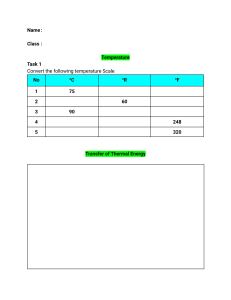
Name Date Class Overview Thermal Energy Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms listed below. insulators radiation forced-air electric conductors convection Thermal energy is transferred by conduction whose transfer is helped by 1. which is used in all the conventional heating systems including 3. solar and hindered by and 4. 5. 2. in the form of electromagnetic waves and 6. Thermal Energy 17 Name Date Class Section 1 ■ Temperature, Thermal Energy, and Heat Section 2 ■ Conduction, Convection, and Radiation Directions: In each of the following statements, a term has been scrambled. Unscramble the term and write it on the line provided. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. If particles move more llsowy the object’s temperature falls. Conduction can take place in solids, liquids, and sages. Thermal energy includes both kinetic and ttnepoail energy. Any material that can flow is lufdi. Any material that allows thermal energy to pass through it easily is a roconcutd. Materials with a high specific heat can absorb thermal energy without a large hngcae in temperature. Radiation is the transfer of energy in the form of vaews. When an object increases in temperature it naigs thermal energy. Many conductors, such as silver and copper, are lemtas. Energy that travels by radiation is often called darinta greeny. Insulators, such as wood and air, are poor conductors of ltmehar rgynee. The transfer of thermal energy by convection and conduction both require atterm. Directions: On the lines provided, explain the differences between conduction, convection, and radiation. Use the information in the exercise above to help you. Write your answers in complete sentences. 13. 18 Thermal Energy Name Date Class Section 3 ■ Using Thermal Energy Directions: Fill in the blanks using the correct terms from the list below. active stroke 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. isolated conduction heating systems thermodynamics heat pump passive thermal energy is the study of the relationships among thermal energy, heat, and work. Most use fuel or electricity as a source of energy. A house with large windows on its south side and few windows on its other sides probably uses a(n) solar heating system. Solar collectors are used in buildings that have solar heating systems. Fuel burned in a stove or fireplace transfers thermal energy to the surrounding air by , convection, and radiation. Before radiant energy can be converted to thermal energy, it must be changed to . The thermal energy of an system doesn’t change. A does work to transfer thermal energy from a cold area to a warm area. A is the movement of a piston up or down. Directions: The terms in each group below are related. Write a sentence that uses all of the terms in each group in a way that shows how they are related. Underline each word of the group in your sentences. 10. radiant energy, solar collector, active solar heating system 11. heating system, radiator, conduction Thermal Energy 19 Name Date Class Key Terms Thermal Energy Directions: In each of the following statements, a term has been scrambled. Unscramble the term and write it on the line provided. 1. The transfer of thermal energy through matter by direct contact of particles is called docniotucn. 2. The transfer of thermal energy by the movement of matter is called vecconniot. 3. The type of energy transfer that does not require matter is iadraniot. 4. Any material in which thermal energy doesn’t flow easily is an roinsulta. 5. An ntieanrl busmcotoin engine burns fuels inside chambers called cylinders. 6. Energy from the sun is airdnta neeygr. 7. A device on a building that absorbs radiant energy from the sun is lraos lleocctro. 8. The thermal energy that is transferred from something with a higher temperature to something with a lower temperature is called eath. 9. Thermal energy is converted into mechanical energy by a thea gennie. 10. A thea umpp moves thermal energy from one location and transfers it to another location at a higher temperature. 11. The pertreuamet is related to the average kinetic energy of all the particles in an object. 12. The total energy of the particles in a material is ethrlam gyeren. 13. The pcciifes thea of a material is the amount of thermal energy it takes to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the material 1 kelvin. 20 Thermal Energy