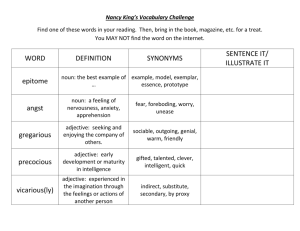
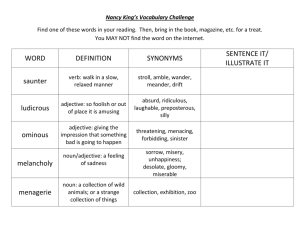
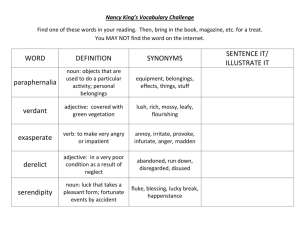
All rights reserved to: Gobindo Deb, Lecturer, Department of English, Hamdard University Bangladesh and Language Trainer, Language Connect. English Grammar Lecture: 22 & 23 Adjective Adjectives are used almost exclusively to qualify/modify nouns/pronouns, as well as any phrase or part of speech functioning as a noun. Adjective is a qualifier. John wears red glasses. A loud group of students passed by. Excellent writing is required for this job. QB: 1. A/an ____is used to qualify or limit the meaning of something. a. noun b. verb c. adjective d. adverb 2. An adjective is a _____ a. naming word b. modifying word c. qualifying word d. substituting word 3. An adjective qualifies a _____ a. verb b. adverb c. pronoun d. none of these 4 characteristics of adjective: 1. They can freely occur in attributive function. (pre-modifier of a noun/pronoun) The old man is sleeping on the street. It’s an ugly painting I choose a round table 2. They can freely occur in predicative function. (post-modifier of noun/pronoun: subject or object complement) The painting is ugly. He thought the painting ugly. She made me happy. 3. They can be pre-modified by the intensifier “very” The children are very happy. 4. They can take comparative and superlative forms. (Inflections: -er, -est or periphrastic: adding more and most) The children are happier now They are the happiest people I know These students are more intelligent. They are the most beautiful paintings I have ever seen. Types of Adjectives: 1. Attributive 2. Predicative QB: 1. The two types of adjectives are___ a. attributive and relative b. predicative and collective c. attributive and predicative d. predicative and alternative All rights reserved to: Gobindo Deb, Lecturer, Department of English, Hamdard University Bangladesh and Language Trainer, Language Connect. Attributive vs. Predicative Adjectives Adjectives that appear directly before (or sometimes directly after) the noun or pronoun they modify are known as attributive adjectives. These can appear anywhere in a sentence, and can modify parts of either the subject or the predicate. Predicative adjectives, on the other hand, always appear after the noun they modify, connected to it by a linking verb. They are one of the three types of subject complements, and they are always part of the predicate—hence their name. Comparative examples: The black dog is barking. The dog was black. Modifying pronouns While adjectives usually modify nouns, they can also modify pronouns. This most commonly occurs when adjectives are predicative. For example: That was great! She is very nice. A few were late.” Attributive adjectives can also modify indefinite pronouns, as in: A happy few were able to attend the show. They were the lucky ones.” In informal speech or writing, it is not uncommon to modify personal pronouns attributively, as in: Wow, lucky you! Silly me, I forgot to turn on the oven.” (N.B: However, avoid using attributive adjectives with personal pronouns in anything other than casual conversation or writing) Other categories of adjectives Category of Adjective Definition Example adjectives Example sentence Proper Adjectives Proper noun ‡_‡K DrcwË hv noun My‡jvi eb©bv K‡i _v‡K| `yB ev Z‡ZvwaK kã Øviv MwVZ k㸔Q hLb GKwU Noun †K modify K‡i †mB k㸇jv‡K GKmv‡_ compound adjective e‡j| G¸‡jv nvB‡db mn ev nvB‡db Qvov `yBfv‡eB MwVZ n‡Z cv‡i Italian, Shakespearean, Alaskan, Middle Eastern, Nordic top-right, last-minute, sugar-free, recordbreaking, expensivelooking, He writes in a Shakespearean style. Compound Adjectives I know this is a last-minute suggestion, but it’s a good idea. All rights reserved to: Gobindo Deb, Lecturer, Department of English, Hamdard University Bangladesh and Language Trainer, Language Connect. Demonstrative Adjectives (or Demonstrative Determiners) Interrogative Adjectives (or Interrogative Determiners) Nominal Adjectives Collective Adjectives Adjective of quality/Descriptive Quantitative adjective Noun ¸‡jv‡K we‡klfv‡e modify K‡i I wb‡`©k (Demonstrate) Kiv eySvq, †mB mv‡_ Kv‡Qi bv `~‡ii †mUvI wb‡`©k K‡i _v‡K| ‡h WH-word wU Adjective wn‡m‡e †Kvb Noun Gi c~‡e© e‡m Ges GKBmv‡_ evK¨wU‡K cÖkœ‡evaK evK¨ wn‡m‡e ‰Zwi K‡i| The + Qualitative adjective ‡h¸‡jv ev‡K¨ noun Gi KvR K‡i| this, that, these, those These cups are very pretty. what, which, whose Whose computer is this? the best, the strongest, the blue He wants the red car, but I want the blue. Nominal Adjectives Gi GKwU aib n‡jv Collective Adjective hv GKwU MÖæc †K eySvq| Noun/Pronoun Gi †`vl¸b, Ae¯’v eySv‡j cwigvb I cwigvc eySvq the rich, the poor, the innocent, the French, the Americans, the Dutch The rich should help the poor. Rich, honest, cold, She is an honest guy. warm, noble, etc. Much, enough, little, Give me some sugar more, no, none, any etc. msL¨v evPK Numeral adjective One, two, three etc All men must die; i) Definite: First, second, third etc Rahim is the third child of his family; a. cardinal Single, double, triple He is a man of few words. b. Ordinal etc. c. Multiplicative All, some, many, few, ii) Indefinite