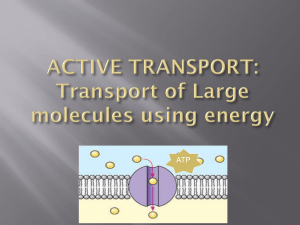
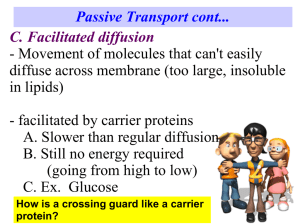
Endocytosis & Exocytosis: Transport Mechanisms in Cells
advertisement
SHS STEM - BIOLOGY 1 Quarter 1 – Module 13 Transport Mechanisms (Endocytosis and Exocytosis) i General Biology 1 – Grade 11 Quarter 1 – Module 13: TRANSPORT MECHANISMS (ENDOCYTOSIS AND EXOCYTOSIS) Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this book are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Regional Director: Gilbert T. Sadsad Assistant Regional Director: Jessie L. Amin DEVELOPMENT TEAM OF THE MODULE WRITER: Christine Lee B. Bayna REVIEWERS/EDITORS: Rowena D. Manaog Freddierick C. Apuli Ma. Lota C. Monte Jade Alberto LAYOUT ARTISTS: Jay Mark Base Jonathan Roda Jessica De Ocampo “Differentiate exocytosis and endocytosis.” STEM_BIO11/12-Ig-h-14 TRANSPORT MECHANISMS (EXOCYTOSIS AND ENDOCYTOSIS) The new normal requires new routines, new ways of working, and as well as new ways of teaching and learning. As we are currently facing this pandemic, education has encountered another obstacle towards effective delivery. This, however, should not hinder education to continue. The Department of Education looked into ways on how education could still push through despite this health crisis. This module is designed to supplement the available learning materials in the Senior High School. The integration of this module with the alternative learning delivery modalities will help to ensure that basic education will be accessible amidst the present crisis. It is based on the Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELCs) as stipulated by DepEd. Teacher The design of the module attempts to be adaptive to different learning modalities. Orient the students, their parents, or those who will guide the learner on how to properly utilize the module. Inform them of the different activities that they must accomplish and the important dates to make sure of compliance. Learner This module was prepared for you. Make sure to answer and perform tasks honestly. Take good care of this module and answer on a separate sheet of paper. Do not forget to finish the tasks assigned to you by your teacher, as well as the period of submission. OBJECTIVES: At the end of this module, you should be able to: 1. define endocytosis and exocytosis 2. differentiate endocytosis (phagocytosis and pinocytosis) and exocytosis 3. explain how materials enter and leave the cell through endocytosis and exocytosis 1 Endocytosis- the process by which large substances or bulk amounts of smaller substances enter the cell without crossing the membrane Exocytosis- the process by which large substances or bulk amounts of small substances exit the cell without crossing the membrane Phagocytosis – the process by which solid substances are ingested Pinocytosis – the process by which liquids / dissolved substances are ingested Plasma membrane- the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment Vesicles- are compartments formed by a lipid bilayer separating its contents from the cytoplasm or a fluid-based extracellular environment Instruction: Read each item carefully. Select the letter of the correct answer and write it on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What cell organelle helps to transport large molecules into or out of the cell? a. Nucleus b. Ribosome c. Mitochondria d. Vacuole 2. Which is NOT true about endocytosis? a. It requires energy to occur. b. It occurs without the help of any cell organelle. c. It takes in nutrients for cellular growth, function, and repair. d. Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis are its types 3. Which is true about exocytosis? a. It is a form of passive transport. b. It occurs without the help of any cell organelle. c. It removes toxins or waste products from the cell’s interior d. Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis are its types 2 4. Which is an example of endocytosis? a. White blood cells engulfing a virus and eliminating it. b. Releasing a neurotransmitter for cellular communication. c. Both a and b d. None of these 5. How are large substances transported through exocytosis? a. When a portion of the cell membrane folds in on itself, encircling extracellular fluid and various molecules or microorganisms. b. When a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane, allowing its contents to be released outside the cell. c. Both a and b d. None of these Instruction: Answer the following questions. Write your answer on the space provided. You are preparing your things for a group study. While preparing, you noticed that your bag is already full of stuffs and you still have some things you want to bring. You only want to bring one bag to avoid hassle, what are you going to do? https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.shutterstock.com%2Fimagevector%2Fseamless-women-bag-stuff-pattern-can442189447&psig=AOvVaw0rr8zsUlE3MQgjBCk9ZsMT&ust=1597117858175000&source=images&cd=vf