Antidepressant Medication Table: Mechanisms, Uses, Side Effects
advertisement

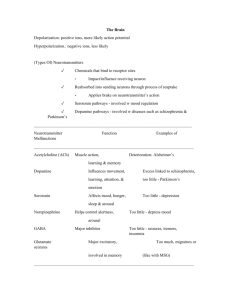
Class Antidepressant Subclass Tricyclics (TCAs) Product Imipramine /Tofranil, clomiprami ne/Anafran il, amitriptylin e/Elavil Mechanism block reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin at synapses; support catecholamine hypothesis (depression 2/2 lower-than-normal levels of the neurotransmitter) Selective Serotonin Reputake Inhibitors (SSRIs) fluoxetine/ Prozac, sertraline/Z oloft, paroxetine/ Paxil block reuptake of serotonin at synapses Monoamin e Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) phenelzine /Nardil, tranylcypro mine/Parna te block action of enzyme that breaks down norepinephrine and serotonin, making these neurotransmitters more available at synapses SNRIs venlafaxine /Effexor, duloxetine/ Cymbalta, desvenlafaz ine/Pristiq bupropion/ Wellbutrin/ Zyban NDRIs Use MDD w/ hopelessness, inability to experience pleasure, vegetative sxs (i.e. appetite, sleep disturbances, anergia); Dysthymic D/O; Panic Attacks, Agoraphobia; OCD (clomipramine/Anafra nil); enuresis (esp. imipramine/Tofranil); chronic pain MDD, Dysthmic D/O; OCD, Panic D/O, Social Phobia, binge eating, premature ejaculation Side effects anticholinergic effects (i.e., dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention, blurred vision) GI sxs, impaired sexual funx, drowsiness, confusion/memory impairment (esp. in older adults); often effects subside within few weeks, if not, may be eliminated by lowering dosage; serious effects: tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, arrhythmia nausea, loss of appetite, impaired sexual funx, agitation, headaches, insomnia; combining w. TCA, MAOI, or other drug that increases serotonin can cause serotonin syndrome (i.e., altered consciousness, agitation, other changes in metnal status; autonomic changes – sweating, dilated pupils; tremor, muscle rigidity, akathaisia – motor restlessness) Caution toxicity if OD; caution w. heart disease or suicidal patients Comparison Relative to TCAs, quicker effectiveness, fewer/less severe side effects (incl. anti-cholinergic effects, sedation, cognitive impairment, cardiovascular effects), safer in OD Atypical or nonresponsive depression (increased appetite, hypersomnia, rejection-sensitivity, mood reactivity, sxs of anxiety/hypochondria sis), MDD, GAD, Social Anxiety D/O, Panic D/O sleep disturbances, nausea/GI concerns, sexual dysfunx, headache, elevated blood pressure MDD, tobacco cessation dry mouth, agitation, insomnia, itching/skin rash, decreased appetite; can aggravate pre-existing seizures or 1 psychosis; can cause anaphylaxis (severe allergic rxn) Mood Stabilizers Lithium Antiseizure drugs lithium carbonate/ Eskalith, Lithonat, Duralith, lithium citrate, Cibalith Carbamaze pine/Tegre tol, Valproic acid/Depak ote unknown; appears to effect dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin Bipolar, stabilizes mood (depressive and manic episodes), redux of mood swings nausea, diarrhea, metallic taste in mouth, weight gain, hand tremor, fatigue, mild cog. Impairment (i.e., confusion, disorientation) require monitoring to avoid lithium toxicity incl. vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, tremor, slurred speech, ataxia, seizures, coma, death useful for tx of dysphoric mania and mania w. rapid cycling altering serotonin levels N/V, tremor, visual disturbances, ataxia monitor blood levels; liver failure w. carbamazepine or valproic acid, agranulocytosis (low white blood cell count) and aplastic anemia w. carbaamzepine chlorproma zine/Thoraz ine, thioridazin e/Mellaril, haloperidol /Haldol block dopamine receptors in the brain; dopamine hypothesis Schizophrenia 2/2 overactivity of dopamine receptors, though research suggests may be 2/2 imbalance of dopamine and other neurotransmitters: Nore, Sero, Glutamate, GABA. Anticholinergic effects: dry mouth, urinary retention, blurred vision, tachycardia, gastric distress, sexual dysfunx Extrapyramidal Side effects: shuffling gait, stooped posture, slurred speech); dystonia (sustained muscle contraction or spasms that cause involuntary movts); akathisia; tardive dyskinesia (abnormal, involuntary movt., esp. in face, tongue, jaw; can be alleviated by gradually withdrawing drug) Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS): rare, life-threatening; muscle rigidity, high fever, seating, unstable blood pressure, altered mental status, autonomic dysfunx; usually develops within 2 wks of drug tx; onset is rapid, and must be immediately dc’d to avoid fatality ++ Positive sxs (i.e., delusions, hallucinations, agitations) of schizophrenia, clozapine/C lozaril, risperidone /Risperdal, effect different dopamine receptors, as well as serotonin, Antipsychotics Traditional APsych Atypical Antipsycho tic schizophrenia, other psychotic d/o or sxs little effect on negative sxs (i.e., affective flattening, anhedonia, social withdrawal); also psychosis, Tourette’s D/O, acute mania anticholinergic effects, sedation, weight gain, neuroleptic