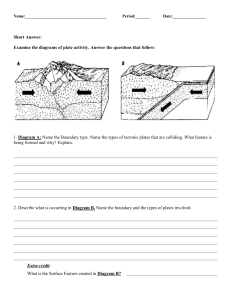
Plate Tectonics Chapter 6 Section 6.1 Earth is made up of materials with different densities • Crust • Mantle • Core Earth’s layers have different properties To explore the interior, scientist study the energy form earthquakes or underground explosions they set off. 1. Core, Mantle, Crust 2. Lithosphere and Asthenosphere The Core • The core is Earth’s densest region and is made up of two parts: 1. The inner core, is a ball of hot, solid metals. 2. The outer core, is a layer of liquid metals that surrounds the inner core. Inner Core * The inner core of the Earth has temperatures and pressures so great that the metals are squeezed together and are not able to move. * The inner core is a solid. Outer Core * The core of the Earth is like a ball of very hot metals. * The outer core is liquid. * The outer core is made up of iron and is very dense. The Mantle • The mantle is the layer below the crust. • The mantle is the thickest layer of the Earth. • It has layers of cool, rigid rock at the top and a layer of hotter softer rock below it. The Crust • Outer and thin layer or cool rock. • 2 types of crust – Oceanic (all the ocean floors) – Continental (all the continents, and major islands) Oceanic and Continental Crust Earth’s crust is thinnest under the oceans and thickest under continental mountain. The crust is home for all life on earth Earth’s Layers • How are the earth’s layers similar to an egg? • Shell=crust • Egg white=mantle • Yolk=core In the Mantle LITHOSPHERE • The word litho- means “stone” or “rock”. • Earth’s crust and the very top of the mantle. • Is the most rigid of all layers. ASTHENOSPHERE • The word asthenes means “weak”. • A layer of hotter softer rock in the upper mantle. • Solid rock that flows slowly (like hot asphalt) Tectonic Plates • Earth’s crust is broken into about 19 pieces • These plates move on top of the asthenosphere The thicker continental crust rises above ocean. The rest of the plate is thin oceanic crust, or sea floor. Earth’s layers and Tectonic Plates are the most important discoveries in geology They helped answer the questions: 1.Have the continents always been where they are today? 2. If not, how did they move to their present positions? Continents change position over time • German scientist Alfred Wegner proposed a hypothesis known as continental drift. • He hypothesized that Earth’s continents were once joined in a single landmass and gradually moved or drifted apart. Evidence for Continental Drift 1. Fossils of Mesosaurus have been discovered in both South America and Western Africa. 1. Climate. Fossils of tropical plants found in icy Greenland, and rocks deeply scratched by ice sheets that once covered the area. 2. Geology, type of rock found in Brazil matched the rock found in western Africa. movie Pangaea and Continental Drift • What is Pangaea? it is Wegner’s name for the supercontinent that once reached from pole to pole. • Pangaea began to split apart some 250 million years ago. • Wegner needed more explanation. Evidence from the Sea Floor • Mid-ocean ridges are huge underwater mountain ranges. www.divediscover.whoi.edu/ridge/axial.html Sea-floor spreading • The ridges form along cracks in the crust. Molten rocks rise, cool and form new oceanic crust. The old one is pulled away to make room for new material. Age of the Sea Floor • The rock samples obtained from the sea floor revealed that the youngest rock is closest to the ridge, and the oldest rock is farthest away. Ocean Trenches Why does Earth remain the same size?? • In the sea floor trenches like deep canyons are found. • At ocean trenches, dense oceanic crust is sinking into the asthenosphere. • Old crust is being destroyed at the same rate that new crust is forming. Scientists now had proof that tectonic plates move • Tectonic plates are the lithosphere layer broken into small and large slabs of rocks. • Tectonic plates rests on the asthenosphere, rocks in this layer moves by convection. • Convection is energy transfer by the movement of a material. • Convection currents are the motions that transfer heat energy in a material. Causes of Plate Movements • Convection currents, slab pull, and ridge push move Earth’s huge tectonic plates. Causes of Plate Movement • In the asthenosphere, heated rock constantly rise, cools, sinks and is heated again. This is convection currents. • Slab pull occurs when gravity pulls cooler, denser rock into the asthenosphere. • Ridge