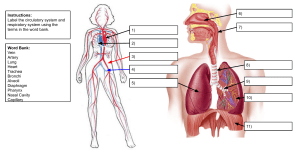
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM ACTIVITY PACKET AND WORKSHEETS BY BIOLOGYGUY Thank you for purchasing this ac9vity packet on the Circulatory System. This ac9vity packet is designed to help your students understand the concepts of the circulatory system. The packet consists of ACTIVITIES and WORKSHEETS that will require students to research, collaborate and problem solve. The packet is aimed at developing 21st Century learning skills (students need to be able to research informa9on using technology, evaluate the reliability of informa9on and apply it), where students will use appropriate technology, to research, and present their findings. No prepara;on is needed, students can get to work immediately. This ac9vity packet will cover the following: 1. What is the circulatory System? 2. The systemic and Pulmonary Circula9on 3. The structure and func9on of the heart 4. The structure and func9on of blood vessels 5. The structure and func9on of the blood 6. Diseases and Disorders of the circulatory system Each ac9vity includes an answer key and rubric. I grade this resource by awarding 5 points per completed unit. Mini projects are graded using the rubrics that are provided. This resource also includes a quiz and answer key. I hope that you enjoy this resource. Best wishes BiologyGuy BIOLOGYGUY © THANK YOU Thank you SPECIAL THANKS TO: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. By Gruff15 (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons blood cells. Database Center for Life Science (DBCLS) [CC-­‐BY-­‐3.0 (hdp://crea9vecommons.org/licenses/ by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons red blood cell By Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator (Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator) [CC-­‐BY-­‐2.5 (hdp:// crea9vecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5)], via Wikimedia Commons. Heart User:Sansculode via commons wikimedia hdp://crea9vecommons.org/licenses/by-­‐sa/2.5/deed.en , for circulatory system Heart diagram. See page for author [GFDL (hdp://www.gnu.org/copyleh/fdl.html) or CC-­‐BY-­‐ SA-­‐3.0 (hdp://crea9vecommons.org/licenses/by-­‐sa/3.0/)], via Wikimedia Commons Blood vessels: By Kelvinsong (Own work) [CC-­‐BY-­‐SA-­‐3.0 (hdp://crea9vecommons.org/ licenses/by-­‐sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons By Rogeriopfm [CC-­‐BY-­‐SA-­‐3.0 (hdp://crea9vecommons.org/licenses/by-­‐sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons, anima9on blood cell. By ZooFari [CC-­‐BY-­‐SA-­‐3.0 (hdp://crea9vecommons.org/licenses/by-­‐sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons, heart diagram 2. Pdefer, hNp://crea;vecommons.org/licenses/by-­‐sa/3.0/deed.en, via Commons Wikmedia, alveoli. By Na;onal Heart Lung and Blood Insitute (NIH) (Na;onal Heart Lung and Blood Insitute (NIH)) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons, stroke By OpenStax College [CC-­‐BY-­‐3.0 (hNp://crea;vecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons, Atherosclerosis By Bryan Brandenburg (hNp://bryanbrandenburg.net/wikpedia-­‐heart-­‐3d//) [CC-­‐BY-­‐SA-­‐3.0 (hNp://crea;vecommons.org/licenses/by-­‐sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons. Heart and vessels. By OpenStax College [CC-­‐BY-­‐3.0 (hNp://crea;vecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons, circulatory system diagram By Pdefer at en.wikipedia [GFDL (www.gnu.org/copyleh/fdl.html) or CC-­‐BY-­‐SA-­‐3.0 (hdp:// crea9vecommons.org/licenses/by-­‐sa/3.0/)], from Wikimedia Commons, alveoli diagram By helix84 (en:Image:Alveoli.jpg) [GFDL (hdp://www.gnu.org/copyleh/fdl.html), CC-­‐BY-­‐SA-­‐3.0 (hdp://crea9vecommons.org/licenses/by-­‐sa/3.0/) or CC-­‐BY-­‐2.5 (hdp:// crea9vecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5)], via Wikimedia Commons, alveoli close up. STANDARDS NEXT GENERATION SCIENCE STANDARDS MS-­‐LS1-­‐3. Use argument supported by evidence for how the body is a system of interac9ng subsystems composed of groups of cells. [Clarifica9on Statement: Emphasis is on the conceptual understanding that cells form 9ssues and 9ssues form organs specialized for par9cular body func9ons. Examples could include the interac9on of subsystems within a system and the normal func9oning of those systems.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the mechanism of one body system independent of others. Assessment is limited to the circulatory, excretory, diges;ve, respiratory, muscular, and nervous systems.] Science Standards 7 The anatomy and physiology of plants and animals illustrate the complementary nature of structure and func9on. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know plants and animals have levels of organiza9on for structure and func9on, including cells, 9ssues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism. b. Students know organ systems func9on because of the contribu9ons of individual organs, 9ssues, and cells. The failure of any part can affect the en9re system. STANDARDS NEXT GENERATION SCIENCE STANDARDS MS-­‐LS1-­‐3. Use argument supported by evidence for how the body is a system of interac9ng subsystems composed of groups of cells. [Clarifica9on Statement: Emphasis is on the conceptual understanding that cells form 9ssues and 9ssues form organs specialized for par9cular body func9ons. Examples could include the interac9on of subsystems within a system and the normal func9oning of those systems.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the mechanism of one body system independent of others. Assessment is limited to the circulatory, excretory, diges;ve, respiratory, muscular, and nervous systems.] Science Standards 5 Plants and animals have structures for respira9on, diges9on, waste disposal, and transport of materials. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know many mul9cellular organisms have specialized structures to support the transport of materials. • b. Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, lungs, and body and how carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen (O2) are exchanged in the lungs and 9ssues. STANDARDS Physiology HS 9. As a result of the coordinated structures and func9ons of organ systems, the internal environment of the human body remains rela9vely stable (homeosta9c) despite changes in the outside environment. