Uploaded by
Kristen Wick
Biomolecules Worksheet: Nucleic Acids, Proteins, Lipids, Carbs
advertisement

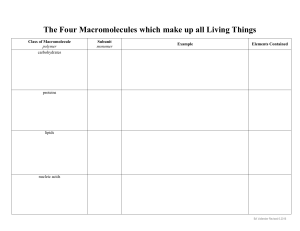
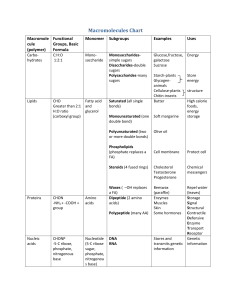
Nucleic Acids Proteins: 1. Makes _________________________ in the body – like bone and muscle tissue, skin, hair, fingernails, etc. 2. _______________ are protein catalysts that control the rates of chemical reactions in the body. 3. Proteins ________________materials throughout the body (like ________________ transporting oxygen) and help move substances through the _______. 4. _______________ are proteins that function in our immune systems. Lipids Carbohydrates: 1. Number one source of immediate _________ in all living things (simple sugars ________________, glucose, and _________________, sucrose). 2. Organisms can ___________ energy for the short-term in long chains of glucose called ____________________. Plants store sugars as ____________ and animals store sugars in muscles and liver tissue as _____________. 3. ____________________ are long chains of single sugars that act as ________________ in organisms. Plants use ________________for cell walls and insects use ____________ for exoskeletons. FUNCTIONS Lipids: 1. Long-term _______________ _______________. 2. Lipids make up the structure of ___________ Nucleic Acids: ___________________. Molecules like _____________________ and _________________ make the cell membrane flexible and semi-permeable. 1. Store and transmit _______________ information. 3. __________ are ______________ coatings that prevent 2. Adenosine Triphosphate (__________) is the energy water loss in plants (cuticle) and aquatic birds and ‘_____________’ of all living things. This means that mammals from waterlogging and drowning. organisms use ATP for energy for all life processes. 4. _____________ and _____________ are chemical _____________ in the body that don’t dissolve. 5. Lipids make ____________ from the cold, ____________, and _______________ for vital organs. Carbohydrate Protein Monomer : __________________________________ Monomer : __________________________________ (hint: Mono means ________) The R Side Chain is one of ______ different structures but the rest of the molecule is the same in all amino acids. RATIO of atoms: C:H:O is ___: ___:___ Carbo’hydrate’ litterally means 1 __________ atom for each molecule of ______________ TWO Sugars: _______________________________ (hint: Di means __________) Polymer : __________________________________ A chain of amino acids is called a ____________________. The bond that joins amino acids is a ____________ bond. MANY Sugars: _____________________________ (hint: Poly means __________) THE ELEMENTS PRESENT in these molecules are: ____ ____ ____ ____ The SUFFIX - ________ means sugar. Monomer : __________________________________ Monomer : __________________________________ The 3 Parts to a Nucleotide: 1. 2. 3. Also...Adenosine Triphosphate (______) is Cellular Energy!!! This has the same 3 parts of a nucleotide but _______ phosphate groups! The energy is stored in the bonds between these negative groups. The parts: One ____________ and Three ___________ ________ tails Saturated means: At room temp: _____________Common in ____________ Heart _______________ Unsaturated means: THE ELEMENTS PRESENT in these molecules are: At room temp: _____________Common in ____________ Heart _______________ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ THE ELEMENTS PRESENT in these molecules are: Polymer : A large amount of ____ ____ and very little ____ _____ or ______ **Where is the energy stored? In the _____ - ______ bonds