malignant syndrome; clozapine alleviate positive and negative sxs; less likely to cause extrapyramidal 2 olanzapine/ Zyprexa,ari prazole/Abi lify norepinephrine, and glutamate receptors Benzodiaze pin diazepam/ Valium, alprazolam /Xanax, triazolam/ Halcion, clonazepa m/Klonopin enhance activity of inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA anxiety, insomnia, muscle spasms, seizures, mod/severe sxs of etoh withdrawal Barbituates thiopental/ Pentothal, amobarbita l/Amytal, secobarbita l/Seconal exert effect by affecting GABA receptors in reticular activating system, medulla, and certain areas of cortex anesthetic, agitated pts; short-term tx for insomnia secobarbital/Seconal past: anxiety, but now use benzo b/c safer Azaspirone buspirone/ Buspar affecting dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin levels Anxiety disorders, esp. GAD can cause agranylocytosis, which is why not really rx’d unless failed others side effects; typically effective for pt w/ poor response to traditional antipsyhotics drowsiness/sedation ataxia/incoordination/motor disturbances, cognitive impairment (i.e., poor concentration, anterograde amnesia; confusion/disorientation in older adults), anticholinergic effects, sexual dysfunx; chronic use can lead to dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal sxs (irritability, insomnia, agitation, dyphoria, GI distress, rebound anxiety – more severe than original sxs; severe withdrawal sxs – seizures, delirium, hallucinations, coma – if abruptly dc after taking high dose for extended period of time) combining w. etoh or other CNS depressant can be fatal drowsiness, dizziness, ataxia, confusion/cognitive impairment, paradoxical excitement; regular use leads to dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal sxs, and seizures, delirium, or death of sudden withdrawal; widely abused and often implicated in accidental deaths and suicides (fatally suppress respiration) dizziness, light-headedness, nausea, headache combining w. etoh can be fatal 2/2 effect on brain structures controlling breathing SEDATIVES, HYPNOTICS, AND ANXIOLYTICS tx of anxiety w.o. causing sedative, muscle-relaxant effects, or addiction 3 Other Drugs NarcoticAnalgesics natural opioids (opium, morphine, codeine), synthetic, semisynthetic (heroin, methadone , oxycodone /Percodan. OxyContin, hydrocodo ne/Vicodin, meperidine /Demerol) mimick effects of body’s natural analgesics (endorphins, enkephalins) pre-operative relaxation/sedation, acute and chronic pain; methodone for heroin addiction (does not produce euphoric effects, but reduces cravings and withdrawal sxs) dry mouth, nausea, pupil constriction, cough suppression, hypotension, sexual dysfunx, respiratory depression; chronic use leads to dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal sxs, and eventually lose pleasure from drug and use only to avoid sxs of withdrawaal; Widely abused drugs; Withdrawal sxs: early sxs like those of bad col or flu (runny nose, watery eyes, nausea, fever, yawning); later sxs include insomnia, muscle/joint pain, abdominal cramps, N/v, diarrhea, elevated blood pressure Psystimulants methylphe nidate/Rital in/Concert a, pemoline/C ylert, amphetami nedextroamp hetamine/ Adderall atomoxetin e/Strattera mimic/potentiate action of norepinephrine and dopamine in brain ADHD, narcolepsy insomnia, decreased appetite/weight loss, stomachaches, dysphoric mood (anxiety, irritability, sadness); can exacerbate tics, so rx w. care for those w. personal/ family hx “drug holidays:” during winter and summer vacations, can help reverse growth suppression block reuptake of norepinephrine; nonstimulant ADHD, ages 6+ decreased appetite, dizziness, fatigue, irritability; in adults, sexual dysfunx and menstrual cramps; possibly increase s/I in children/adolescents E.g. propranolol /Inderal inhibit activity of sympathetic nervous system by blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, which then slow heart rate and lower blood pressure HTN, cardiac arrhythmias, migraine headaches, essential tremor; physical sxs of anxiety (i.e., palpitations, tremors, sweating) bradycardia, hypotension, sexual dysfunx, fatigue, nausea, vision changes, dizziness, depression; avoid abrupt withdrawal (headaches, tremors confusion, HTN, cardiac arrhythmia) Norepinep hrine Reuptake Inhibitors (NRIs) Betablockers also drugs of abuse, such as cocaine and methamphetamin e less effective than benzos for cognitive sxs of anxiety (i.e., worry, apprehension) 4 Antialcohol Drugs disulfiram/ Antabuse, naltrexone (ReViia, Vivitrol) disulfiram/Antabuse inhibits etoh metabolism; when taken w. etoh, causes N/V, SOB, tachycardia, other unpleasant sxs; etoh abuse and dependence naltrexone/Revia/Vivit rol: opioid receptor antagonist; reduces pleasurable effects of/craving for etoh disulfiram/Antabuse (in absence of etoh: drowsiness, skin rash, headache, restlessness, impotence; overdose: seizures, low b.p. chest pain, SOB, death); naltrexone/ReVila/Vivitrol (stomach pain, N/V, fatigue, headache, joint/muscle pain; high dose can cause liver damage) 5