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how the complementary ac9vity of major body systems provides cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide. CONTENTS PAGE 8 1. UNIT 1: WHAT IS THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? 10 2. UNIT 2: THE SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY CIRCULATION 16 3. UNIT 3: THE STRUCUTRE AND FUNCTION OF THE HEART 4. UNIT 4: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD 20 VESSELS 5. UNIT 5: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD 24 30 6. UNIT 6: DISEASES AND DISORDERS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 33 7. UNIT 7: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: APPLYING KNOWLEDGE 37 8. VOCABULARY 38 9. QUIZ 40 10. Mini projects UNIT 1: WHAT IS THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? Using appropriate resources research the following ques;ons 1. What organs are found in the circulatory system? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the job of the circulatory system? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 3. Label the key parts of the circulatory system: A______ carry blood away from the heart V________ carry blood towards the heart C___________________ are 9ny blood vessels that allow materials to pass from the blood to cells BIOLOGYGUY © This organ is called the __________ Its job is to pump ____________ Using appropriate resources research the following ques;ons 1. What organs are found in the circulatory system? _Heart, Veins, Capillaries, Arteries, blood (not an organ but important) 2. What is the job of the circulatory system? Func9on of the circulatory system is to transport essen9al materials, including oxygen to the cells in our body and transport waste products such as carbon dioxide away from our cells. 3. Label the key parts of the circulatory system: ANSWER KEY UNIT 1: WHAT IS THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? ARTERIES carry blood away from the heart VEINS carry blood towards the heart CAPILLARIES are 9ny blood vessels that allow materials to pass from the blood to cells BIOLOGYGUY © This organ is called the HEART Its job is to pump BLOOD UNIT 2: THE SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY CIRCULATION? Using appropriate resources research the following ques;ons 1. There are 2 types of circula9on in the circulatory system. One is concerned with the lungs the other is concerned with the body. What are the names of these two types of circula9on? _________________________________ __________________________________ (Circulates blood to the lungs) (Circulates blood around the body) 2. Label the 1. 2. 3. 4. 6. CLUES: 1. where gaseous exchange occurs 2. P_______ vein which carries blood from the lungs 3. The main vein which carries blood from the body back to the heart V_____C_____. 4. The largest artery in the body. 5. The main vein in the kidneys R_____ Vein. 6. Main artery which supplies blood to the liver, H______ A______. BIOLOGYGUY © 5. Using appropriate resources research the following ques;ons 1. There are 2 types of circula9on in the circulatory system. One is concerned with the lungs the other is concerned with the body. What are the names of these two types of circula9on? ANSWER KEY UNIT 2: THE SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY CIRCULATION? _PULMONARY CIRCULATION_ SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION (Circulates blood to the lungs) (Circulates blood around the body) 2. Label the PULMONARY CIRCULATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 6. RENAL VEIN Pulmonary artery AORTA HEPATIC ARTERY 5. CLUES: 1. where gaseous exchange occurs 2. P_______ vein which carries blood from the lungs 3. The main vein which carries blood from the body back to the heart V_____C_____. 4. The largest artery in the body. 5. The main vein in the kidneys R_____ Vein. 6. Main artery which supplies blood to the liver, H______ A______. BIOLOGYGUY © VENA CAVA LUNGS UNIT 2: THE SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY CIRCULATION? Thank you 1. MIX AND MATCH. For each leder that appears on the diagram there is a box that describes what is happening. Read each box then label the boxes to match the diagram. Cut them out and s9ck into your notebook. Thank you for purchasing this interac9ve notebook for the circulatory system. This resource includes informa9on about the fun aventricle c9vi9es, lab ideas and a quiz with an __The right __ The circulatory right atrium system, pumps blood through answer key. pumps blood out K a valve into the right along the pulmonary vein towards the ventricle. This resource lungs. covers the following topics: K __ The veins carry _ _ _ I n t h e l u n g s the blood back to the 1. What is the circulatory system? carbon dioxide and right atrium of the High Oxygen 2. How does water the cis irculatory exhaled out system work? heart via the largest (O2) of the body. of the Oxygen heart and blood vessels vein, the 3. Vena The Cava. func9on J is inhaled and added 4. The func9on of the blood. J C CLow Carbon J A to the blood. The __The Aorta, carries Dioxide 5. Blood types. blood it then sent to B K J I the blood away from K (CO ) the h eart 6. How t o c are f or y our c irculatory s ystem. 2 the heart. It then I B A H HsCystem. branches form 7. to Diseases and disorders of the circulatory A __ The cells then other arteries. These B send back through I a r t e r i e s l e a d t o D the capillary hope enjoy this rwall esource. d i ff e r e nI t o r g athat n s you D waste products such around the body, F E as carbon dioxide and such as Best the W renal ishes, water, which the cell D artery in the kidney does not need a n d t h e c a r o 9 d E artery in the brain. G __ Once the arteries E v e r y o r g a n w i l l F E BiologyGuy. reach the organs, receive oxygen rich F they form small 9ny blood. GG F E v e s s e l s c a l l e d capillaries. Nutrients, essen9al materials a n d o x y g e n p a s s through the walls of the capillaries into the cells. __The leh ventricle pumps the blood out of the heart along the Aorta, the body’s largest artery. __The heart receives oxygen rich blood from the lungs via the pulmonary vein. E F F E biologyGuy © __ The Capillaries c a r r y i n g c a r b o n dioxide and waste products then feed into veins. __The oxygen rich blood enters the heart through the led atrium, it then gets pumped through a valve into the led ventricle. 