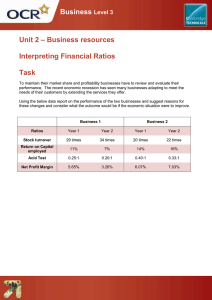
Ratios (1) Financial Ratios help the users to assess the Financial position of the entity Financial performance of the entity Users of financial Statements Investors & potential investors Lenders Suppliers Customers Public Employees Government & its Agencies Competitors General Public Uses of ratios Comparing actual data with budgeted data Comparison with the competitors Comparison with the Industry averages Comparison with past years Categories of financial ratios Liquidity / Short Term Solvency AH I. II. (2) I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. VIII. IX. (3) I. II. III. IV. (4) I. CAF-5 M To assess the ability to meet the short term obligation (Short term Solvency) II. Profitability To assess the financial performance III. Activity / Efficiency / Turnover / working capital turnover To assess efficient utilization of assets / investment in WC IV. Debt / Gearing / Leverage / Long term Stability To assess the ability to meet the Long term obligation (Long term Solvency) V. Potential Investor / investment / Market To assess the profit / return on investor's investment ADVANTAGES OF RATIOS ANAYLYS 1. 2. 3. 4. It simplifies the financial statements. It helps in comparing companies of different size with each other. It helps in trend analysis which involves comparing a single company over a period. It highlights important information in simple form quickly. A user can judge a company by just looking at few numbers instead of reading the whole financial statements. LIMITATIONS OF RATIO ANALYSIS 1. Inflation may distort comparison over time. 2. Different accounting policies may distort inter - company comparison 3. The accounting information used to prepare the ratios may be out of date. 4. The information presented in publish accounts in usually precise making the detailed analysis impossible. 5. Using industry average as basis for comparison may be misleading as they are averages of ratios from multiple companies. 6. Changes in accounting policies from year to year may genearate misleading ratios. I. LIQUIDITY / SHORT TERM SOLVENCY To assess the ability to meet the short term obligation (Short term Solvency) 1 Ratios CAF-5 (A) Working Capital Current Assets Less Current Liabilities (B) Current Ratio Current Assets___ Current Liabilities AH It will be in times . 2 :1 is ideal It represents the margin of safety or cushion available to the creditors. It is an index of the business financial stability. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Better liquidity position I. Financial difficulty II. Larger inventories –Risk of obsolescence II. Lower inventories III. Less credit purchases III. Longer creditor’s credit periods. (C) LIQUID RATIO / ACID TEST RATIO / QUICK RATIO Current assets – inventory Current Liabilities It will be in times . 1 :1 is ideal It measures the business capacity to pay off current obligations immediately and is more accurate test of liquidity than the current ratio. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Better liquidity ratio I. Financial difficulty II. Longer debtors’ credit period II. Lower inventories III. Larger creditor period III. Shorter debtor’s credit period. (II) PROFITABILITY To assess the financial performance (A) Gross Profit Ratio (GP Ratio) Gross Profit x 100% Net Sales M It will be in %. Higher is better It shows the relationship between gross profit and sales and the efficiency with which a business produces its products. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Increase in selling price I. Decrease in selling price II. Reduction in cost II. Increase in cost III. Undervaluation of opening stock or III. Overvaluation of opening stock or overvaluation of closing stock undervaluation of closing stock. IV. Achieving of economies of scale (B) Net Profit Ratio Net profit x 100% Net Sales It will be in %. Higher is better It shows the overall profitability of business. It shows how efficiently the business is being conducted to ensure higher profits. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Efficient operating expenses I. Uncontrolled expenses 2 Ratios II. III. IV. V. Low financial cost. Low tax rate Increase of incomes Gains on disposal CAF-5 II. III. IV. V. High financial cost High tax rate Low in incomes Loss on disposals (C) PBIT over sales Ratio PBIT x 100% Net Sales AH It will be in %. Higher is better It shows the overall profitability of business. It shows how efficiently the business is being conducted to ensure higher profits. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Efficient operating expenses I. Uncontrolled expenses II. Increase of incomes II. Low in incomes III. Gains on disposal III. Loss on disposals (D) Return on Capital Employed ( ROCE ) _______PBIT________ x 100 % Avg. Capital employed M It will be in %. Higher is better Capital employed = Equity + borrowings(Long term) It is considered to be the best measure of overall profitability of business and indicates how well the management has used the investment made by owners and lenders into the business. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Higher profitability I. Lower profitability II. Efficient funds management II. Inefficient funds management (E) Return on Equity (ROE) PAT – Preference dividend(classified as equity) x 100% Avg. Equity It will be in %. Higher is better It measures the overall efficiency of a company. This ration is of great importance to present and prospective shareholders as well as management. Higher ratio Low Ratio I. Higher profitability I. Lower profitability II. Efficient funds management II. Inefficient funds management (F) Return on Assets(ROA) __________PBIT___________ X 100% Avg. Assets It will be in %. Higher is better It measures the overall efficiency of a company in general profits using its assets efficiently. HIGHER RATIO LOW RATIO I. High profitability I. Lower profitability II. Efficient asset management II. Inefficient asset management 3 Ratios CAF-5 (G) Expense to Sale Ratio COS/Selling expense/Admin expense x 100% Net Sales AH It will be in %. Lower is better It shows the relationship between gross profit and sales and the efficiency with which a business produces its products. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Decrease in selling price I. Increase in selling price II. Increase in cost II. Decrease in cost III. Overvaluation of opening III. Overvaluation of opening stock or stock or undervaluation of undervaluation of closing stock (COS) closing stock (COS) M III. ACTIVITY / EFFICIENCY / TURNOVER / WORKING CAPITAL TURNOVER To assess efficient utilization of assets / investment in WC (A) Inventory Turnover Ratio Cost of Sales Avg. Inventory It will be in times. Higher is better It measures the velocity of conversion of stock into sales. