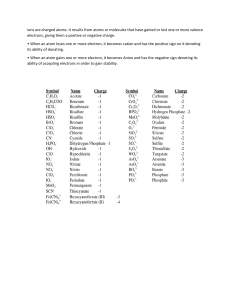
chemistry YOU CAN DO IT . Done by Fatima : Alameri Shortest between 2 * distance waves frequency [u) number of Per Seco ne waves ④ wavelength DO the that pass Yun [HZ] it " from org in crest & frequency " " origin NOT affect to OR to " trough amplitude wave Stthomas Fength → frequency Common properties f¥÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷ ⑦ transverse waves .. \ l ' , \ L G - - ] quantum ⑦ electromagnetic could be of only energy or Flame When radiation emitted quanta in " discrete units " . test . metal ions arehe§pfsftTTd - exited - here Y Atomic Emission ÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷f¥÷÷i Atomic Absorption spectrum spectrum :÷÷÷÷÷÷ "" - when exited energy atom release their . " the wavelength absorbed = Wavelength " emitted 102 Bohr 's atomic - L model ⑧ ⑧ CAN & I WILL Ground state the lowest energy level Bohr represented each * Quantum # of orbital expressed orbit n each by " by g.anthem atom farther from " the gain energy newdes = more energy " number rn Electron :i of the hydrogen atom transitions " " n =3 Exited state when . i:c:::÷÷÷::: . when the limitations of Bohr model electron . . 1 Bohr’s model explained the atomic . emission spectrum of HYDROGEN. when the energy of the electron release to But he didn’t explain why other elements have unique emission spectra. : n =3 Bohr’s model seemed to prove that Could have different energy levels. But it didn’t explain why these specific energy levels existed . Bohr’s model identified the placement of some electrons. But it didn’t explain why atoms behave the way they do chemically. Compare electron n / cloud energy of the release to 1. 2 Louis de Broglie any moving particle Quantum Whole act numbers orbit the like of machanical electrons that - will an nucleus wavelength a WAVE atom only . . in - . Heisenberg you CANNOT uncertainty principle with interact or measure withoutdisturbingit.it impossible an object that it is sates velocity # position the exact particle f at ⑤ the only the quantity be measured for pro billing in de - predicts → wavelength wave charters tics ) a . can I occupy to . I ② - - I -1 . constant ①Photon interact ② Both veocity MV ↳ that - equation plank 's I. =h_ ✓ region that all moving Particles have of is : ② Broglie know time electron an certain a same to velocity + with position an are electron at rest modified mass Quantum ④ Machaut cat model |made Schrodinger apply on ⑤I by I , " exepte all elements HYDROGEN ↳ s - %t J's •o - of the equation give the probability finding electron at ↳ given point . ma q¥_E jpg Ig Dls S 1. 2 orbital atomic - 90% probility to find electrons closer to the neucless , & 10% outside . arms . 0 less chance ! ) Principle quantum - describe the , * as you energy move sublevel # Ma . S spherical p shape dumbell d out increase - ⑧ relative ' " "" F 4 number f . the size µ) Principle Energy energy level sub level ( ) n How the total - ' - 2 2 3- 3 4 4- - s Sp Spd spdf " Ex :3 25 35 each orbital have only 2 3px,3py,3pz 4px,4pyx.4pz ( - Np de Forbis d) [ can hold -7 - the Z Px orbits oppiste f . - up to / Py / ] 2 electrons [ Pz " P can hold upto 6 electrons] " +2 (sohu.is/-7dxy/dyZ/dxz/dx2-y/dz a) do the electron have to be . 11 orbit /¥ • - electrons AO 4s . " . 