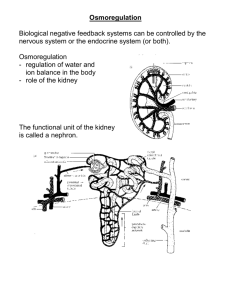
9.4 WATER BALANCE • Humans cannot survive without water for more than a few days (water reserves depleted faster than food) • Avg. adult loses 2 L of water/day (urine, sweat, exhalation) • A 1% drop in fluid (body mass) causes thirst, 5% drop causes extreme pain/collapse, 10% drop causes death Can you drink urine? What!?!?! The body’s internal environment of extracellular fluid (fluid that surrounds the cells/tissues and plasma portion of blood) must remain at a constant volume, solute content and temperature. Recall Osmosis…. • Hyperosmotic – solution on one side has a high [solute] and low [water] • Hypoosmotic – solution on one side has a high [water] and low [solute] • Isoosmotic – same solute and water [] on either side. (ideal condition) Osmoregulation & Excretion • Osmosis is a crucial process in regulating homeostasis • Actively regulating osmotic pressure of bodily fluids is known as osmoregulation. • All organisms need to keep their intracellular and extracellular fluids isoosmotic. • Some species of marine animals do not need to regulate their extracellular fluid as water flows freely through them. • To maintain homeostasis, cells need to regulate their ionic balance, pH, and [osmotic] • Animals maintain this balance through the process of excretion. Excretion is the elimination of waste products and foreign matter from the body • In humans, the excretory system is used When proteins are metabolized, the amino group must be removed and discarded by the body. This is called DEAMINATION. The by-product of deamination is ammonia, which is extremely toxic to the body. The liver takes one molecule of ammonia and adds it to HCO3- to make urea (water soluble) which is eliminated in the urine. Urea is 100 000 times less toxic than ammonia. •Side note: ammonia (NH3), a water soluble gas, is quite toxic, 0.005 mg can kill a human. Fish are able to pass ammonia out through their gills, but land animals cannot do this, they must store ammonia and find a way to get rid of it. Urine Output Increased water intake Decreased water intake or Increased exercise increased urine output Decreased urine output ADH ~ ANTI DIURETIC HORMONE • causes the kidneys to increase water reabsorption • produced by the hypothalamus and released by the pituitary • ADH controls reabsorption of the last 15% of water that passes through the nephron in the Loop of Henle and the distal tubule ADH and the Nephron • Descending loop of Henle is permeable to water and ions, but ascending tubule is only permeable to NaCl • Without ADH the rest of the tubule remains impermeable to water • ADH makes upper part of distal tubule and collecting duct permeable to water • The remaining urine becomes more concentrated HOMEWORK: Pg. 445 # 1-7, 9, 12 Ch. 9 Quiz will be _____________