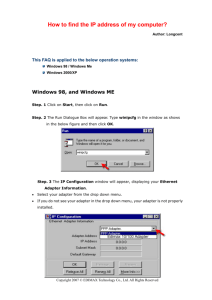
Lesson 1 Lesson 1 Understanding Local Area Networking Learning Objectives Students will learn to: Examine Local Area Networks, Devices, and Data Transfer Identify Network Topologies and Standards ODN Skills Understand local area networks (LANs). Understand network topologies and access methods. 1.2 1.5 Lesson Summary — Lecture Notes You should begin this lesson by introducing yourself and the course. The rest of the lesson is an introducing to networking. Therefore, you should start with explaining what a network is and then explain what a LAN is and give some examples of LANs. Most LANs are within a building or set of buildings that are all close together. You can then describe that, in order to make up a network, you must have something to share and a method to share that data (such as a network and a protocol or protocols to share the data). You can then describe a home network (a very simple and very small network) and a large company network. As some networks are large and complex, and network engineers and administrators come and go, administrators may not always be available when a problem occurs. An administrator may forget about a setting, a configuration, or a solution to a problem, so network documentation is extremely important. To help create some of the documentation, Microsoft Visio comes in handy when creating diagrams. The next part of the lesson starts describing a simple LAN consisting of a hub. You could mention that hubs are legacy devices but it is still a good place to start so that students can understand how hubs and switches function. Of course, in the example, you have a server providing a service and the PC, Mac and laptop requesting services from the server. After they understand a simple LAN, you can then explain what a SOHO is (as shown in in Figure 1-2). A SOHO may be a small satellite office or even a simple home office. Rather than have dedicated servers and expensive routers, you would use an inexpensive router, which will allow you to share a DSL or cable modem connection to the Internet among multiple users. 1-1 Lesson 1 To create a network, a host will need to have a network adapter. Therefore, you would explain what a network adapter is and then explain the different types of adapters. They would differ by how they connect to the host and what connections and speeds they support. You could then show how to install and configure a network adapter. To add a host with a NIC to a wired network, you would then use a patch cable. If you have one handy, you can show the students a patch cable. Be sure to mention that it is a cable used for Ethernet networks and has RJ-45 connectors. One of the common characteristics for network connections is network speed. Therefore, that you can explain that most network cables use serial data transfers and that their speeds are specified in megabits per second (or Mbps). This should not be confused with Megabytes per second (MBps). For a host to communicate on a network, it has to have a logical address. For a TCP/IP network, the logical address is the IP address. You would then explain the four octets ranging from 0 to 255 and how the subnet mask relates to the IP address. You could then discuss classful networks consisting of Class A, B and C networks and their default subnet masks. To show the students an IP address in use, you will then show how to configure an IP address in Windows and how it communicates with another computer by using the ping command. Explain how the ping command is a very handy tool when testing network connectivity and testing the sending’s host IP configuration (loopback/localhost). Mention that the ping command uses the ICMP protocol. Now that the students have an understanding of a wired network, explain that wireless LANs are very common. Discuss the various devices that connect to a wireless network (besides computers, phones and pads). The next part of the lecture talks about how to protect your network by adding a network into a perimeter network or DMZ. You can then discuss the different ways to form a DMZ. The next part of the lesson describes the network topology. Consider digging a bit deeper by describing logical topology and physical topology. For example, today’s Ethernet usually forms a physical star topology, but the signals still form a bus topology. The most common type of network is an Ethernet network. Therefore, you can then cover the different Ethernet standards. While it is okay for students to know the original standards (such as 10Base 5 and 10Base2) in today’s world, they need to know today’s popular standards (including 100Base-TX and 100Base-T). The next part of the lesson discusses various models, including the client-server model and peer-to-peer model. You will need compare and contrast these two models. You can then cover different types of servers, including Windows, Linux and UNIX. You can then cover the different versions of Windows servers and their related client operating system. 