32=92 2py,2pz Zpx , levels energy (X. y ) S orbitals ? "" ①axiofP " of amount " - A I know can each electron will BET.sn: it ' [ " " f- hold up to 14] go is:: orbitals ' (p ] hold upto 20 electron configuration - ← arrangement of Aufbal from the electrons principle largest less to come befors energy * note " it 3d have 4S higher energy ' . - lowest energy d electron configuration highest energy Hydrogen * atomic number : I . Electrons I * Electron configuration * * outermost highest shell energy her : orbital notation : * Velence → * Shell : 11 highest principle * Blocks : energy S b because of 1501 : I : 2g 2- the " - electron electron configuration of NITROGEN ④ orbital notation : FTII Ipx ⑦ electron configuration When I have d block Vel ence shell add dts electrons to get shell (highest * . 15 25 - - 2py Zpz ②p3 \ Priciple energy level : . 2 the Vel ence . ⑦ Vetere electrons : 5 ceseuyons ④ electron ⑤ Block :p dot diagram : N: *i; ji i: :÷¥÷÷÷i hydrogen so have subtract the electron 2 electrons it from configuration . electron configuration of Neon * electrons : 10 configuration : 25 2p6 * electron 15 * - - Orbital notation : ' * velence Shell : 2 * Valence electrons : 8 *Block : P * Nobad [ He] gas " * Electron - - notation : 2ps dot : : - structure : electron *electrons : * electron 17 configuration 15-25 - * orbital configuration 2ps - : 35 3ps - notation : 7¥ Px Py Pz * velence shell : 3 * velence electrons : 7 * block : P * herbal [ Ne] gas 35 - notation : 3ps *electron dot structure : : ÷, n . of chlorine Exceptaliens of electrons configurations 4S III . 3d IB one will move 3d to If each it one from 451 because : of d will be is filled Stable If . CHAPTER 2 2.1 orgm°zed33k#.gowne↳,n,to4group 10 Antoine Lavoisier metals non - metals earths gases . ÷ ÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷ H÷t :i÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷ 3 ① Lothar Meyer - • 2 ① John Newlands arranged 14 known elements increasing atomic according to : mass a 4 ① Dmitri Mendeleev "÷÷ . . . .. elements . :::÷:÷::: :::: am Periodic law elements increasing . Period # atomic . . #s÷÷÷÷:÷÷:÷÷÷÷ arrange order of !÷÷:÷ A Wich is eachapeayjgeds.hauediffJ.at ÷:* + the properties repeated regular in : . symbol - ↳ atomic mass . interval . ⑦ a ③ 2. I AM represent've elements group [2. 2) & [13-18] I * it show # wide Physical - & chemical Mth transition group of range properties . elements [3-12] * inched the 2 row below * Metals shiny elements , that are good conductors of heat & * Alkaline *Alkali metals - elements highly in reactive group electricity I exept earth metals the 2nd group highly reactive BUT hydrogen . Alkali metals are transition elements Transition * less Inner transition metals the 2 rains metals below the table reactive group [3-12] * - - * - - Nobat group 18 very gases - nonmetals unreactive Halogens elements higley in group reactive 27 more reactive . s p - - 2.2 2 6 S&p d- so f- → 14 * ighst-fnper.g.gl#eyel " they are blocks representative elements :3 velence electrons [group #) " 15252153 ③p④ 6 ↳ I group 16 highest energy level / :/ :/ /÷ ÷÷ # Highest Princip E level # l 2 terce period velence electron - l l 2 2 l 2 6 6 16 6 7 7- Group 7 8 - 17 18 : - Elements o § GROUP the same in g ( en Ce → S → group 15 ve have similar properties . electrons d block & trans ti ons - the filled S orbital [se coned highest the is example 4S [1/2 → [ D n is highest the energy level ) metals energy level . - : 3d [I ] to - ] electrons How • example : to know the velence electrons [group ] of d Add Cdts) electrons - 4 45 L 3d 2+41=6 f block to inner transition metals p * to know the f- (n 2) - Example : Gs 4f → orbital lanthanide ÷ [ actinide S S p d f 2. 