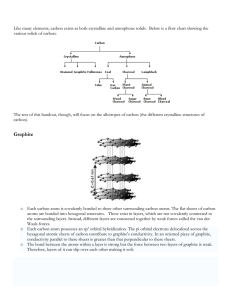
Allotropes of Carbon and Silicon Dioxide Covalent Structures Carbon in many forms… Allotropes O An element is said to have allotropes when it exists in the same state in more than one structural form. O The allotropes of an element have the same or similar chemical properties, but their physical properties are different. O There are three common allotropes of carbon - diamond, graphite and the fullerenes. Carbon allotropes Carbon allotropes Diamond Graphite C60 Fullerene Bonding Each carbon bonded to four other carbon atoms. Arranged tetrahedrally. Each carbon bonded to three other carbon atoms. Arranged in layers of hexagonal rings. Structure Giant covalent Giant covalent Each carbon bonded to three other carbon atoms. Spherical molecules made up of 20 hexagons and 12 pentagons. Simple covalent sp3 sp2 sp2/sp3 Hybridization C-C bond length/nm 0.154 0.143 (in the plane) 0.335 (between the layers) 0.140 (between two hexagons) 0.145 (between a hexagon and a pentagon) Carbon allotropes Diamond Graphite C60 Fullerene Melting point/K 3500 3700 Sublimes at 800 Density/g cm-3 3.53 2.25 1.65 Electrical conductivity None Good Poor Very Good Good Poor Insoluble in all kinds of solvents Very hard Insoluble in all kinds of solvents Soft Soluble in non-polar solvents e.g. toluene Very hard Conduction of heat Solubility Hardness Check your understanding… O Why is diamond so much harder than graphite? O Diamond is so much harder than graphite because all the carbon atoms in diamond are held together by strong covalent bonds in a giant lattice structure. The weak forces of attraction between the layers of carbon atoms in graphite are easily broken. Check your understanding… O Why does graphite conduct electricity while diamond does not? Why is graphite a better conductor than C60? O The presence of a cloud of free/delocalised electrons in between layers of carbon atoms in graphite enables it to conduct electricity. All the electrons in the carbon atoms present in diamond are involved in the formation of strong covalent bonds and thus there are no free electrons available to conduct electricity. Check your understanding… O Compare the melting points of diamond, graphite and C60. O Graphite has the highest melting point (3700 oC) because a lot of energy is needed to break the strong C-C bonds (sp2/ bond length 0.143 nm) between the carbon atoms in graphite. Check your understanding… O Diamond also had a high melting point (3500 oC) because a lot of energy is needed to break the strong C-C bonds (sp3/ bond length 0.154 nm) between the carbon atoms in diamond. O C60 fullerene sublimes at 800O C as it still consists of molecules, though the molecules are large. Only weak intermolecular forces are needed to be overcome. Check your understanding… O Why is graphite used in lead pencils and also as a lubricant? O Graphite is used in lead pencil and as a lubricant because it consists of layers of carbon atoms that are held weakly together and thus can slide over one another easily when a force is applied. Check your understanding… O Why are diamond and graphite almost totally insoluble in all kinds of solvent? How would you explain the solubility of C60 in non-polar solvents? O Diamond and graphite are almost totally insoluble in all kinds of solvent because of their giant covalent structures. C60 fullerene is soluble in non-polar solvents because it consists of molecules (though the molecules are large). Silicon and silicon dioxide Silicon and silicon dioxide O Silicon and silicon dioxide have structures similar to diamond. In silicon dioxide, each silicon is bonded to four oxygen atoms and each oxygen atom is bonded to two silicon atoms. The properties are similar to diamond.