1-2 Lesson 1 Key Terms 8P8C - A common connector or plug used on the end of the network cable. Also known as RJ-45. Broadcast – A method of communication where packets are sent to every host on the network. centralized computing – A model where all computing for a network is done by a large central device. client-server – A model that distributes applications between servers such as Windows Server 2008 and client computers such as Windows 7 or Windows Vista machines. CSMA/CA – Short for carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance. It is used as a method for multiple hosts to communicate on a wireless network and AppleTalk. CSMA/CD – Short for carrier sense multiple access with collision detection. It is the method for multiple hosts to communicate on a Ethernet. computer telephony integration (CTI) - When a company’s telephone system meets its computer system. Here, special PBXs that used to control phones as a separate entity can now be controlled by servers with powerful software. CTI-based server - When a company’s telephone system meets its computer system. Here, special PBXs that used to control phones as a separate entity can now be controlled by servers with powerful software. data transfer rate – Network speed, also known as bit rate. This is defined as the maximum bits per second (bps) that can be transmitted over a network. database server - A server that provides data for applications. demilitarized zone (DMZ) - Also known as a perimeter network, a small network that is set up separately from a company’s private LAN and the Internet. distributive computing – A model where computing is provided by each host. Ethernet – A networking standard that has a set of rules that govern the transmission of data between network adapters and various central connecting devices. file server – A server that stores files for computers to share frames – A group of bytes packaged by a network adapter for transmission across the network. full duplex – A type of communication where traffic is sent in both directions at the same time. half duplex – A type of communication where traffic is sent in both directions, but only one at a time. host – A device or computer has an IP address 1-3 Lesson 1 hub - A basic central connecting devices (sometimes referred to as CCDs) that connects each of the networked computers, known as hosts, to one another by way of copper-based cables. A hub is considered a legacy device. IEEE 802.3 – A standard that defines carrier sense multiple access with collision detection or CSMA/CD. Because computers on a default Ethernet LAN all share the same channel, CSMA/CD governs the way that computers co-exist with limited collisions. IP address – A logical address that identifies a device or host connected on a network. local area network (LAN) – A group of these computers that are confined to a small geographic area, usually one building. medium dependent interface (MDI) – A port used to daisy chain or stack one or more hubs or switches. mesh topology – A topology where every host or server is connected to every other host or server. messaging server - Email servers, but also fax, instant messaging, collaborative, and other types of messaging servers. For a Windows Server to control email, special software known as Exchange Server has to be loaded in addition to the operating system. Microsoft ISA Server – Microsoft’s firewall and proxy server. Microsoft Visio - A common tool used for network documentation multistation access unit (MAU) – A central connecting device usually associated with Token Ring. network adapter - Also known as a network interface card or NIC, it is the device that enables you to send and receive data to and from your computer. network controller – A controlling server such as a Microsoft domain controller, it is in charge of user accounts, computer accounts, network time, and the general well-being of an entire domain of computers and users. network documentation - Any information that helps describe, define, and otherwise explain how computers are connected in a physical and logical way. network operating systems – An operating system used by a server to provide network services. network topology – A method that defines the physical connections of hosts in a computer. peer-to-peer (P2P) – A model that has each computer has an equal ability to serve data and to access data, just like any other computer on the network. perimeter network - Also known as a DMZ, a small network that is set up separately from a company’s private LAN and the Internet. print server - A server controls printers that can be connected directly to the server or (and more commonly) are connected to the network. ring topology – A topology that forms a ring or loop. 1-4 Lesson 1 RJ45 – A common connector or plug used on the end of the network cable. serial data transfer – A method where data is sent, one bit at a time. star topology – A topology where each computer is individually wired to a central connecting device with twisted-pair cabling. switch – A device similar to a hub that connects computers to a central point. However, different from a hub, a switch will only forward traffic to its destination instead of broadcasting. Transceiver – A device or component that can transmit and receive data. unicast – A communication method where traffic is only sent to the computer or host that is meant to be sent to. virtual LAN (VLAN) – A group of hosts with a common set of requirements that communicate as if they were connected together with a common set of requirements that communicate as if they were connected together in a normal fashion on one switch, regardless of their physical location. web server – A server that share data and provide information about a company using HTML web pages.. wireless access point (WAP) – A central connecting device used in wireless networks. wireless LAN (WLAN) – A network that uses wireless signals. 