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Efficient inventory Management I. Inefficient inventory Management II. Higher sales II. Lower sales (B) Inventory Holding Period ____Avg. Inventory____ x 365 days Cost of sales (Annual) It will be in Days. Lower is better It measures the period for which the goods remain in stock before getting sold. Use 12 instead of 365 then answer will be in Months and Use 52 to have an answer in weeks HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Inefficient inventory Management I. Efficient inventory Management II. Lower sales II. Higher Sales (C) Debtors Turnover Ratio _____Credit sales __ Avg. Debtors It will be in times. Higher is better It measures the velocity of debt collection of business. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Better control over debtors I. Poor control over debtors II. Shorter credit periods II. Longer credit periods III. More discounts offered III. Less discounts offered (D) Debtors Collection Period _____Average Debtors______ x 365 days Credit Sales (Annual) 4 Ratios CAF-5 M AH It will be in Days. Lower is better but should be within credit period allowed to credit customers It indicates the number of days for which a business has to wait before its debtors are converted into cash (An average days after which amounts are collected from debtors) If credit sales are not given in question then use Total Sales Use 12 instead of 365 then answer will be in Months and Use 52 to have an answer in weeks HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Inefficient collection I. Efficient collection II. Longer credit Periods II. Shorter credit periods III. Less discounts offered III. More discounts offered (E) Creditors Turnover Ratio Credit Purchases_(Annual)__ Avg. Creditors It will be in times. Higher is better as it shows credit worthiness. However, higher ratio may indicated that credit period is not fully availed as legitimate credit period should be availed. If credit purchases are not given in the question then use total Purchases If Purchases are not given , use cost of sales It measures the velocity of paying to payables of the business. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Timely payment to supplies I. Late payment to suppliers II. Credit worthiness II. Less Credit worthiness III. More discounts availed III. Less discounts availed (F) Creditors Payment Period Average Creditors ____ x 365 days Credit Purchases(Annual) It will be in Days. Lower is better as it shows credit worthiness, but it should be closer to credit period allowed. Use 12 instead of 365 then answer will be in Months and Use 52 to have an answer in weeks If credit purchases are not given in the question then use total Purchases If Purchases are not given , use cost of sales It indicates the number of days of credit period enjoyed by the business in paying creditors. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Late Payment to suppliers I. Timely payments to suppliers II. Less credit worthiness II. Credit worthiness III. Less discounts availed III. More discounts availed. (G) Assets Turnover Ratio Net Sales_______ Avg of (Total Assets Less CL) AVG of (Equity + LTL) It will be in times. Higher is better It measures the efficiency and profit earning ability of business assets. It indicated how well the assets are utilized to earn revenue. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Efficient utilization of assets I. Inefficient use of assets II. High productivity of assets II. Low productivity (H) Working capital cycle / Cash operating cycle Inventory Period + Debtors collection period - Creditors Period It will be in Days. Lower is better 5 Ratios CAF-5 It reflects the period of one operating cycle from when the time suppliers are paid to the time when inventory is produced and cash is received from customers. HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Lower inventory turnover IV. High inventory turnover II. Poor control over debtors V. Better control over debtors III. Timely payment to suppliers VI. Late payment to suppliers (IV) DEBT / GEARING / LEVERAGE / LONG TERM STABILITY M AH To assess the ability to meet the Long term obligation (Long term Solvency) (A) Debt Equity Ratio / Gearing Ratio L.T.Debt Equity 1:1 is good but depends upon business It indicates the relationship between external finance and internal equity HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Higher debts I. Lower debts II. Less risk shared by openers II. More risk shared by owners III. Less solvent business III. Better solvency position Formula 2 ( Recommended) L.T.Debt Equity +L.T.D 1:1 is good but depends upon business It indicates the relationship between external finance and Total finance(Internal + external) HIGHER RATIO LOWER RATIO I. Higher debts I. Lower debts II. Less risk shared by openers II. More risk shared by owners III. Less solvent business III. Better solvency position (B) INTEREST COVER / DEBT SERVICE RATIO _ PBIT Interest It will be in times. Higher is better It indicates whether the business earned sufficient profits to pay periodically the interest charges. HIGH RATIO LOW RATIO I. Higher profitability I. Lower profitability II. Less use of debts II. More use of debts III. Ability to make further debts III. Less credit worthiness TYPES OF QUESTIONS 1. Only Ratio Calculation. May be only current year and may be Current and comparative year as well. Current year ratio calculation and Comparison with other company If two years information is available and ratios are required for current year only, then in case of mixed ratios, use average values I.e.(Opening value + Closing Value) / 2 for balance sheet items. However, if ratios for both year are required then use respective closing values of each year. 2. Ratios analysis and comment/Analyze Then I. Calculate Ratios II. Should know the meaning of ratio III. What Could be the possible reason for the change / variation ( 3 or 4 reason depend on Question) 6 Ratios CAF-5 (S-2017 Q-7) M AH Q-1 CAF-5 Ratios – Past Papers Q-2 (A-2017 Q-5) Mirza Ali Hassan , ACA Page 1 7 Ratios CAF-5 CAF-5 Ratios – Past Papers M AH Q-3 (S-2018 Q-7) Q-4 (A-2018 Q-7) Mirza Ali Hassan , ACA Page 2 8 Ratios CAF-5 Ratios – Past Papers AH CAF-5 M Q-5 (S-2019 Q-7) Mirza Ali Hassan , ACA Page 3 9 Ratios CAF-5 Ratios – Past Papers M AH CAF-5 Mirza Ali Hassan , ACA Page 4 10