Anti-Parkinson Drugs By: Sara Tufer (B.Pharm, MSc pharmacology) Introduction • PD is slowly progressive degenerative diseases of the brain that affects dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia Nigra(SN). • Affects the nerve cells in the areas of the brain called, basal ganglia, which are important in determining how the body moves. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 2 Introduction … • The nerve cells in the SN produces dopamine(D) – D is important for planning and controlling movement • The action of D is balanced with another neurotransmitter(NT) called Acetylcholine(Ach) Both NT ensures smooth ,coordinated movement . 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 3 Classification I. Drugs affecting brain dopaminergic system a. Dopamine precursor : Levodopa (I-dopa) Peripheral decarboxylase inhibitors: Carbidopa, Benserazide. b. MAO-B inhibitor: Selegiline c. COMT inhibitors: Entacapone, Tolcapone 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 4 Classification… d. Dopaminergic agonists: Bromocriptine, Ropinirole, Pramipexole e. Dopamine facilitator: Amantadine. II. Drugs affecting brain cholinergic system Central anti-cholinergics – Trihexyphenidyl, Procydidine, Biperiden. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 5 Strategy of treatment • In addition to an abundance of inhibitory dopaminergic neurons, the striatum is also rich in excitatory cholinergic neurons that oppose the action of D. • Many of the symptoms of parkinsonism reflect an imbalance between this two neurons 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 6 Strategy of treatment… Aim of therapy: • To restore dopamine in the basal ganglia and antagonizing the excitatory effect of cholinergic neurons – Thereby reestablishing the correct D/Ach balance 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 7 Dopamine Precursor : Levodopa (l-dopa) Mechanism of action • D does not cross the BBB but its immediate precursor levodopa does. o After its actively transported into the CNS and it will be converted to D in the surviving neurons of the SN • Thereby restoring dopaminergic neurotransmission in the neostriatum. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 8 Dopamine Precursor : Levodopa (ldopa)... • In the SNc, levodopa is converted to dopamine by the enzyme l-amino acid decarboxylase(L-AAD) and inactivated by the enzymes MAO and COMT. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 9 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 10 Why Levodopa Must Be Administered With Carbidopa ? Carbidopa: a dopamine decarboxylase inhibitor • ↓ the metabolism of levodopa in the periphery, thereby ↑ing the availability of levodopa to the CNS. • The addition of carbidopa lowers the dose of levodopa needed by 4-to 5 fold • Thus, ↓es the severity of adverse effects arising from peripherally formed D. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 11 Dopamine Precursor : Levodopa (ldopa)... Therapeutic uses • Levodopa + carbidopa :Parkinson disease. • In approximately 2/3 of patients, the combination markedly ↓ the severity of symptoms for the 1st few years of treatment. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 12 Dopamine Precursor : Levodopa (ldopa)... Pharmacokinetics • Levodopa is rapidly absorbed from the small intestines ; o by utilizing the active transport process meant for aromatic amino acids. • Bioavailability of levodopa is affected by: I. Gastric emptying II. Amino acids present in food compete for the same carrier for absorption 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 13 Dopamine Precursor : Levodopa (ldopa)... Blood levels are lower when taken with meals Thus, levodopa should be taken on an empty stomach, typically 30 minutes before a meal. • Levodopa undergoes high 1st pass metabolism in GI mucosa and liver. • The plasma half-life of levodopa is 1-2 hours. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 14 Dopamine Precursor : Levodopa (ldopa)... Adverse effects: anorexia, nausea, and vomiting CNS effects: Visual and auditory hallucinations ,dyskinesias, mood changes, depression, psychosis, and anxiety. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 15 Dopamine Precursor : Levodopa (ldopa)... • Long-term levodopa therapy is associated with a variety of motor complications. • This complications can occur as early as 6 months after starting levodopa therapy, especially if excessive doses are used initially – End-of-dose “wearing off ” (motor fluctuations) 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 16 Dopamine Precursor : Levodopa (ldopa)... Interactions • Pyridoxine ( Vitamin-B6) ↑ the peripheral breakdown of levodopa and diminishes its effectiveness • Levodopa and Nonselective MAOIs – Because they bring hypertensive crisis caused by enhanced catecholamine production. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 17 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 18 Dopamine Precursor : Levodopa (ldopa)... • In many psychotic patients, levodopa exacerbates symptoms, possibly through the buildup of central catecholamines. • Antipsychotic drugs are generally contraindicated in PD. – Because they potently block dopamine receptors and may augment parkinsonian symptoms. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 19 MAO-B inhibitor • Include :Selegiline, rasagiline, and safinamide Selegiline, selectively inhibits MAO type B, the enzyme that metabolizes dopamine. • By ↓ing the metabolism of dopamine, it ↑ dopamine levels in the brain. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 20 MAO-B inhibitor… • When given with levodopa, it enhances the actions of levodopa and markedly ↓ the required dose. At therapeutic doses • Preferentially inhibit MAO-B over MAO-A. • Has little potential for causing hypertensive crises – But ,it loses its selectivity when given above recommended doses(at high doses) 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 21 Catechol-O-methyl-transferase (COMT) inhibitors • Methylation of levodopa by COMT to 3-O-methyldopa is a minor pathway for levodopa metabolism. • Inhibition of peripheral dopamine decarboxylase by carbidopa causes formation of significant concentration of 3-O-methyldopa. – 3-O-methyldopa :competes with levodopa for active transport into the CNS and reduce central uptake of levodopa. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 22 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 23 Catechol-O-methyl-transferase (COMT) inhibitors… • Two selectively and reversibly COMT inhibitors – Entacapone and Tolcapone • Inhibition of COMT leads to – ↓ plasma concentrations of 3-O-methyldopa – ↑ed central uptake of levodopa, and greater concentrations of brain dopamine. • Indicated for managing wearing off 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 24 Catechol-O-methyl-transferase (COMT) inhibitors… Pharmacokinetics • Oral absorption of both drugs occurs readily and is not influenced by food. • Tolcapone has a relatively long duration of action compared to entacapone, which requires more frequent dosing. • Both drugs are extensively metabolized and eliminated in feces and urine. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 25 Catechol-O-methyl-transferase (COMT) inhibitors… Adverse effects • Both causes diarrhea, postural hypotension, nausea, anorexia, dyskinesias, hallucinations, and sleep disorders. • Intense hepatic necrosis(most seriously), is associated with tolcapone use. – Its use is limited by reports of fatal hepatotoxicity 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 26 Dopamine Receptor Agonists • Includes : Bromocriptine ,Ropinirole , Pramipexole , Rotigotine , and Apomorphine. • They have a longer duration of action than that of levodopa • Are effective in patients exhibiting fluctuations in response to levodopa. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 27 Dopamine Receptor Agonists… • Bromocriptine, pramipexole, and ropinirole are effective in patients with PD complicated by motor fluctuations and dyskinesias. • Apomorphine is an injectable dopamine agonist that is used in severe and advanced stages of the disease. • Adverse effects severely limit the utility of the dopamine agonists 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 28 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 29 Dopamine Receptor Agonists… Pharmacokinetic 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 30 Dopamine Facilitator: Amantadine • Amantadine has several effects on a number of NTs implicated in parkinsonism – ↑ing the release of dopamine – Blocking cholinergic receptors – Inhibiting the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) type of glutamate receptors. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 31 Dopamine Facilitator: Amantadine… • It is less efficacious than levodopa, and tolerance develops more readily. • The drug may cause restlessness, agitation, confusion, and hallucinations • At high doses, it may induce acute toxic psychosis. • Orthostatic hypotension, urinary retention, peripheral edema, and dry mouth also may occur. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 32 Drugs Affecting Brain Cholinergic System • Include: Trihexyphenidyl, Procydidine, Biperiden • They are much less efficacious than levodopa • Play only an adjuvant role in anti-parkinsonism therapy. 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 33 Drugs Affecting Brain Cholinergic System… • The actions of benztropine and trihexyphenidyl are similar; – Blockade of cholinergic transmission produces effects similar to augmentation of dopaminergic transmission o Since it helps to correct the imbalance in the D/Ach activity • They induce mood changes and confusion, and produce xerostomia, constipation, and visual problems typical of muscarinic blockers 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 34 Thank you 02/02/2022 Antiparkinsoinan drugs 35



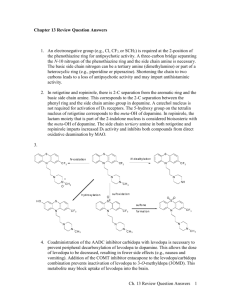
![The Power of NOW[3741]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/025690828_1-687eebfb243c6979cdc2ac319fc077fd-300x300.png)