1-5 Lesson 1 Lesson 1 Server Overview Knowledge Assessment Multiple Choice Circle the letter that corresponds to the best answer. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Which of the following regenerates a signal and broadcasts that signal to every computer connected to it? a. Hub b. Switch c. Router d. Firewall Which of the following is not a central connecting device? a. Hub b. Switch c. SOHO router d. Windows 7 client You need to install a network adapter to a computer so that it can be connected to a network that uses twisted-pair cabling. What type of port does the network adapter need to use? a. RJ11 b. RJ45 c. RG-58 d. Fiber optic Where can you go in Windows 7 to access the Properties of a network adapter? a. Device Manager b. Ping c. Advanced Firewall d. Task Manager You need to connect a computer’s network adapter to a switch. You want the connection to be able to send and receive data simultaneously. What type of connection do you need? a. Half duplex b. Full duplex c. Simplex d. 100 Mbps 1-6 Lesson 1 6. 7. 8. 9. You need to connect a computer at a rate of 100,000,000 bits per second. What speed network adapter should you install? a. 10 Mbps b. 100 MB/s c. 100 Mbps d. 1000 Mbps You need to connect to a router that has the IP address 192.168.1.100 on a standard, default Class C network using the subnet mask 255.255.255.0. Which of the following is a valid IP address for your network adapter? a. 192.168.0.1 b. 192.168.1.1 c. 192.168.100.1 d. 192.168.1.100 You have just installed a network adapter and configured an IP address and subnet mask. What command can you use to verify that the IP address is configured and listed properly? a. Ping b. Tracert c. CMD d. Ipconfig You need to ping your own computer to see if it is alive. Which of the following would qualify as command-line syntax to do so? a. ping localclient b. ping 128.0.0.1 c. ping loopback d. ping network adapter 10. You have been instructed to connect a computer to a group of hosts that have been segmented from the regular network. What kind of network is this? a. LAN b. WLAN c. WAN d. VLAN Fill in the Blank Fill in the correct answer in the blank space provided. 1. The manager of IT asks you to connect a perimeter network to the firewall, which will be separate from the LAN. This type of network is known as a DMZ 2. A star topology can be defined by connecting several hubs to a switch. 3. 802.3u Ethernet networks run at 100 Mbps. 4. A BitTorrent client is a program used to download files quickly from a P2P network. 1-7 Lesson 1 5. The Token Ring network architecture is physically a star and logically a ring. 6. 802.3ab Ethernet networks run at 1000 Mbps. 7. A Half duplex connection is one in which data can be both sent and received, but not at the same time. 8. A ring topology can be defined as connecting several computers together in a circle without the use of a hub or a switch. 9. When several computers are connected in a small geographic area, it is known as a local area network. 10. A wireless access point acts as a central connecting device and allows laptops, PDAs, and handheld computers to communicate with each other. Case Scenarios Scenario 1-1: Planning and Documenting a Basic LAN Proseware, Inc. requires you to implement a 20-computer LAN. Fifteen of these computers will be Windows 7 clients and five will be Windows Server 2008 computers. The company also requires a 24-port switch, router, DSL Internet connection, DMZ with web server, and a laptop for the CEO. Create a diagram of the network documentation for this in Microsoft Visio or on paper. Refer to Figures 1-1 through 1-3 for types of devices in the Visio networking stencils. Figure 1-23 shows an example of what this documentation might look like. Scenario 1-2: Selecting the Right Type of Networking Model The ABC Company requires a network that can support 50 users. Which is the correct type of networking model to use and why? In this case the best networking model to select is client-server. Client-server networks are meant for more than 10 users. If a network has 10 users or less, peerto-peer might be acceptable. Scenario 1-3: Selecting Network Adapters for your LAN Computers A company you are consulting for requires the installation of five new computers. Each computer’s network adapter should be able to communicate at 1000 Mbps over its preexisting twisted-pair cabling and should be able to send and receive data simultaneously. Which Ethernet standard should you select, and what technology should you utilize? The network adapters should be compliant with the 802.3ab standard allowing them to transfer 1000 Mbps over twisted pair cabling. You should also configure them for full duplex mode so that they can send and receive signals at the same time. Scenario 1-4: Configure the Correct Subnet Mask A computer is not connecting to certain network devices properly. The IP address information is as follows: IP address: 192.168.1.210 1-8 Lesson 1 Subnet mask: 255.254.0.0 How should the subnet mask be configured so that the computer can communicate properly with all networking devices and other hosts on the network? The subnet mask should be configured as 255.255.255.0. This is a default Class C subnet mask that is normally used with IP addresses that start with 192. 1-9