GI Lower: Hepatitis, Crohn's, Colitis, Obstruction Study Notes
advertisement
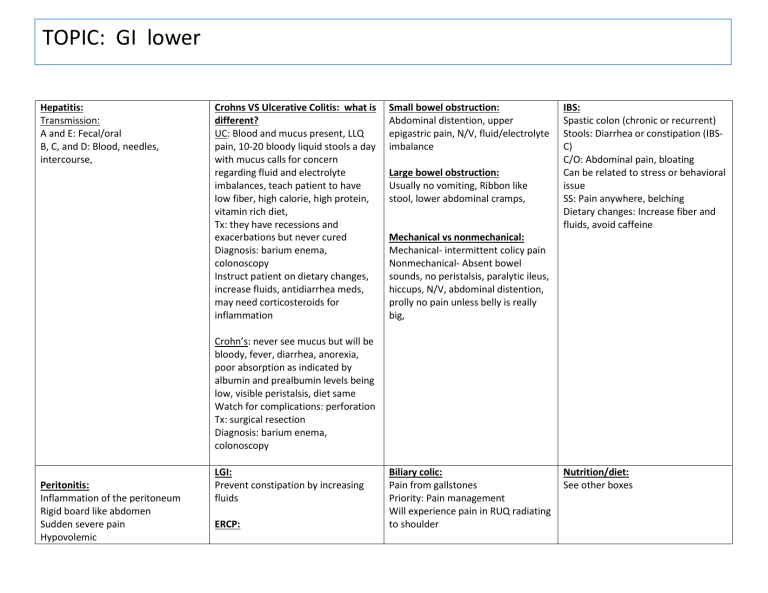
TOPIC: GI lower Hepatitis: Transmission: A and E: Fecal/oral B, C, and D: Blood, needles, intercourse, Crohns VS Ulcerative Colitis: what is different? UC: Blood and mucus present, LLQ pain, 10-20 bloody liquid stools a day with mucus calls for concern regarding fluid and electrolyte imbalances, teach patient to have low fiber, high calorie, high protein, vitamin rich diet, Tx: they have recessions and exacerbations but never cured Diagnosis: barium enema, colonoscopy Instruct patient on dietary changes, increase fluids, antidiarrhea meds, may need corticosteroids for inflammation Small bowel obstruction: Abdominal distention, upper epigastric pain, N/V, fluid/electrolyte imbalance Large bowel obstruction: Usually no vomiting, Ribbon like stool, lower abdominal cramps, IBS: Spastic colon (chronic or recurrent) Stools: Diarrhea or constipation (IBSC) C/O: Abdominal pain, bloating Can be related to stress or behavioral issue SS: Pain anywhere, belching Dietary changes: Increase fiber and fluids, avoid caffeine Mechanical vs nonmechanical: Mechanical- intermittent colicy pain Nonmechanical- Absent bowel sounds, no peristalsis, paralytic ileus, hiccups, N/V, abdominal distention, prolly no pain unless belly is really big, Crohn’s: never see mucus but will be bloody, fever, diarrhea, anorexia, poor absorption as indicated by albumin and prealbumin levels being low, visible peristalsis, diet same Watch for complications: perforation Tx: surgical resection Diagnosis: barium enema, colonoscopy Peritonitis: Inflammation of the peritoneum Rigid board like abdomen Sudden severe pain Hypovolemic LGI: Prevent constipation by increasing fluids ERCP: Biliary colic: Pain from gallstones Priority: Pain management Will experience pain in RUQ radiating to shoulder Nutrition/diet: See other boxes Abdominal distention, diminished peristalsis May get comfort in fetal position Sharp mid epigastric pain Can be caused by peptic ulcer, appendicitis TPN: Given through central line Change “bag” q24hr Monitor glucose q2hr Monitor albumin Removal of stones, remove them by going down throat, will numb throat prior to procedure Patient will be NPO until gag reflex returns appendicitis: infection in appendix RLQ pain, at McBurney’s point What assessment will you expect to see done in the patient that may have appendicitis? Pain is relieved when flexing the knees Diverticulosis / itis Osis: The disease Itis: Inflammation SS: Fever, LLQ pain, rebound tenderness, tachycardia, chills, abdominal distention, N/V, bloody stools, can lead to peritonitis Tx: Broad spectrum antibiotics, NPO in the hospital with an NG tube, IV fluids When they can eat again slowly increase fiber Complications: Peritonitis, abscess due to pockets, bleeding Acute cholecystitis: Inflamed gallbladder due to blocked bile duct RUQ pain Requires ERCP if the bile duct is blocked, and it is.









