Aspirin Medication Template: Uses, Side Effects, and Nursing
advertisement

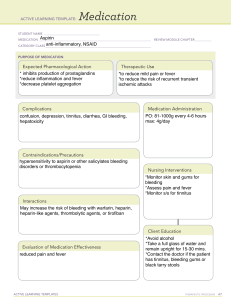
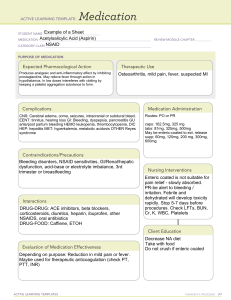
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: Medication SERHAT KONDAKCI STUDENT NAME______________________________________ Aspirin/ASA MEDICATION___________________________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER____________ CATEGORY CLASS__NSAID _____________________________________________________________________ PURPOSE OF MEDICATION Expected Pharmacological Action Pain analgesic and blood thinner Complications stomach or gut irritation indigestion nausea Contraindications/Precautions bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia uncontrolled high blood pressure asthma peptic or stomach ulcers liver or kidney disease Therapeutic Use Treat pain, fever, headache, and inflammation. It can also reduce the risk of heart attack. Medication Administration - Usual doses for mild to moderate pain are 350 or 650 mg every 4 hours or 500 mg every 6 hours. - Doses for rheumatoid arthritis include 500 mg every 4-6 hours; 650 mg every 4 hours; 1000 mg every 4-6 hours; 1950 mg twice daily. - Heart attacks are prevented with 75, 81, 162 or 325 mg daily. Nursing Interventions Assess patient for signs of bleeding (petechiae, ecchymosis, bloody or black stools, bleeding gums). Interactions Anti-inflammatory painkillers Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and other antidepressants Warfarin Methotrexate Evaluation of Medication Effectiveness Pain relief Improved heart health ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES Client Education Drink adequate fluids while taking aspirin. Advise patient to avoid alcohol when prescribed high doses of aspirin. Baby aspirin is preferred for acute or prophylactic management of heart disease.