3 Radii Atomic * radius * * Atomic (size of half radii - Singel ar - plural radius ] the It depend atom the distance between 2 of 2 youT.LT on the type of bonds metalInon metal nudie identical bonded atoms metal bond . nonmetal bond ⑧ 00 Howdoseoneaeomaeypeofaemi.a.b.nu - * Atom Size is effected by closely bonded crystal : y To T - lattice the radius in - to a neighboring atom Group the electron clouds . overlap is one I.at?I e:Ii sI:iIeesnebe:yeen " " "" bonded . trends Fff 3 be :c.ie:S: . . .mu?s:: : : :on.:.i: eas . • G- ⑤ period trends FE . - decreases WHY? I electron & increase the same as Protons ( ( move you will across atractt the electrons effective nudie charge electron static the period force . [in → the same Wich will . half * is . ], shell decrease the size . atoms . Ionic what gain is or ions lose Radii . ? electron gain ⑥ ↳ electrons = - ' • :÷ ÷: ÷→s¥*ef*÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ iii. mitral • Cation mental * atoms , the their velence to have the Anion lose electrons period * non behind e 9 neaves no bat * gas * size decrease [less ] because is . in " "" " their more electrons ① non Trends "" : :÷÷÷÷ electrons m¥ ) electrons negative charge :c a [gain metals - metal period o - decrease group ⑧ Trends ¥1 in group group → 15-17 + → ions - ions - • group - • - 1-14 de increase 15 - 17 dsgaion . sizes how many electrons C)CE et Rule : * Don't Oct = 8 electrons ve - lose 3 or gain more electrons . than in hence shell . the Ionization - b energy requires to remove 1 electron [always in the ① group ag.g tf / trend - high ionization energy - energy - higher thehioenn.in?:tifnneneu7I?YP holds the , more will be - ⑤ Period * the [So - → low ionization ] shell outermost trends Group 18 electrons energy required] has ionization highest energy . - increase WHY? "" ""÷÷÷÷÷ "" " " " " * Seco need - ionization energy energy required to remove the 2nd electron higher than the first * third ionization energy - . - energy required - to remove the higher than 3rd electron the second . Electronegativity b [attract'o/shaving Unit = ] electrons paintings > electronegtivity > attraction -0-0-0 x ① It × -0 Cl ⑦ e -0 Shane ① period electrons trends si - increase Group trends * .. ÷÷÷÷÷i÷÷: Chapter 3 3. I electron dot chemical bond : - force that holds 2 Boron example or ① Got more → by atoms . [attract between atoms ion formation → no to have the lose electrons :* pseudo no bat gas Fake - Getting Stai , +3 configuration - blog by : . . * Non gain formation ion Anion * nearest with +2 ① B. ] ions Negative cation t *When atom or - metals electrons :÷÷÷÷:i::÷ " "" i :: Chlorine → chloride group charge I + 2 +2 13 +3 18 O I :÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷:÷ : OCurrin a - group 12-24 : • electron static force :÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ ÷/* Positive structure 3. 2 :÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷÷ ① Ionic bond electrostatic force that holds oppositely charged :÷÷÷÷ a - 4 : ONLY 2 elements contain ✓↳ cation + Na Anion + Cl → Nat t CT t energy 2. electron configuration Is [Ne]3 - 3. Orbitit → [ Ne] [ AD - Na CI II 17 + energy notation f . ④ is t ti t + Na Oi Oi Oi 7¥ (l + Qi Qi octet 7iQ Omi I Na 4. Electron dot Na.o ÷! : Ci - structure → [ Nat tf !! :] : - + energy How calculate the overall to total charge in compound = charge ° E×= ① exchange the signs without . µ ② [other element ]t÷) ][ number element t 3Na(÷÷ ) + d 3-3/2=0 overall I 1Nms -) + LED j µ⑦ H . 