales • Services • Purchase • Stock • Manufacturing Functionalities of SAP Business One: Administration Banking CRM Financial Opportunities Sales Purchase Business Partners Inventory Resources MRP ( Material Resource Planning ) Production Project Management Service Human Resources Reports Process of Procurement Identify Goods or Service Record for Audit Explore and select Vendors Pay for Goods or Service Submit Purchase Requisition Receive Order Create Purchase order Process of Sales Approach the client Discover clients need Provide a solution Close the sale Complete the sale and follow up Process of Manufacturing Raw Material Disposal/ Production Process Recycle Manufacturing Delivery Packaging What is GST? • GST stands for Goods and Service Tax • GST Act passed in parliament on 29th march 2017 and implemented on 1st July , 2017 • It replaced many indirect taxes like Value Added Tax (VAT) , Excise duty , service tax etc. • It is levied on supply of Goods and Services • It is multi-stage, destination-based tax that is levied on every value addition Objective of GST • ‘One Nation, One Tax’ • Subsume majority of indirect taxes • Eliminate the cascading effect of taxes (set off tax credits) • To increase the taxpayer base • Online easy procedures • Improved logistic and distribution system(e-way bill, reduce documentation process) Components of GST • CGST (Central Goods and Service Tax) • SGST (State Goods and Service Tax) • IGST (Integrated Goods and Service Tax) • UTGST (Union Territory Goods and Service Tax) What is TDS? • Stands for Tax Deducted at Source • 1% , 2% , 5% , 10% is the rate of TDS and this is implemented as per income tax section 192 and 194 • One kind of advance tax • TAN (Tax deduction Account Number) is used in any TDS related issues • Only online payment Form used in Return • Form 24Q :- Salary • Form 26Q :- Non Salary • Form 26QB :- TDS on Property • Form 27Q :-Other than the salary to Non Resident TDS Certificate • Form 16 :- Salary • Form 16A :- Non Salary • Form 16B :- TDS on property How TDS process happened? Step 5 Step 4 Step 3 Step 2 Step 1 • Payer Deducts tax from payment • Payer deposit tax to Government • Payer files return of TDS • Payer issues TDS Certificate to Payee • Payee claims refund of TDS in his ITR What is TCS? • Stand for Tax Collected at Sources • Collected by an E-commerce operator for provide goods and services on the online platform • Charged as percentage on the net taxable supplies • It dealt under section 52 of the CGST Act • Who own, operate and manage e-commerce platforms are liable to collect TCS • 0.5 % CGST and 0.5% SGST or 1% IGST is rate of TCS • IGST and CGST will payable to the central Government • SGST will payable to state government • It should be deposited to the government within 10 days in end of month • Hotel accommodation , clubs, transportation of passengers and housekeeping are exceptions Chart of Accounts • All the financial accounts in the general ledger • Helps reader to locate specific accounts • Revenue , Expenditure , Equity, Assets and Liabilities are the Chart of Accounts • Balance sheet and Income-Expense account of any company Chart of Accounts Revenue Expenditure Equity Assets Liabilities Chart of Accounting Revenue • Sales • Other Incomes Expenditure • • • • • • Advertising Bank charge Depreciation Rent Insurance Operating expenses Assets • • • • • • Fixed assets Goodwill Patents Cash Bank Accounts receivables • Stock Liabilities • Accounts payable • Bank loan • Income tax payable Equity • Capital • Drawings • Reserve and surplus How to prepare Profit and Loss statement? • Collect information about Revenue and expenses • List sales • List of Cost of Goods Sold (Purchase + Opening stock - closing Stock Purchase Return) • Gross Profit = Total Revenue - COGS • List your all expenses • EBITDA= Gross Profit - All expenses • EBIT= EBITDA - Depreciation – Amortization • EBT= EBIT – Interest • Net Profit = EBT – Tax How to prepare Balance sheet? Step 1: Pick the balance sheet date Step 2: List all of your assets Step 3: Add up all of your assets Step 4: Determine current liabilities Step 5: Calculate long-term liabilities Step 6: Add up Liabilities Step 7: Calculate Owner’s Equity Step 8: Add up liabilities and owner’s equity Thank You