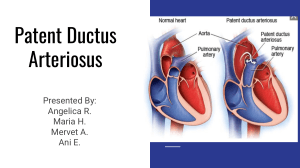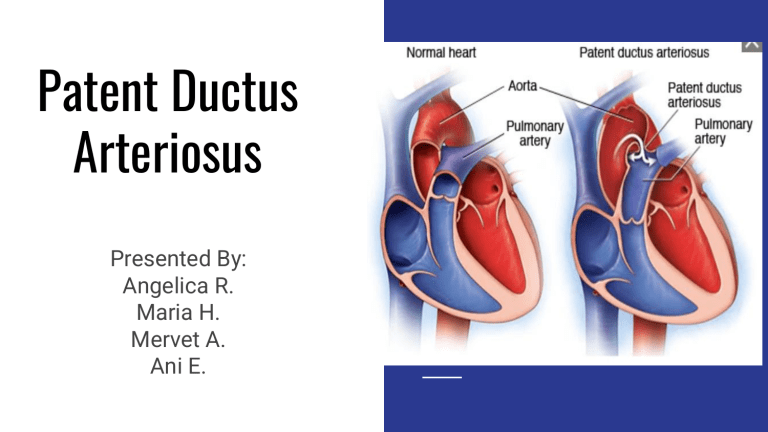
Patent Ductus Arteriosus Presented By: Angelica R. Maria H. Mervet A. Ani E. Pathophysiology Ductus arteriousus remains open after birth. This creates a left to right shunt of blood from the aorta (high pressure) to the pulmonary artery (low pressure) and results in recirculation of pulmonary blood through the lungs Clinical Manifestations : ● Murmurs ● Fatigue / Activity Intolerance ● Signs of HF(wheezing, coughing, lower extremity edema) ● Widened pulse pressure ● Bounding Pulses ● Rapid heart rate ● Persistent fast breathing ● Poor feeding Nursing Interventions Clustering Care Monitoring frequently VS, ECG, electrolyte levels, intake, weight, I&O. Administer Indomethacin and Ibuprofen Lysine per MD orders If the infant receives indomethacin, watch for possible adverse effects, such as diarrhea, jaundice, bleeding, and renal dysfunction. Oxygen therapy per MD orders If the infant is not able to feed, encourage the mother to express breast milk so infant can be fed via NG tube Monitor fluids to prevent fluid overload Pre-operative Before surgery (cardiac catheterization or closed heart surgery), explain all treatments and tests to parent/caregiver, and tell them about expected IV lines, monitoring equipment, and postoperative Post-operative after surgery, the child may have a central venous pressure catheter and an arterial line in place so careful assessment of VS, I&O.