12 UNIT 2: THE SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY CIRCULATION? Thank you Thank you for purchasing this interac9ve notebook for the circulatory system. This resource includes informa9on about the fun aventricle c9vi9es, lab ideas and a quiz with an __The __ right atrium system, I The circulatory J right pumps blood through answer key. pumps blood out K a valve into the right along the pulmonary vein towards the ventricle. This resource lungs. covers the following topics: K __ The veins carry H _K _ _ I n t h e l u n g s the blood back to the 1. What is the circulatory system? carbon dioxide and right atrium of the High Oxygen 2. How does water the cis irculatory exhaled out system work? heart via the largest (O2) of the body. of the Oxygen heart and blood vessels vein, the 3. Vena The Cava. func9on J is inhaled and added 4. The func9on of the blood. J C CLow Carbon J A to the blood. The __The Aorta, carries D Dioxide 5. Blood types. blood it then sent to B K J I the blood away from K (CO ) the h eart 6. How t o c are f or y our c irculatory s ystem. 2 the heart. It then I B A H HsCystem. branches form 7. to Diseases and disorders of the circulatory A __ F The cells then other arteries. These B send back through I a r t e r i e s l e a d t o D the capillary hope enjoy this rwall esource. d i ff e r e nI t o r g athat n s you D waste products such around the body, F E as carbon dioxide and such as Best the W renal ishes, water, which the cell D artery in the kidney does not need a n d t h e c a r o 9 d E artery in the brain. G E Once the arteries __ E v e r y o r g a n w i l l F E BiologyGuy. reach the organs, receive oxygen rich F they form small 9ny blood. GG F E v e s s e l s c a l l e d The Capillaries c a r r y i n g c a r b o n dioxide and waste products then feed into veins. __The C leh ventricle pumps the blood out of the heart along the Aorta, the body’s largest artery. capillaries. Nutrients, essen9al materials a n d o x y g e n p a s s through the walls of the capillaries into the cells. A heart receives __The oxygen rich blood from the lungs via the pulmonary vein. E F F E __The B oxygen rich blood enters the heart through the led atrium, it then gets pumped through a valve into the led ventricle. 13 biologyGuy © G __ ANSWER KEY 1. MIX AND MATCH. For each leder that appears on the diagram there is a box that describes what is happening. Read each box then label the boxes to match the diagram. Cut them out and s9ck into your notebook. UNIT 2: THE SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY CIRCULATION? The systemic and pulmonary circula9on work together to pump oxygen, glucose, hormones and essen9al nutrients around the body. Explain what would happen if the Pulmonary system was removed. Support your argument with evidence. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ BIOLOGYGUY © 1. The systemic and pulmonary circula9on work together to pump oxygen, glucose, hormones and essen9al nutrients around the body. Explain what would happen if the Pulmonary system was removed. Support your argument with evidence. ANSWERS WILL VARY, LOOK TO SEE IF THEY HAVE supported their argument with evidence. If the pulmonary system was removed the body would not be able to get oxygen. It would also not be able to get rid of waste products such carbon dioxide and water. These would accumulate in the body and increase the body’s toxicity. You can see from the diagram that the pulmonary system is linked to the lungs, without this circula9on CO2 would not be able to leave the capillaries in the and O2 would not be able to enter the capillaries BIOLOGYGUY © 1. ANSWER KEY UNIT 2: THE SYSTEMIC AND PULMONARY CIRCULATION? UNIT 3: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE HEART? 1. Label the diagram of the heart: C A D B ANSWERS A=___________ B=___________ C=___________ D=___________ E=____________ 2. How many chambers are there in the heart?_________________________________ 3. Which side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs?____________________________ 4. What is the name of the artery that pumps blood from the heart to the rest of the body? _______________________________________________________________________ 5. What are the 4 main valves of the heart? _______________________________________________________________________ 6. What is the func9on of the valves in the heart? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ BIOLOGYGUY © E UNIT 3: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE HEART? ANSWER KEY Label the diagram of the heart: C A D B E ANSWERS A=_LEFT ATRIUM_ B=LEFT VENTRICLE C=AORTA_______ D=RIGHT ATRIUM E=RIGHT VENTRICLE_ 2. How many chambers are there in the heart?_____________4___ 3. Which side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs?_______RIGHT SIDE_______ 4. What is the name of the artery that pumps blood from the heart to the rest of the body? _________________________________AORTA_____________________ 5. What are the 4 main valves of the heart? PULMONARY VALVE, TRICUSPID VALVE, AORTIC VALVE, MITRAL VALVE 6. What is the func9on of the valves in the heart? THEY KEEP THE BLOOD FLOWING ONE WAY, THEY STOP BLOOD FLOWING BACK INTO THE CHAMBER THAT THEY LEFT BIOLOGYGUY © 1. UNIT 3: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE HEART? 