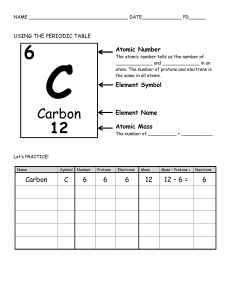
ATOMS, ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS WHAT IS ATOM? Atoms tiny particles that compose or made up all matter either in the form of mixture or of pure substance like elements or compounds. 3 sub-atomic particle of an atom: Electron Proton Neutron THE ATOMIC THEORY Democritus - “Matter composed of tiny particles called Atomos” Atomos is Greek word , meaning-(not to be cut or to be divided). John Dalton - “atoms” Theory: The Billiard Ball Model Atom is a hard indestructible sphere. was disproved when Subatomic Particles discovered. -Electron (-) Joseph John Thomson -Proton (+) Eugen Goldstein -Neutron (neutral) James Chadwick & Harold Urey THE ATOMIC THEORY Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 3. Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one element. In any compound, the ratio of the numbers of atoms of any two of the elements presents is either an integer or a simple fraction. (Proust’s Law or Law of Definite Proportion) 4. A chemical reaction involves only the separation, combination or rearrangement of atoms; it does not result in their creation or destruction. THE ATOMIC THEORY Joseph John Thomson Model: The Raisin-bread Model The Plum-pudding Model “An atom is a sphere of positive particles” THE ATOMIC THEORY Ernest Rutherford disproved the Thompson’s Theory (after 5 years) used the gold foil experiment to prove the presence of protons inside the nucleus of an atom. (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sNQsdrqsD_s) THE ATOMIC THEORY Ernest Rutherford disproved the Thompson’s Theory (after 5 years) used the gold foil experiment to prove the presence of protons inside the nucleus of an atom. (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sNQsdrqsD_s) THE ATOMIC THEORY Ernest Rutherford Experiment: The Gold Foil/ Film Experiment Results: 99% passed <1% deflected According to him: (Proposal) Atom is mostly an empty space (99% passed) Contains very small nucleus & in the nucleus there is protons & neutrons. Most of its Mass & (+) particles are concentrated in the nucleus (<1% deflected) Electrons are scattered around the nucleus. Model: Nuclear Model THE ATOMIC THEORY Niel Bohr Model: Planetary Model Revised Rutherford’s atom to create a more stable model of the atom. “Electrons move around in the circular paths called orbitals, wherein the energy of orbitals is quantized.” THE ATOMIC THEORY Erwin Schrodinger Model: The “Quatum-Mechanical Model” / “Electron Cloud Model” “Electron moves in a 3D space/structure, which is called “electron cloud” Electron move around the nucleus in a “cloud” not “orbits” The closer position to the nucleus the higher chance to find electrons THE ATOMIC THEORY ATOMIC NUMBER, MASS NUMBER AND ISOTOPES Atomic Number (Z) represents the total number of proton in the nucleus of an atom. Mass Number (A) is the total number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus. (This is true to all elements except for hydrogen with only 1 proton with no neutron.) ATOMIC NUMBER, MASS NUMBER AND ISOTOPES Sample Problem: How many protons, neutrons, & electrons are in an atom of 197Au? 197 – mass no. of an Au 79 – atomic no. of Au 118 – no. of Neutrons 118 – neutrons 79 – electrons 79 - protons ATOMIC NUMBER, MASS NUMBER AND ISOTOPES Sample Problem: Give the complete chemical symbol for the nuclide that contains 18protons, 18electrons, & 22 neutrons Mass Number? Mass number = no. of protons/electrons + neutrons = 18 + 22 = 40 Atomic Number? 18 Complete Chemical Symbol? Ar (Argon) ATOMIC NUMBER, MASS NUMBER AND ISOTOPES Isotopes are elements with same atomic number but different mass numbers. Most elements have isotopes. A good example is hydrogen which has three isotopes. Hydrogen (Proteum) (Z=1, A=1), deuterium (Z=1, A=2) and tritium (Z=1, A=3).