Excretion and osmoregulation
in mammals
•
In mammals, both Excretion and osmoregulation are
carried out mainly by the urinary system.
The urinary system consist of the kidneys ,ureters, urinary
bladder, and urethra.
• The urine from the kidneys flows down the ureters to the
bladder where it is stores temporarily before being
expelled via the urethra
•
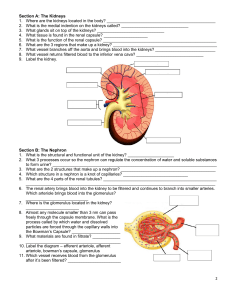
Structure of the kidney
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located on the back of the
abdomen
Kidneys has three main parts:
Cortex: outer part of the kidney
Medulla: inner most part of the kidneys
.
Renal pelvis :area of the center of the
kidneys where urine collects here.
Funnel-shaped
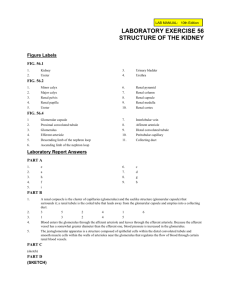
The nephron
The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney.
Once the renal artery enters the kidney, it divides and subdivides,
ultimately forming small vessels called Afferent arterioles.
Each afferent arterioles subdivides further to form a ball-shaped tuft
of capillaries called the Glomerulus.
The glomerulus capillaries then coalesce to form an efferent
arteriole.
This subdivides further to form a network of capillaries that surround
the renal tubule.
The latter capillaries coalesce once more to form a Venule which
takes deoxygenated blood to the renal vein.
Each glomerulus is partially enclosed by a cup-shaped structure called
The nephron con.
The renal capsule or Bowman's capsule leads to a coiled tube called the renal
tubule.
The glomerulus, Bowman's capsule and renal tubule form what is called nephron
Each kidneys contains about 1.5 million of nephron.
The first part of the renal tubule is a coiled tube called proximal convoluted
tubule ( pct. ) in the cortex
Continuous with the PCT is U-shaped tube called loop of Henle in the medulla
The loop of Henle leads into another coiled tube called distil convoluted tubule
{DCT } In the cortex
The DCT leads to the collecting duct which drains its content ( urine ) into pelvis
which then flows into the bladder via the ureter