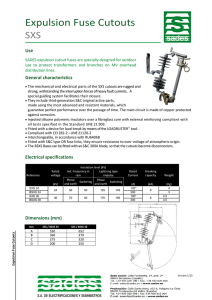
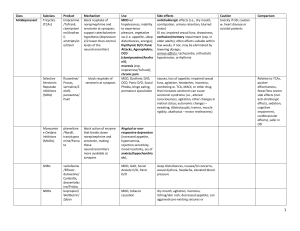
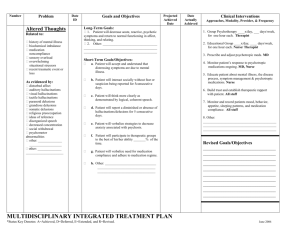
Positive Sxs
advertisement

Schizophrenia Lori Ridgeway PSYC 3560 What is Schizophrenia? Deterioration in fx Psychosis Extreme disturbances in thoughts, perceptions, emotions, motor fx Affects social, occupational, personal fx Hallucinations ________________ Withdrawal Positive & negative sxs Positive Sxs Bizarre ________________ to behavior ________________ Ideas that have no basis in fact Persecution most common Other types Grandeur Control Reference Positive Sxs, Cont’d… Hallucinations Sensory perceptions in absence of stimuli Premorbid perception & attention problems ______________ most common Other types Visual Olfactory Tactile Somatic Positive Sxs, Cont’d… Disorganized thinking & speech Formal thought disorders Can’t think &/or speak logically Loose associations (______________) most common Other types Neologisms Perseveration Clang Inappropriate affect Emotions don’t match situation Negative Sxs Pathological ________________ in behavior Poverty of speech Alogia Reduction in speech or speech content May say little or may convey little meaning Flat affect Show almost ________________ Anhedonia vs. inability to express emotion Negative Sxs, Cont’d… Loss of volition Avolition Apathy, ________________ Trouble with goal-directed behavior Social withdrawal Withdraw into own ideas & fantasies Separate further from reality Loss of social skills Psychomotor Sxs Motoric disturbances Gestures not related to environment Catatonia ______________ Posturing Rigidity Waxy flexibility Excitement Dx Criteria _______ or more characteristic sxs present for 1 mo Delusions Hallucinations Disorganized speech Disorganized or catatonic behavior Negative sxs Social/occupational dysfunction Signs of disturbance for 6 mos Exclusions Subtypes: ________________ Prominent delusions or auditory hallucinations Usually related & has theme Persecutory or grandiose most common Better cognitive/affective functioning Disorganized speech, catatonic behavior, flat/inappropriate affect not prominent Later onset Less impairment Better outcomes Subtypes: Disorganized Disorganized speech &/or behavior Flat or inappropriate affect ________________ Any delusions/hallucinations are fragmented & no theme Early onset Greater impairment Worse prognosis Subtypes: Catatonic Psychomotor disturbance Immobility Excessive activity purposeless Peculiar voluntary movements catalepsy = ________________ posturing Negativism rigid posture, can’t move Gender Differences Overall prevalence approx. 1% Age of onset Men 18 to 25 years of age Women ________________ years of age Late onset much less common in men Women better premorbid functioning Women more positive sxs Men more negative sxs Women better outcomes Cultural & Social Factors Hallucinations with religious content Beliefs that seem delusional Language differences (i.e., disorganized speech) Higher rates in ________________ Overdiagnosis Poverty & divorce More common in lower SES groups Approx. 0.5% in high SES, but 2% in low SES Stress/poverty “Downward drift” Course ________________ phase Active phase Early onset More negative sxs More brain abnormalities & cognitive impairment Worse premorbid fx & prognosis Contributors to better outcomes Acute onset / late onset Mood disturbance Early treatment Being female Comorbidity ________________ disorders Anxiety disorders Personality disorders May be prodromal Suicide 10% commit suicide 30%-40% make at least one attempt Biological Explanations Genetics ______% among first-degree relatives Twin studies Adoption studies Biochemical differences Type I (positive sxs) Dopamine hypothesis Bio , Cont’d… Structural differences Type II (negative sxs) in brain ___________________________ Abnormal blood flow Decreased size of temporal lobe Psychological Explanations Psychodynamic Behavioral Schizophrenogenic _____________ Operant conditioning Cognitive perceptual disturbances Problems when try to underst& Sociocultural Explanations ________________ Family dysfunction Label applied to nonconformists Self-fulfilling prophecy Rosenhan (1973) Double-bind hypothesis Expressed emotion Sociocultural-existential Constructive process Self-cure Diathesis-Stress ________________ view of cause Combination of factors Predisposition combined with environment Biological factors better identified Childhood Onset Difficult to dx Insidious onset Differences Some sxs common in other disorders Delusions & hallucinations less elaborate Visual hallucinations more common Odd movements/postures PDD/Autism Sx or normal child behavior?