Push occurs when material from mid ocean ridges push the plates. Putting things together • Geologists combined their knowledge of Earth’s plates, the sea floor and the asthenosphere to develop the theory of plate tectonics. What does the theory of plate tectonics state? • Earth’s lithosphere is made up of huge, moving plates that are carried over Earth’s surface. • Most earthquakes, volcanoes and mountain ranges appear where tectonic plates meet. Plates move apart Section 3 Tectonic plates have different boundaries • A plate boundary is where the edge of two plates meet. • There are 3 boundaries A. divergent boundary B. convergent boundary C. transfrom boundary • Divergent boundary occurs where plates move apart. • Found mostly in the ocean. • Convergent boundary occurs where plate push together. • Transform boundary occurs where plates scrape past each other. Mid Ocean Ridges and Rift Valleys • As the sea floor spreads, it creates a gap between the ridges called Rift Valley. • Mid- ocean ridges, rift valleys form along divergent boundary, as the sea floor spreads apart. The boundary overview movie Sea-Floor Rock and Magnetic Reversals • Patterns of Magnetic Reversal recorded in ocean- floor rocks provide evidence of plate movement. • Magnetic reversal is when the north pole becomes south and the south pole becomes north. Continents splits apart at divergent boundaries • On land the hot material rises in the mantle causes the curst to bulge upward, then it cracks. As rift valley widen, continents begin to split apart. • If the rift valley continued to widen, the thinned valley floor sinks lower and lower until it is below sea level. • The valley will be flooded by nearby oceans or rivers forming a a sea or a lake. Hot spots can be used to track plate movements • A plume of magma from the mantle melts the rock in the plate above it until a volcano forms. • They provide a fixed point to measure plate movements. Plates converge or scrape past each other Ch 6, section 4 Tectonic plates push together at convergent boundaries. • At convergent boundaries, crust is either folded or destroyed. • When one plate sinks beneath another is called subduction. There are 3 types of convergent boundaries 1. Two continental plates meet 2. Two oceanic plates meet 3. An oceanic plate and a continental plate meet. Continental-Continental Collision • Occurs where two plates carrying continental crust push together. • Neither plates can sink under the other because they have the same density. • The edges will crumple and fold when they collide. • The folded crust can be pushed up high to form mountains. • The Alps are forming as a result of the European and African plates pushing together. European Alps The Himalayas Subduction When one plate sinks beneath another is called subduction. 1. Oceanic-Oceanic Subduction 2. Oceanic-Continental Subduction. Oceanic-Oceanic Subduction • Occurs where one plate with oceanic crust sinks, or subducts under another plate of oceanic crust. • The older plate sinks because it is denser than the younger plate. • When the older crust reaches the asthenosphere it melts in the intense heat. Two main features from oceanic-oceanic subduction 1. Deep ocean trenches. 1. Island arcs. 1. Deep ocean trenches They are deep canyons that form in the ocean floor as the plate sinks. 2. Island arcs They are volcanic island forms in parallel to a deep ocean trenches. Oceanic-Continental Subduction • Occur when ocean crust sinks under continental crust. • The oceanic crust sinks because it is older and denser than the continental crust. Two main features form oceanic- continental subduction 1.Deep ocean trenches it forms as the oceanic plate sinks. 1.Costal mountains (volcanic islands) magma rises through the cracks in the crust and forming volcanoes on the surface Tectonic plates scrape past each other at transform boundaries • At transform boundaries, crust neither formed nor destroyed. • As the plates move their edges scrape and grind against each other • Transform boundaries occur mostly on 1.The sea floor near mid-ocean ridges 2.On land seen as long cracks in Earth’s surface. San Andreas Fault The theory of plate tectonics helps geologists today • Scientists learned 1. The planet’s lithosphere has been moving for millions of years. 2. Earth’s past and it helped them predict Earth’s future as well as the sites or future volcanoes, earthquakes, mountain building. Open Your Book Pg 216 Do question 19, 20, and 22