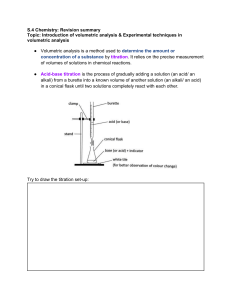
Notre Dame University Natural Science Department Chemistry for Engineering (Laboratory) Name: Bai Hayyat K. Paglala Group #: 4 Date Submitted:September 27,2021 Experiment No. 4 TITRATION OBJECTIVE: To familiarize the steps on how to conduct the Titration :To learn how to calculate the Normality of acids or bases. Instructions: 1. Answer this activity by group but all member should submit an individual paper. 2. Each group should submit a powerpoint presentation discussing this topic. 3. Next meeting the teacher will randomly select a group to present the topic. Research: 1. Enumerate the steps/ procedure on how to conduct titration. Step 1. Use a pipette and pipette filler to add 25 cm3 of alkali solution to a clean conical flask. Step 2. Add a few drops of a suitable indicator and put the conical flask on a white tile. Step 3. Fill the burette with dilute acid. Flush the tap through to remove any air bubbles. Ensure the burette is vertical. Step 4. Slowly add the acid from the burette to the conical flask, swirling to mix. (The mixture may at first change colour, and then back again when swirled.) Step 5. Stop adding the acid when the end-point is reached (when the colour first permanently changes). Note the final volume reading. Step 6. Repeat steps 1 to 5 until three results are repeatable (in close agreement). Ideally these should lie within 0.10 cm3 of each other. 2. List down the materials and chemicals needed in the experiment. Materials for a Titration Procedure: o Burette o White tile (used to see a color change in the solution) o Pipette o pH indicator (the type depends on the reactants ) o Erlenmeyer or conical flask o Titrant (a standard solution of known concentration; a common example is aqueous sodium o carbonate) o Analyte, or titrand (the solution of unknown concentration) 3. Draw and label the setup for Titration. Guide questions: 1. What are the possilbe causes of error in titration? Various factors can cause errors in titration results, including incorrectly read volumes, incorrect concentration values, or incorrect technique. 2. Calculate for the normality of the following: a. 0.30M HCl b. 4M NaOH c. 0.54M H2SO4 d. 0.98M Ba(OH)2 3. What is the normality of a solution that contains 1.5g of sulfuric acid dissolved in 10L?