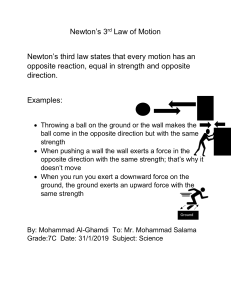
1. Imagine a head-on collision between a large truck and a small compact car. During the collision: (A) the truck exerts a greater amount of force on the car than the car exerts on the truck. (B) the car exerts a greater amount of force on the truck than the truck exerts on the car. (C) neither exerts a force on the other, the car gets smashed simply because it gets in the way of the truck. (D) the truck exerts a force on the car but the car doesn't exert a force on the truck. (E) the truck exerts the same amount of force on the car as the car exerts on the truck. Two students, student "a" who has a mass of 95 kg and student "b" who has a mass of 77 kg sit in identical office chairs facing each other. Student "a" places his bare feet on student "b's" knees, as shown below. Student "a' then suddenly pushes outward with his feet, causing both chairs to move. 2. In this situation, (A) neither student exerts a force on the other. (B) student "a" exerts a force on "b", but "b" doesn't exert any force on "a". (C) each student exerts a force on the other but "b" exerts the larger force. (D) each student exerts a force on the other but "a" exerts the larger force. (E) each student exerts the same amount of force on the other. 3. A book is at rest on a table top. Which of the following force(s) is(are) acting on the book? 1. 2. 3. 4. (A) (B) (C) (D) A downward force due to gravity. The upward force by the table. A net downward force due to air pressure. A net upward force due to air pressure. 1 only. 1 and 2 1, 2, and 3. 1, 2, and 4. (E) none of these, since the book is at rest there are no forces acting on it. 4. When a rubber ball dropped from rest bounces off the floor, its direction of motion is reversed because: (A) energy of the ball is conserved. (B) momentum of the ball is conserved. (C) the floor exerts a force on the ball that stops its fall and then drives it upward. (D) the floor is in the way and the ball has to keep moving. (E) none of the above. 5. A large box is being pushed across the floor at a constant speed of 4.0 m/s. What can you conclude about the forces acting on the box? (A) If the force applied to the box is doubled, the constant speed of the box will increase to 8.0 m/s. (B) The amount of force applied to move the box at a constant speed must be more than its weight. (C) The amount of force applied to move the box at a constant speed must be equal to the amount of the frictional forces that resist its motion. (D) The amount of force applied to move the box at a constant speed must be more than the amount of the frictional forces that resist its motion. (E) There is a force being applied to the box to make it move but the external forces such as friction are not 'real' forces, they just resist motion. 6. A horizontal force accelerates a box from rest across a horizontal surface (friction is present) at a constant rate. The experiment is repeated, and all the conditions remain the same with the exception that the horizontal force is doubled. What happens to the box/s acceleration? a. It increases to more than double its original value b. It increases to exactly double its original value c. It increases to less than double its original value d. It stays the same 7. Action-reaction forces a. b. c. d. Sometimes act on the same object. Always act on the same object. May be at right angles. Always act on different. 8. A golf club hits a golf ball with a force of 2400 N. The golf ball hits the club with a force e. f. Slightly less than 2400 N. Exactly 2400 N. g. h. Slightly more than 2400 N. Close to 0 N. 9. Which of the following describes an object in equilibrium? a. A ball thrown straight up, at the highest point. b. A car going around a curve at a constant speed. c. A car moving with a constant velocity down a hill. d. the earth orbiting the sun. 10. In the absence of all forces, a moving object will i. j. k. l. Slow down and eventually stop. Move at a constant velocity. Immediately cone to rest. Cannot determine without more detail. 11. An example of a force which acts at a distance is m. n. o. p. Tension. Weight. Static friction. Kinetic friction. 12. If you exert a force F on an object, the force which the object exerts on you will q. Depend on whether or not the object is moving. r. Depend on whether or not you are moving. s. Depend on the relative masses of you and the object. t. Always be F. 13. A constant net force acts on an object. Describe the motion of the object. u. v. w. x. Constant acceleration Constant speed Constant velocity Increasing acceleration 14. A stone is thrown straight up. At the top of its path, the net force acting on it is y. z. aa. bb. Greater than its weight. Greater than zero, but less than its weight. Instantaneously equal to zero. Equal to its weight. 15. A net force F acts on a mass m and produces an acceleration a. What acceleration results if a net force 2F acts on a mass 4m? cc. dd. ee. ff. 8a 4a 2a a/2 16. A net force F acts on a mass m and produces an acceleration a. What acceleration results if a net force F/2 acts on a mass 4m? gg. hh. ii. jj. 8a 4a 2a a/2 17. A 9 N cart is pulled using a handle with an applied force of 35 N at constant velocity. a) What is the normal force the ground exerts on the cart? b) What is the frictional force acting on the cart? c) What is the coefficient of friction? 18. A 7 kg cart is pushed using an applied force of 30 N. The coefficient of friction is 0.20. a) What is the normal force? b) What is the frictional force? c) What is the net horizontal force? d) What is the acceleration of the cart? 19. What is the vertical component of a) the 8 N force shown on the right? b) What is the horizontal component of the 8 N force? 20. What applied force is required to accelerate a 5 N rock upward at 1.5 m/s2? 21. A 7 N cart is pushed using a handle that is at an angle of 30o above the horizontal, or ground. The force on the handle is 47 N, and friction opposes the cart’s motion with a force of 15 N. a) What is the normal force the ground exerts on the cart? b) What is the net horizontal force responsible for moving the cart? 22. If the same force is applied to objects with different masses, which object will accelerate fastest? 23. How should forces be arranged to produce the greatest net force?