e&ved=0CAIQjRxqFwoTCNC7yJHej-sCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAV Relate the situation above on how cells transport materials into and out of the cell. 3 Instruction: Explain how materials are transported into and out of the cell. Write your answer on the box provided. https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fbiologydictionary.net%2Factivetransport%2F&psig=AOvVaw2oaQfz49NHn44bcI1oyrTd&ust=1597119854216000&source=images&cd= vfe&ved=0CAIQjRxqFwoTCOC9sMTlj-sCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAJ https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fbiologydictionary.net%2Factivetransport%2F&psig=AOvVaw2oaQfz49NHn44bcI1oyrTd&ust=1597119854216000&source=images&cd= vfe&ved=0CAIQjRxqFwoTCOC9sMTlj-sCFQAAAAAdAAAAABAJ 4 Water and small solutes enter and leave the cell by diffusing through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane or by being pumped or moved across the membrane by transport proteins. However, large molecules—such as proteins and polysaccharides, as well as larger particles—generally cross the membrane in bulk, packaged in vesicles. Vesicles and cell membranes are both comprised of a lipid bilayer, which is why they are capable of fusing with the cell membrane. This fusion between vesicles and the plasma membrane facilitates bulk transport both into and out of the cell. Like active transport, these processes require energy. Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle. It occurs when a portion of the cell membrane folds in on itself, encircling extracellular fluid and various molecules or microorganisms. The resulting vesicle breaks off and is transported within the cell. Endocytosis serves many purposes, including: Endocytosis ➢ taking in nutrients for cellular growth, function, and repair. ➢ capturing pathogens or other unknown substances that may endanger the organism. ➢ disposing of old or damaged cells Types of Endocytosis Reece, et.al., Campbell Biology, 138. 5 Exocytosis is the process by which cells move materials from within the cell into the extracellular fluid. It occurs when a vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane, allowing its contents to be released outside the cell. Exocytosis serves the following purposes: Endocytosis ➢ removing toxins or waste products from the cell’s interior ➢ facilitating cellular communication ➢ facilitating cellular membrane growth, repair, signaling and migration Types of Exocytosis https://pediaa.com/difference-between-endocytosis-and-exocytosis/ In constitutive exocytosis, extracellular signals are not required. The majority of molecules traveling to the plasma membrane do so using this pathway. In regulated exocytosis, the expulsion of the materials is controlled, or regulated, by extracellular signals that cause membrane depolarization. 6 Practice Task 1 Instruction: Write TRUE if the statement is correct, if FALSE change the underlined word/s to make the statement correct. __________1. Endocytosis and exocytosis are types of passive transport. __________2. In order for the cell to maintain homeostasis, waste materials are removed from these cells via endocytosis. __________3. In regulated exocytosis, the release of materials is controlled by extracellular signals. __________4. White blood cells engulfing a virus and eliminating it is an example of exocytosis. __________5. Endocytosis is the process of taking in a particle or substance from outside of the cell using a vesicle. __________6. Phagocytosis and Pinocytosis are types of endocytosis. __________7. Vesicles are little sacs that separate its contents from the cytoplasm. __________8. Exocytosis helps in facilitating cellular communication. __________9. Pinocytosis is the process by which cells internalize large particles like damaged cells and bacteria. __________10. Disposing of old or damaged cells is done through Exocytosis. Practice Task 2 Instruction: Compare endocytosis and exocytosis by filling out the table below. Endocytosis Definition Function Types Examples 7 Exocytosis Practice Task3 Instruction: Answer the following questions. Write your answer on the space provided. 1. Explain how a phagocyte destroys bacteria. 2. Explain exocytosis in neurotransmission. 3. Do you think exocytosis and endocytosis can occur within the same cell? 4. Explain the importance of endocytosis and exocytosis. 8 REFLECT! ADDITIONAL QUERIES? 9 Post-Test Instruction: Read each item carefully. Choose the letter of the BEST answer. 