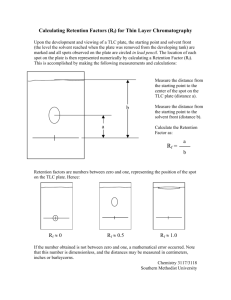
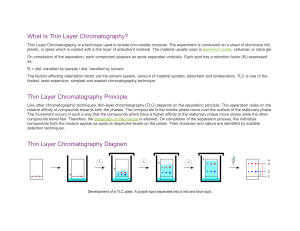
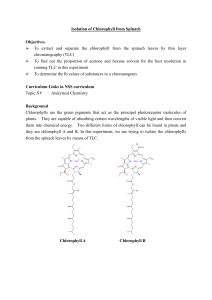
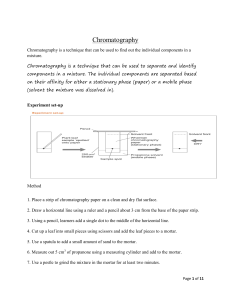
Thin Layer Chromatography Investigations Leighton Dann and Paul Beaumont Science & Plants for Schools www.saps.org.uk TLC One of a number of types of chromatography: • gas/liquid • affinity • paper TLC Separation of complex mixtures between two phases: - a stationary phase and a mobile phase TLC Phases • the stationary phase is a thin layer of absorbent particles, in this case silica gel • the mobile phase is the solvent Fisher Scientific UK. Tel: 01509 555500 Cat No: TLC-410-610X Thin Layer Chromatography Separation of: • photosynthetic pigments in leaves • anthocyanins in leaves, flowers, fruit and vegetables • Place ca. 3 cm2 leaf in mortar • [If tissue is coarse, silver sand may be added] • Grind until all tissue broken up • Add ca. 750 ml propanone • Pour off supernatant into a container and seal Method Method • Supernatant and residue from grinding leaf in propanone Method • Mark (with a pencil) a plate 1.5 cm up from the base on the edge of both sides • Use a ruler across these marks to mark two spots 2 cm apart in the middle of the plate 1.5 cm 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 Method • Use Pasteur pipette to place small drops of supernatant • Dry off before adding another lot of drops • Continue until there is a concentrated line of colour 1.5 cm 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 Method • Repeat process until a second line is produced (or one line across the whole plate) 1.5 cm 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 Method • Plate into a 600 cm3 beaker, replace foil • Remove plate when solvent nearly at top • Immediately mark solvent front Solvent system Cyclohexane : propanone : petroleum ether (low boiling point) 5:3:2 Pigment Colour RF value carotene pheophytin a pheophytin b chlorophyll a chlorophyll b xanthophylls xanthophylls xanthophylls yellow-orange grey light grey blue green green yellow yellow yellow 0.91 0.75 0.63-0.75 0.63 0.58 0.53 0.47 0.32 Coleus Anthocyanin results