3 ( Naz N) charge is Zero Write the Ex of ratio elements . : Na CI AI Clz Mg3 Nz I :L I :3 3: 2 lattice Crystal ↳ 3 dimensional [ [ - why arrangement ions t surrounded ions - does by surrounded crystal it is effected - by ions - by t ] ] ions depends How strongly attract parties . Physical properties number of " °" q shapes ? - is "Z" . lattice have different - of particles ↳ " ded - f Mg Melting Point Ability of material to conduct - depends on high melting electricity the charged freely → → = liquid . no No state = boiling it moving conduct good particles electricity conductor electrolyte liquid = require amount point to of of electricity solution conduct that electricity . is large a energy break the bond : Solid Point lattice , because mooring particles Example boiling - & hardness crystal ionic strong ① Energy endothermic exothermic b b energy is absorbed Formation of energy compound ionic is is released always → exothermic lattice energy z energy required * to separate 1 moi of ions Whenever ionic compound if it is absorbed the is formed : same amount it will break apart of energy released to Lattice energy . is effected by : - * Size of atom [ ionic radii ] tonic charges [ cation & anion charges] Small size to more large charge & lattice energy more lattice energy 3.3 Formula unit the chemical formula [represents the simplest of of ratio Oxidation numbers d compound ionic the ions ] charge of monoatomic ion [number of electrons transferred ] . ① Formulas for binary ionic compound . I 2 elements * cation Example : is . first written . - ② potassium and from K←, charges the iodide groups - exchange " not Ks Is - KIU ② Cesium and Cs Csz nitride ONLY numbers the " charge . ①Formulas for polyatomic ionic compound - ion of Exampled fare ② Ammonium to made up more table and than 2 atom ⑨ iPod 89] phosphate to CCNH )#PO4③ - , (NH ) , . 3 ( POD , (NHu)zCpoDJ ② Calcium is chlorate and "" ④@ 10550 (Ca) . . ( Clo )+z , ¢a)CcloDzJ [just exchange numbers] f Oxygen - Naming an Oxyanionb . An element (non more * they have ) metal oxygen more atom d with 1 or . than I oxy anion . me%ea.ggxe.no#.eateJi Example : - I - N0③ Nitrite → more oxygen - N0② I Nitrate → less o xy g# Naming chlorine * chlorine 1. the can oxy anion form 4 oxyanion greatest # of oxygen 3 2 . . chlorite perchlorate 2 . I fewer than the greatest chlorate fewer . . 4 . the lowest hypochlorite one ① Naming [ ionic compounds the name Monoatomic cation cation → Anion → monoatomic Example Same ' add . first] name ' ide : NaCl banion cation - Soudiide * there the some elements transition in who metals MORE THAN I oxidation have number . Exempt Fez Oz Fe O for # o +10%0 Oxygen electrons f Roman # f # \o f- repnesintig of ' is in So group we 16 , with need to charge C- 2) , make it - z I - ' > II 2 - ¥+1 - g " Fe 1×2 3 - 4 - - z O l)oxide s - G - 7 - 111 IV v VI ru s 3. 4 metals # but Metallic bond ionic they share some properties - attraction between metallic electron : cation for delocalized electrons sea model : ( metal atoms in a Valence electrons metallic Solid to form ' a sea share their ' of electrons JB → Metal sea cation of electrons a !÷÷÷:÷÷ :c : " . of metals properties 1. Melting & boiling * they Wich is because the bond 2. Malleability , - turn into sheet is STRONG very ductility , and metal " - be as a wire durability - - flexible " points high very are . strength can . - 3. Thermal & electrical *the of movement around metals metals conductivity delocalized cation good . electrons makes conductors . 4. Hardness * very as hard to break the number increase , it will be . of valence more electron stronger . [delocalized] ⑤ Metal mixture Alloys of elements metallic - the properties : * a different result of properties properties heating & cooling similar metals atomic . alloys t replace . - Subtitutioual - that has . alloys s holes of size / lhterstital [ interstices) filled with atom . is smaller size Compare ion the re pal if external force an because the is charges added is the same metal they won't nepal , but the shape will change . .