1. Use the diagram to help you sequence the flow of blood through the heart. F Cut out the sentences and s9ck them in order G A B H K E I G J C D ___Blood returning from the body is rich in carbon dioxide It travels back to the heart via the VENA CAVA. The Superior Vena Cava brings blood from your upper regions. The Inferior Vena Cava brings blood from your lower regions. ___Blood passes through the Tricuspid Valve ___The blood is taken to the lungs via the pulmonary artery. The cycle will then con9nue ___The right ventricle contracts forcing blood through the pulmonary Valve ___The Leh Ventricle is surrounded by thick muscle when it contracts the blood is forced through the AORTIC VALVE towards the aorta ____Blood enters the RIGHT VENTRICLE ___The AORTA takes blood to different parts of the body ___Blood from the Vena Cava enters the RIGHT ATRIUM ___Blood passes into the 1st chamber the Leh Atrium ___Blood enters the Leh Ventricle A. Blood enters the heart via the pulmonary vein BIOLOGYGUY © ___Blood passes through the Mitral valve UNIT 3: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE HEART? Use the diagram to help you sequence the flow of blood through the heart. F G A B H K E I G J ANSWER KEY 1. C D G. Blood returning from the body is rich in carbon dioxide It travels back to the heart via the VENA CAVA. The Superior Vena Cava brings blood from your upper regions. The Inferior Vena Cava brings blood from your lower regions. I. Blood passes through the Tricuspid Valve L. The blood is taken to the lungs via the pulmonary artery. The cycle will then con9nue K. The right ventricle contracts forcing blood through the pulmonary Valve E. The Leh Ventricle is surrounded by thick muscle when it contracts the blood is forced through the AORTIC VALVE towards the aorta J. Blood enters the RIGHT VENTRICLE F. The AORTA takes blood to different parts of the body H. Blood from the Vena Cava enters the RIGHT ATRIUM B. Blood passes into the 1st chamber the Leh Atrium D. Blood enters the Leh Ventricle A. Blood enters the heart via the pulmonary vein BIOLOGYGUY © C. Blood passes through the Mitral valve UNIT 4: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD VESSELS 1. Study the diagrams of the 3 main blood vessels Capillary VEIN 1. Which blood vessel receives blood from the heart?____________________ 2. Which blood vessel sends blood to the heart?_________________________ 3. Which blood vessel receives blood from arteries and sends blood to veins? ___________ 4. Which blood vessel has the thickest layer of smooth muscle? ________________ 5. Which blood vessel has valves? ________________________________________ 6. Which blood vessel has an external elas9c layer?__________________________ BIOLOGYGUY © ARTERY ANSWER KEY UNIT 4: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD VESSELS 1. Study the diagrams of the 3 main blood vessels Capillary VEIN 1. Which blood vessel receives blood from the heart? ARTERY 2. Which blood vessel sends blood to the heart? VEIN 3. Which blood vessel receives blood from arteries and sends blood to veins? CAPILLARY 4. Which blood vessel has the thickest layer of smooth muscle? ARTERY 5. Which blood vessel has valves? _VEIN_ 6. Which blood vessel has an external elas9c layer? ARTERY BIOLOGYGUY © ARTERY UNIT 4: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD VESSELS 1. What are the 3 main blood vessels that are in the circulatory system? A______________ V__________________ and C_______________________ 2. Which blood vessel is the thickest and under the highest pressure? ______________ 3. Which blood vessel is the thinnest? ________________________________________ 4. Which blood vessels carry oxygenated blood away from the heart? ______________ 5. Which blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart? _______________ 6. Capillaries are one cell thick, meaning that their contents can leak in and out of the blood vessel. How might this feature assist the overall func9on of the circulatory system. Explain your answer. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 7. Compare capillaries, veins and arteries. What are their jobs? What things are similar? What things are different? CV Capillaries CVA VA BIOLOGYGUY © CA Veins Arteries 1. What are the 3 main blood vessels that are in the circulatory system? ARTERIES VEINS AND CAPILLARIES 2. Which blood vessel is the thickest and under the highest pressure? _ARTERY_ 3. Which blood vessel is the thinnest? _____________CAPILLARY_______________ 4. Which blood vessels carry oxygenated blood away from the heart? __ARTERY_ 5. Which blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart? ___VEIN_________ 6. Capillaries are one cell thick, meaning that their contents can leak in and out of the blood vessel. How might this feature assist the overall func9on of the circulatory system. Explain your answer. THIS WILL ASSIST THE FUNCTION OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BECAUSE IT WILL ENABLE ESSENTIAL MATERIALS, OXYGEN AND WASTE PRODUCTS, LIKE CARBON DIOXIDE, TO LEAVE AND ENTER THE BLOOD. 7. Compare capillaries, veins and arteries. What are their jobs? What things are similar? What things are different? *1 CELL THICK *CARRY OXYGENATED AND *DEOXYGENATED BLOOD CA CARRY OXYGENATED BLOOD CARRY DEOXYGENATED BLOOD CVA TRANSPORT BLOOD AND MATERIALS *THICK MUSCULAR WALLS *BLOOD TRAVELS AT HIGH PRESSURE *CARRIES OXYGENATED BLOOD *CARRY BLOOD AWAY FROM THE HEART *LARGEST ARTERY IS AORTA Arteries Veins *WALLS THICKER THAN CAPILLARIES *BLOOD TRAVELS AT LOW PRESSURE *CARRIES DEOXYGENATED BLOOD *CARRY BLOOD BACK TO THE HEART *LARGEST VEIN IS VENA CAVA CARRY BLOOD VA BIOLOGYGUY © CV Capillaries ANSWER KEY UNIT 4: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD VESSELS UNIT 5: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD? 1. What are the components of blood? P____________, R______________, W________________, P________________ 2. Which component of blood is responsible for cloung blood? _________________ 3. Which part of the blood fights disease and infec9ons?________________________ 4. Which part of the blood carries oxygen and carbon dioxide?___________________ 5. Which part of the blood carries glucose, hormones and other materials?