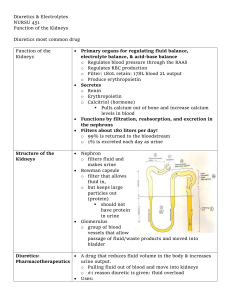
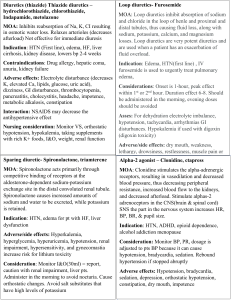
Basic science Nephrology fellow R4 Chiu, Yuhuan Kidney function • Control of water balance • Control of electrolyte balance • Excretion of water-soluble waste • Control of acid-base balance • Control of blood pressure (water, electrolyte, renin) • The production of active vitamin D (action of 1𝞪-hydroxylase) control of calcium-phosphate metabolism • The production of erythropoietin control of Hb level Anatomy Physiology Site of action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, e.g. acetazolamide Site of action of loop diuretics, e.g. furosemide. Inhibition of Na+K+2Cl– co-transporter Site of action of thiazide diuretics, e.g. bendroflumethazide. Inhibition of Na+Cl– synporter Site of action of potassium sparing diuretics, e.g. spironolactone. Inhibits the binding of aldosterone to its cytoplasmic receptor The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Secondary hyperparathyroidism Tertiary hyperparathyroidism Erythropoietin production produced by peritubular cells ↓when GFR falls to <50 mL/min exacerbated by reduced Iron intake