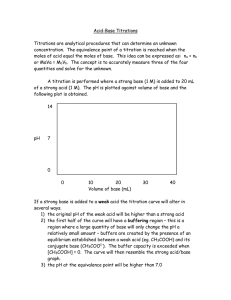
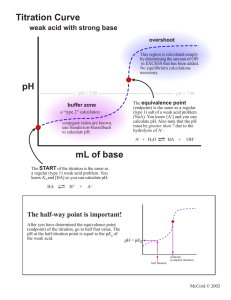
Power Point On Titration What is Titration? Titration, process of chemical analysis in which the quantity of some constituent of a sample is determined by adding to the measured sample an exactly known quantity of another substance with which the desired cjnonstituent reacts in a definite, known proportion. There are four types of Titration. Acid-base Titrations.Redox Titrations.Precipitation Titrations.Complexometric Titrations. Diagram to represent titration End point of Titration Detecting the end-point of a titration End-point is a physical change that indicates the completion of a titration. It is a signal for the user to stop adding any more titrant to the analyte. It is usually indicated by some form of a visual indicator like a colour change, a visible precipitate, or a change on an electronic readout. Back Titration What is back titration? Back Titration, also called indirect titration, is a titration done in reverse. Typically employed in acid-base titrations, a back titration is used when the concentration of an excess reactant is known, but the concentration of the analyte needs to be found out. Materials for a titration procedure Materials for a Titration Procedure burette •white tile (used to see a color change in the solution) Pipette pH indicator (the type depends on the reactants) Erlenmeyer or conical flask titrant (a standard solution of known concentration; a common example is aqueous sodium carbonate) analyte, or titrand (the solution of unknown concentration) Acid-Base Titration An acid-base titration is a quantitative analysis of acids and bases. Diagram to represent Acid-base titration Redox Titration A redox titration is a type of titration based on a redox reaction between the analyte and titrant. Diagram to represent Redox titration Precipitation Titration Precipitation titration is a titrimetric method which involves the formation of precipitates during the experiment of titration. Diagram to represent precipitation titration Complexometric Titration Complexometric titration is a form of volumetric analysis in which the formation of a colored complex is used to indicate the end point of a titration. Diagram to represent Complexometric titration Salt Preparation Titration Examples Titration Method Method Use a pipette and pipette filler to add 25 cm3 of alkali solution to a clean conical flask. Add a few drops of a suitable indicator and put the conical flask on a white tile. Fill the burette with dilute acid. Flush the tap through to remove any air bubbles. Ensure the burette is vertical. Slowly add the acid from the burette to the conical flask, swirling to mix. (The mixture may at first change colour, and then back again when swirled.) Stop adding the acid when the end-point is reached (when the colour first permanently changes). Note the final volume reading. Repeat steps 1 to 5 until three results are repeatable (in close agreement). Ideally these should lie within 0.10 cm3 of each other. List of apparatus used in titration Purette Pipette conical Flask Ring Stand Burette Clamp Acid-Base Titration Acid-base formula Redox Equation redox equation: - + MnO4 + 8H + 5Fe Mn 2+ 2+ + 4H2O + 5Fe 3+ Precipitation Titration Precipitation equation Ag+(aq) + Cl–(aq)→ AgCl(s). Complexometric Titration Complexometric equation M2+ + H4Y → MH2Y + 2H