__________ Red Blood Cell White Blood Cell Platelets Blood Vessel Plasma 6. What component of a red blood cells enables it to carry oxygen? H____________ 7. What are the 4 main blood types? _____, ________, ________, _________ 8. Based on the diagram to the right, a person with AB blood type can receive blood from which other blood type? ______________________________________ 9. What type of blood can someone with blood type B receive? _____________________________________ BIOLOGYGUY © BLOOD COMPATABILITY DIAGRAM 1. What are the components of blood? PLASMA, RED BLOOD CELLS, WHITE BLOOD CELLS, PLATELETS 2. Which component of blood is responsible for cloung blood? PLATELETS 3. Which part of the blood fights disease and infec9ons? WHITE BLOOD CELLS 4. Which part of the blood carries oxygen? RED BLOOD CELLS 5. Which part of the blood carries glucose, hormones and other materials? PLASMA ANSWER KEY UNIT 5: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD? Red Blood Cell White Blood Cell Platelets Blood Vessel Plasma 6. What component of a red blood cells enables it to carry oxygen? HEMOGLOBIN 7. What are the 4 main blood types? O, A, B, AB 8. Based on the diagram to the right, a person with AB blood type can receive blood from which other blood type? CAN RECEIVE O, B, A and AB 9. What type of blood can someone with blood type B receive? CAN RECEIVE O and B BIOLOGYGUY © BLOOD COMPATABILITY DIAGRAM UNIT 5: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD There are 4 blood types _____, ______, _____, ______. Each type of blood has different surface structures called an9gens, people with blood type A, have A an9gens which are ________ in shape, people with blood type B have _________ which are square in shape, people with blood type AB, have both A and B ________. People with blood type _____, do not have any an9gens. People with blood type A have an9bodies that are Y shaped, they are called _________, an9 bodies. If someone receives blood that is not compa9ble with their own blood it will result in their blood cloung. This is because the an9bodies in their plasma bind with the an9gens of the blood which is not compa9ble. For example blood type A has An9-­‐B an9bodies, which will bind to Blood type B an9gens. Therefore if a person with blood type A receives blood that is blood type B, their blood will______________ KEY WORDS: CLOT, O, A, AB, B, ANTIGENS, CIRCULAR, O, ANTIGENS, ANTI-­‐B BIOLOGYGUY © 1. Look at the diagram below then complete the gaps in the paragraph. There are 4 blood types A, B, AB, O. Each type of blood has different surface structures called an9gens, people with blood type A, have A an9gens which are CIRCULAR in shape, people with blood type B have ANTIGENS which are square in shape, people with blood type AB, have both A and B ANTIGENS People with blood type _O_, do not have any an9gens. People with blood type A have an9bodies that are Y shaped, they are called _ANTI-­‐B _, an9 bodies. If someone receives blood that is not compa9ble with their own blood it will result in their blood cloung. This is because the an9bodies in their plasma bind with the an9gens of the blood which is not compa9ble. For example blood type A has An9-­‐B an9bodies, which will bind to Blood type B an9gens. Therefore if a person with blood type A receives blood that is blood type B, their blood will___CLOT__ KEY WORDS: CLOT, O, A, AB, B, ANTIGENS, CIRCULAR, O, ANTIGENS, ANTI-­‐B ANSWER KEY 1. Look at the diagram below then complete the gaps in the paragraph. BIOLOGYGUY © UNIT 5: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD UNIT 5: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD 1. The lungs are an important organ which allow carbon dioxide to be removed from the blood and oxygen to enter the blood. Gaseous exchange takes place in the alveoli of the lungs. These structures are small air sacs which are surrounded by capillaries. Look at the diagrams and use the keywords to complete the sentences. The lungs are part of the _______________ When we breath in we inhale ____________ When we breath out we exhale __________ At the end of bronchioles are small air sacs called ______________________________ CAPILLARY The leaky blood vessels allow ____________ To leave the blood. They allow ______________ to enter the blood. The oxygen rich blood is then pumped back to the ____________ KEYWORDS: HEART, CAPILLARIES, OXYGEN, CARBON DIOXIDE, SACS, ALVEOLI, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM BIOLOGYGUY © The alveoli consist of small air __________ They are surrounded by 9ny blood vessels Called _____________________________ These blood vessels are so thin that they enable materials to leak in and out the blood vessel 1. The lungs are an important organ which allow carbon dioxide to be removed from the blood and oxygen to enter the blood. Gaseous exchange takes place in the alveoli of the lungs. These structures are small air sacs which are surrounded by capillaries. Look at the diagrams and use the keywords to complete the sentences. The lungs are part of the _RESPIRATORY SYSTEM_ When we breath in we inhale OXYGEN_ When we breath out we exhale CARBON DIOXIDE_ At the end of bronchioles are small air sacs called ___ALVEOLI__ ANSWER KEY UNIT 5: THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BLOOD CAPILLARY The leaky blood vessels allow CARBON DIOXIDE To leave the blood. They allow OXYGEN to enter the blood. The oxygen rich blood is then pumped back to the HEART KEYWORDS: HEART, CAPILLARIES, OXYGEN, CARBON DIOXIDE, SACS, ALVEOLI, RESPIRATORY SYSTEM BIOLOGYGUY © The alveoli consist of small air SACS They are surrounded by 9ny blood vessels Called ___CAPILLARIES_ These blood vessels are so thin that they enable materials to leak in and out the blood vessel UNIT 6: DISEASES AND DISORDERS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM biologyGuy © Thank you There are many diseases and disorders of the heart and circulatory system. Heart disease is any condi9on that reduces the strength or func9oning of the heart and blood vessels. ARTERIOSCLEROSIS: is a group of disorders that causes a thickening and hardening of the arteries, by Thank you for purchasing this interac9ve notebook for the a build up of plaque. This effects the ability of arteries to pump blood as the walls of the arteries are system. his resource includes about the no longer circulatory elas9c, and blood flow is rT educed. It is caused by a poor idnforma9on iet, high in saturated fats and cholesterol, smoking and high blood pressure. The best treatment or this isease s preven9on. circulatory system, fun ac9vi9es, lab ideas afnd a qduiz wiith an Make sure that you eat a healthy balanced diet, rich in omega 3 fady acids, protein and low in fat and answer key. bad cholesterol. Exercise regularly ARTHEROSCLEROSIS: is a condi9on hich fady substances build up on the inner lining of the This resource covers in twhe following topics: arteries. This build up severely narrows the arteries, and can slow or stop the flow of blood through the arteries, with fatal consequences. The cause and treatment of Atherosclerosis is similar to 1. What is the circulatory system? arteriosclerosis. 