1. How are dissolved ions transported inside the cell? a. Phagocytosis c. Regulated b. Pinocytosis d. Constitutive 2. Which is NOT a function of exocytosis? a. Removing toxins b. Cellular membrane growth c. Signaling and migration d. Capturing pathogens 3. Which is a function of endocytosis? a. Removing toxins b. Facilitating cellular communication c. Signaling and migration d. Disposing damaged cells 4. Which of the following shows the correct steps in endocytosis? I- The phagocytic vesicle fuses with lysosomes, which recycle or destroy the vesicle’s contents. II- A particle or substance binds to receptors on the cell’s surface, stimulating the release of pseudopodia III- Pseudopodia surround the object until their membranes fuse, forming a phagocytic vesicle. IV-The phagocytic vesicle pinches off from the cell membrane, entering the cell. a. I, II, III, IV c. III, IV, I, II b. II, III, IV, I d. IV, III, II, I 5. Which of the following shows the correct steps in exocytosis? I-The vesicle fuses to the plasma membrane, during which the two bilayers merge. II- A vesicle is formed, typically within the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus or early endosomes. III-The vesicle’s contents are released into the extracellular space. IV- The vesicle travels to the cell membrane. a. I, II, III, IV b. II, IV, I, III c. III, IV, II, I d. IV, III, I, II 10 6. What is the difference between constitutive and regulated exocytosis? a. Constitutive uses energy, regulated does not b. Regulated uses energy, constitutive does not c. Constitutive requires extracellular signals, regulated does not d. Regulated requires extracellular signals, constitutive does not 7. Which of the following are types of endocytosis? I-Phagocytosis II-Pinocytosis III-Constitutive IV-Regulated a. b. c. d. I and II III and IV I, II, and III I, II, III, and IV 8. Which is NOT an active transport? a. Phagocytosis b. Pinocytosis c. Endocytosis d. None of these 9. What process takes in substances into the cell? a. Phagocytosis b. Pinocytosis c. Endocytosis d. All of the above 10. Which process does NOT transport substances outside the cell? a. Regulated b. Constitutive c. Pinocytosis a. Exocytosis 11 Answer Key PRE-TEST 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. DO THIS D B C A B 1. Remove the stuffs that are not needed and put inside the bag those that are important. 2. In cells, large substances are taken in by endocytosis while waste products are released through exocytosis. EXPLORE A. 1. A particle or substance binds to receptors on the cell’s surface, stimulating the release of pseudopodia 2. Pseudopodia surround the object until their membranes fuse, forming a phagocytic vesicle. 3. The phagocytic vesicle pinches off from the cell membrane, entering the cell. 4. The phagocytic vesicle fuses with lysosomes, which recycle or destroy the vesicle’s contents. B. 1. A vesicle is formed, typically within the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus or early endosomes. 2. The vesicle travels to the cell membrane. 3. The vesicle fuses to the plasma membrane, during which the two bilayers merge. 4. The vesicle’s contents are released into the extracellular space. PRACTICE TASK 1 1. Active 2. Exocytosis 3. True 4. Endocytosis 5. True 6. True 7. True 8. True 9. Phagocytosis 10. Endocytosis 12 PRACTICE TASK 2 Endocytosis Definition Function Types Examples Exocytosis The process of taking in large substance from outside of the cell. ➢ Absorbing nutrients for cellular function ➢ Eliminating pathogens ➢ Disposing of old/damaged cells Note: There are other possible answers ➢ Phagocytosis ➢ Pinocytosis White blood cells engulfing a virus and eliminating it. Note: There are other possible answers The process of taking substances outside the cell. ➢ Removing toxins or waste products ➢ Repairing the cell membrane ➢ Facilitating communication between cells Note: There are other possible answers ➢ Regulated exocytosis ➢ Constitutive exocytosis Note: There are other possible answer. Releasing a neurotransmitter for cellular communication. Note: There are other possible answers PRACTICE TASK 3 1. Phagocytes aim to destroy pathogens by engulfing them and subjecting them to toxic chemicals. 2. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis. 3. Yes, endocytosis and exocytosis can occur in the same cell. It is how a cell transport and export material in and out of the cell. 4. Exocytosis and endocytosis are important in maintaining homeostasis. POST TEST 1. B 2. D 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. D 7. A 8. D 9. D 10. C 13 References Books Reece, J., et.al., Campbell Biology. California: Pearson Education Inc., 2014. Website https://www.ck12.org/biology/cell-transport/lesson/Cell-Transport-Advanced-BIOADV/#:~:text=Cell%20transport%20refers%20to%20the,that%20they%20are%20selecti vely%20permeable. https://ib.bioninja.com.au/standard-level/topic-1-cell-biology/14-membranetransport/active-transport.html http://life.nthu.edu.tw/~b830473/transmechanism.html#:~:text=It%20is%20of%20semina l%20importance,in%20and%20out%20of%20itself.&text=Given%20the%20importance %20of%20membrane,facilitated%20diffusion%2C%20and%20active%20transport https://www.technologynetworks.com/immunology/articles/endocytosis-and-exocytosisdifferences-and-similarities-334059 https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-wmopen-biology1/chapter/endocytosis-andexocytosis/ https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Plasma-Membrane https://biologydictionary.net/vesicle/ 14