2. How does the circulatory system wHEART ork? ATTACK Normal Artery Coronary artery (supplies blood 3. The func9on Artery of twhe h eart a nd b lood v essels all and oxygen to 4. The func9on of the blood. heart) 5. Blood Normal Blood flow types. Coronary 6. How t o c are f or y our c irculatory s ystem. artery plaque Narrowing a rtery 7. Diseases and disorders of the circulatory system. I hope that you enjoy this resource. ATHEROSCLEROSIS plaque Best Wishes, Restricted Blood flow Dead heart muscle heart muscle HEART ATTACK: This is a serious condi9on of the heart, that occurs when the blood flow to the heart slows or s tops completely, resul9ng in damage to the muscle of the heart. The cause of heart adack can be fady build ups in the BiologyGuy. arteries (atherosclerosis) and hardening of the arteries (arteriosclerosis) which effect the flow of blood. Symptoms of heart adack include, sudden pain or pressure in the chest. The pain may extend to one or both arms, the jaw, back or abdomen. Other signs include, shortness of breath, cold skin, vomi9ng and loss of consciousness. If you feel that you are someone is having a heart adack you should call for medical assistance immediately. HYPERTENSION: this is a condi9on in which a person’s blood pressure stays at a level that is higher than normal. It is commonly known as high blood pressure. It can lead to heart adack or stroke. STROKE: This is a serious condi9on that occurs when the artery of the brain becomes blocked or breaks. This prevents the nerve cells that are in the brain from receiving oxygen and materials that they need to func9on properly. Depending on which part of the brain is effected by the stroke, will result in symptoms that relate to that brain func9on. Some pa9ents experience difficulty in moving and speaking. Many of the disorders and diseases of the heart and circulatory system are very closely linked. It i30 s important to prac9ce healthful behaviors and care for your heart in order to stay healthy. UNIT 6: DISEASES AND DISORDERS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. What disorder results In the hardening and thickening of the arteries?___________ 2. What is the difference between Atherosclerosis and Arteriosclerosis? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3. What is a heart adack?________________________________________________ 4. What are the symptoms of a heart adack?_________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 5. How is atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis linked to heart adack? Explain your answer with examples. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 6. What is another word for High Blood Pressure? _____________________________ 7. What is a stroke?_____________________________________________________ 8. Why might people that experience a stroke some9mes have difficulty moving or speaking? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 9. What are some 9ps and foods that you can eat to reduce the chances of heart disease? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 31 biologyGuy © READ THE INFORMATION ON DISEASES AND DISRODERS THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS UNIT 6: DISEASES AND DISORDERS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. What disorder result in the hardening and thickening of the arteries arteriosclerosis 2. What is the difference between atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis? Arteriosclerosis is the thickening and hardening of the arteries, ATHEROSCLEROSIS is the narrowing of the arteries due to plaque build up. 3. What is a heart adack? Where part of the heart is damaged due to a lack or total loss of blood supply. It is a serious condi9on that could result in death 4. What are the symptoms of a heart adack? sudden pain or pressure in the chest. The pain may extend to one or both arms, the jaw, back or abdomen. Other signs include, shortness of breath, cold skin, vomi9ng and loss of consciousness 5. How is atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis linked to heart adack? Explain your answer with examples. The narrowing of the arteries from atherosclerosis and the hardening and thickening of the arteries from arteriosclerosis can mean that blood supply in the artery is restricted as there is less room for the blood to travel. This can result in blood clots and complete blockages that stop the flow of blood resul9ng in a heart adack 6. What is another word for High Blood Pressure? HYPERTENSION 7. What is a stroke? This is a serious condi9on that occurs when the artery of the brain becomes blocked or breaks. This prevents the nerve cells that are in the brain from receiving oxygen and materials that they need to func9on properly 8. Why might people that experience a stroke some9mes have difficulty moving or speaking? Because the part of the brain that might be damaged by the lack of blood supply and oxygen could be the region of the brain that controls speech and movement 9. What are some 9ps and foods that you can eat to reduce the chances of heart disease? Make sure that you eat a healthy balanced diet, rich in omega 3 fady acids, protein and low in fat and bad cholesterol. Exercise regularly 32 biologyGuy © ANSWER KEY READ THE INFORMATION ON DISEASES AND DISRODERS THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS 1. Using your knowledge of the circulatory system explain how the cells, 9ssue and organs within the circulatory system work together to enable it to perform its func9on of pumping materials around the body and removing waste products such as carbon dioxide. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 2. Heart adack is a serious condi9on where parts of the heart die as a result of a blockage or break within the blood vessel that suppliy it with blood and oxygen. Explain how a heart adack could effect the overall func9oning of the body. Explain your answer and use evidence to support your argument. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ BIOLOGYGUY © UNIT 7: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: APPLYING KNOWLEDGE BIOLOGYGUY © 1. Using your knowledge of the circulatory system explain how the cells, 9ssue and organs within the circulatory system work together to enable it to perform its func9on of pumping materials around the body and removing waste products such as carbon dioxide. ANSWERS WILL VARY The cells, 9ssue and circulatory system all work together to transport materials around the body. Red blood cells, transport the oxygen and carbon dioxide and the plasma which is the fluid in the blood carries materials. The heart, arteries, veins and capillaries are the organs and 9ssues which circulate the red blood cells and plasma. The heart is the organ which pumps the blood, the veins, arteries and capillaries are the vessels which carry it. 2. Heart adack is a serious condi9on where parts of the heart dies as a result of a blockage or break within the blood vessel that supplies it with blood and oxygen. Explain how a heart adack could effect the overall func9oning of the body. Explain your answer and use evidence to support your argument. ANSWERS WILL VARY Heart adacks can result in parts of the heart dying or becoming damaged. If the heart is damaged, that means that the heart 9ssue and muscle that surround the heart might not work correctly, this could result in the heart not bea9ng correctly, or perhaps bea9ng with less force that before. If the heart is not bea9ng correctly this means that the blood will not be pumped around the body as efficiently. This means that essen9al materials, oxygen and waste products might not be transported effec9vely. This could cause toxins to rise in the body, for pa9ents to feel dizzy due to poor circula9on and oxygen levels. ANSWER KEY UNIT 7: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: APPLYING KNOWLEDGE 1. Explain how the circulatory system and respiratory system are linked. Explain your answer and include evidence to support your argument. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 2. The func9on of the circulatory system is to transport oxygen and materials around the body and remove waste products such as carbon dioxide form the blood. Explain with examples how the circulatory system is able to get oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. Use evidence to support your answer and use specific examples. (You may draw a diagram to help you explain your answer) _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ BIOLOGYGUY © UNIT 7: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: APPLYING KNOWLEDGE 1. Explain how the circulatory system and respiratory system are linked. Explain your answer and include evidence to support your argument. ANSWERS WILL VARY: The circulatory system and respiratory system are closely linked because the circulatory system transports oxygen around the body to the key cells that need it, and removes carbon dioxide, a waste product of respira9on. The respiratory system allows oxygen into the body and allows carbon dioxide to leave the body. The respiratory system and circulatory system make contact with one another in the alveoli. The alveoli contain 9ny air sacs which are surrounded by capillaries. The capillaries allow oxygen to flow into the blood, and carbon dioxide to flow out of the blood and into the alveoli where they will be exhaled. 2. The func9on of the circulatory system is to transport oxygen and materials around the body and remove waste products such as carbon dioxide form the blood. Explain with examples how the circulatory system is able to get oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. Use evidence to support your answer and use specific examples. (You may draw a diagram to help you explain your answer) Suitable picture BIOLOGYGUY © The circulatory system is able to get oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the blood as it works closely with the respiratory system. The respiratory system, includes the lungs, which can inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide. These gasses get into the circulatory system via the alveoli sacs. These sacs are surrounded by 9ny, 1 cell thick blood vessels called capillaries. The capillaries enable oxygen to leak into them from the alveoli, and carbon dioxide to leak out of them. ANSWER KEY UNIT 7: THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: APPLYING KNOWLEDGE VOCABULARY from the heart. Thank you for purchasing this interac9ve notebook for the circulatory saystem. resource informa9on the of the ARTERIOSCLEROSIS: group o f Tdhis isorders that icncludes auses a thickening and ahbout ardening arteries, circulatory resul9ng in rseduced ow. ystem, bflood un aflc9vi9es, lab ideas and a quiz with an answer key. ATHEROSCLEROSIS: a condi9on in which there is a build up of fady substances on the inside of arteries. Resul9ng in reduced blood flow. This resource covers the following topics: VEIN: Blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart. Most blood in the veins is 1. What the circulatory system? deoxygenated, the ois nly vein that carries oxygenated blood is the pulmonary vein. 2. How does the circulatory system work? CAPILLARY: This fis the thinnest is in places one cell thick, allowing 3. The unc9on of the blood heart vessel. and bIt lood vessels materials ow ofunc9on ut of the o bf lood into cells. 4.to flThe the abnd lood. 5. Blood types. RED BLOOD CELL: the cell that contains hemoglobin and carries oxygen and carbon 6. How to care for your circulatory system. dioxide. 7. Diseases and disorders of the circulatory system. PLATELET: a component of blood which is responsible for cloung blood and sealing wounds. I hope that you enjoy this resource. PLASMA: this W is ishes, the yellow Best fluid like substance of blood, it mainly consists of water, and carries e ssen9al substances and materials that can be delivered to cells. HYPERTENSION: condi9on in which a person has a blood pressure level that is higher BiologyGuy. than normal. VENTRICLE: Lower Chamber of the heart, which pumps blood out of the heart. ATRIUM: Upper chamber of the heart which pumps blood into the ventricle. 1. Produce a personal dic9onary to help you remember the key vocabulary words, include the word, defini9on, sentence that includes the word and a picture. WORD DEFINITION SENTENCE PICTURE 37 biologyGuy © Thank you ARTERY: Muscular walled blood vessel which mainly carries oxygenated blood away CIRCULATORY SYSTEM QUIZ NAME___________ SCORE_________ 1. What is the name given to the system that contains the heart, blood vessels and blood. A. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM B. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM C. CARDIO SYSTEM D. PUMPING SYSTEM 2. What is the name of the chambers of the heart that are located at the top and pump blood into the lower inner heart chambers? A. VENTRICLES B. ATRIUM C. VALVES D. ARTEREIS 3. There are special features within the heart that keep blood flowing in the right direc9on what is the name of this feature? A. VEIN B. ARTERY C. VALVE D. SWITCH 4. What are the name of the blood vessels which carry blood away from the heart. A. ARTERIES B. VEINS D. CAPILLARIES 5. What is the name of the only vein that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart? A. AORTA VEIN B. VENA CAVA C. PULMONARY VEIN 6. What is the name of the condi9on in which blood supply to the heart slows or stops, resul9ng in damage to the heart muscle? A. HEART ATTACK B. HYPERTENSION C. ATHEROSCLEROSIS D. ARTERIOSCLEROSIS 7. What is the name of the condi9on in which the arteries harden and become narrower, restric9ng the flow of blood. A. HEART ATTACK B. HYPERTENSTION C. ATHEROSCLEROSIS D. ARTERIOSCLEROSIS 9. Which blood type can receive blood from any person? A. AB B. A C. B D. O biologyGuy © 8. Which component of blood assists in closing wounds and cloung blood? A. PLASMA B. RED BLOOD CELLS C. WHITE BLOOD CELLS D. PLATELETS 10. The circulatory system is a crucial system that helps the body func9on normally. Explain what a stroke is, how could this effect the overall func9on of an organism. 38 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM QUIZ A. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM B. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM C. CARDIO SYSTEM D. PUMPING SYSTEM 2. What is the name of the chambers of the heart that are located at the top and pump blood into the lower inner heart chambers? A. VENTRICLES B. ATRIUM C. VALVES D. ARTEREIS ANSWER KEY NAME___________ SCORE_________ 1. What is the name given to the system that contains the heart, blood vessels and blood. 3. There are special features within the heart that keep blood flowing in the right direc9on what is the name of this feature? A. VEIN B. ARTERY C. VALVE D. SWITCH 4. What are the name of the blood vessels which carry blood away from the heart. A. ARTERIES B. VEINS D. CAPILLARIES 5. What is the name of the only vein that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart? A. AORTA VEIN B. VENA CAVA C. PULMONARY VEIN 6. What is the name of the condi9on in which blood supply to the heart slows or stops, resul9ng in damage to the heart muscle? A. HEART ATTACK B. HYPERTENSION C. ATHEROSCLEROSIS D. ARTERIOSCLEROSIS 7. What is the name of the condi9on in which the arteries harden and become narrower, restric9ng the flow of blood. A. HEART ATTACK B. HYPERTENSTION C. ATHEROSCLEROSIS D. ARTERIOSCLEROSIS 9. Which blood type can receive blood from any person? A. AB B. A C. B D. O 10. The circulatory system is a crucial system that helps the body func9on normally. Explain what a stroke is, how could this effect the overall func9on of an organism. Stroke is a condi9on where the blood supply to the brain stops, as a result of a break or blockage in the artery of the brain. A person with a stroke could die or have severe consequences, such as difficulty speaking or moving. Strokes therefore effect the overall func9on o39 f an organisms as a whole, because the neurons that are damaged or die can no longer send and receive messages about the body. biologyGuy © 8. Which component of blood assists in closing wounds and cloung blood? A. PLASMA B. RED BLOOD CELLS C. WHITE BLOOD CELLS D. PLATELETS BLOOD LAB 1. Thank you Scenario: You have been asked by you local doctors office to produce a model of blood and its components. You need to make a 3D scale model that is as accurate yYou purchasing this ai snterac9ve notebook for to the as pThank ossible. ou fsor hould also provide hort paragraph or legend describe your circulatory system. This resource includes informa9on about the model. I hope that you enjoy this resource. 2. Scenario: Your elementary science teacher wants you to create a model of the heart, so that sBest he can each the Wtishes, structure and func9on of the heart to her students. Create a scale model of a heart using household materials, describe its structure and func9on. RUBRIC: BiologyGuy. SCORE 1. I have a model that looks like a heart. ___/5 2. My model has labels to iden9fy the key structures. ___/5 3. My model has 4 chambers ___/5 4. My model is neat and well presented. ___/5 5. My model has a descrip9on with it to describe the structure and func9on of the heart. ___/5 40 biologyGuy © circulatory system, fun ac9vi9es, lab ideas and a quiz with an RUBRIC:answer key. SCORE This resource covers the following topics: produced a model of blood that shows the 4 components of blood; plasma, 1) I have What he cbirculatory system? red 1. blood cells, is wthite lood cells and platelets. __/5 How does the circulatory ork? 2) My 2. model shows accuracy in terms of stystem he size w and ra9o of each blood component. 3. The f unc9on of t he heart blood ___/5 and vessels 3) My 4. model is cfunc9on olorful and ell pbresented. ___/5 The of wthe lood. 4) My 5. model has at ypes. legend/ descrip9on, which describes the parts of the blood and Blood their func9on. __/5 6. How to care for your c irculatory s ystem. 7. Diseases and disorders of the LAB circulatory system. HEART