several, little, etc. Pronominal adjective This is his pen. Pronoun hLb †Kvb noun Which, his, my, your, whose, etc. Which pen have you bought? Gi mvg‡b e‡m adjective Gi KvR K‡i Note: Avm‡j Interrogative adjective,(wKQz) relative adjective, possessive adjective ¸‡jv Pronominal Gi g‡a¨B c‡o| Possessive adjective This is his car. Pronoun Gi Possessive My, his, her, our, etc. case hLb Gi mvg‡b e‡m †K K‡i Relative adjective Which, whose, what Atifa asked me which shirt I liked. wKQz Relative pronoun ev‡K¨ Noun Gi c~‡e© e‡m Adjective Gi KvR K‡i| ev‡K¨ †Rvi †`Iqvi Rb¨ Emphasizing adjective Own, very, else I saw it with my own eyes. When all else left my cause. e¨eüZ nq †h adjective My very adversary took my part. AvKw¯§K Abyf~wZ cÖKvk Kivi What Exclamatory adjective What folly! Rb¨ What an idea! All rights reserved to: Gobindo Deb, Lecturer, Department of English, Hamdard University Bangladesh and Language Trainer, Language Connect. Participles as adjective Present participle Past participle Attributively used He gave his surprising views I met an offended man Predicatively used His views were very surprising The man seemed very offended Adjective Phrases An adjective phrase is an adjective and any additional information linked to it that work together to describe a noun or pronoun in a sentence. This additional information can include determiners or adverbial modifiers. The adjective around which an adjective phrase is formed is known as the head word or head adjective of the phrase. Adjective phrases can be either attributive (appearing before the nouns they modify) or predicative (appearing after a linking verb) For example: You have a beautiful voice. He is a very good swimmer. The helicopters are controlled remotely. I am perfectly content on my own. They felt relieved to return home. Prepositional phrase as adjective phrase For example: The cat on the shed was old. Please hand me that book over there. The man in the room rushed to the spot. The girl with blue eyes stirred my mind. Relative Clauses (Adjective Clauses) Relative clauses (also known as adjective or adjective/adjectival clauses) are dependent clauses that provide descriptive information about a noun or noun phrase or pronoun. Relative clauses are introduced by either a relative pronoun or, less commonly, a relative adverb. Unlike attributive adjectives, they always appear directly after the noun they modify. For example: There’s the woman who always sits next to me on the bus. The book that I wrote is being published in January. The escaped giraffe, which had been on the loose for weeks, was finally captured. The house where I was born is a very special place. I love casual Fridays, when we get to wear jeans to work. Order of adjectives [ AO MSC ACP OMP] 1. Articles (a, an, the) 2. Opinion (good, bad, strange, lovely) 3. Measurement (big, small, tiny, huge) All rights reserved to: Gobindo Deb, Lecturer, Department of English, Hamdard University Bangladesh and Language Trainer, Language Connect. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Shape (curved, straight, round, square) *** Condition/Description (wet, dry, clean, sad, happy) Age (old, young, new, ancient) *** Color (red, yellowish, transparent, blue) Pattern (checked, striped, plaid, flowered) Origin (American, British, eastern, western) Material (wooden, plastic, steel, cloth) Purpose (sleeping, shopping, work, gardening) Examples: I bought an enormous rectangular Turkish rug on my vacation. (AMSO) An old political idea (APC) The latest educational reform (APC) A green wine bottle (APC) Leather dancing shoes (PC) A wonderful old house (AOC) A small round black leather handbag (AMSCM) A little modern square brick house (AMASM) A fat old white horse (AMAC) QB: 1. The man was carrying a ____bag. a. black small plastic b. small and black c. small black and plastic (MCM) d. plastic small black 2. The tenants were asked to throw all recyclable trash into____ a. the green big plastic bag b. the big plastic green bag c. the big green plastic bag (AMCM) d. the green plastic big bag 3. Fill in the blank: The house was ____building. a. a nice old stone (AOA) b. a nice stone old c. a stone old nice d. an old nice stone Adjectives sued as noun: As plural Noun: The rich, the poor, the cautious, the wicked, the interested, etc. (The + adjective) - The rich don’t know how the poor live As singular: The future, the beautiful, etc. - He is a lover of the beautiful wKQz wKQz Adjective mivmwi Noun wn‡m‡e e¨eüZ nq Ges G¸‡jv Singular I Plural `yBfv‡eB e¨eüZ nq| Proper Adjective hv Noun n‡q hvq: Bangladeshi(s), Indian(s), Australian(s), Canadian(s), Italian(s) G¸‡jv Noun I Adjective `yB¸b m¤úbœB nq| wKQz Adjective mivmwi e¨w³‡K eySvq A_v©r Noun n‡q hvq- Juniors, seniors, mortals, inferiors, superiors, superiors, nobles, criminals, savages, elders, minors etc. wKQz Adjective mivmwi e¯‘MZ wRwbm †K eySvq A_v©r Noun n‡q hvq - secrets, totals, liquids, solids, valuables, eatables, etc. G Qvov wKQz Phrase G Adjective ¸‡jv Noun wn‡m‡e e¨eüZ nqIn general; in future; in short; in secret; before long; at present; for good; at best; through thick and thin; for better or for worse; in black and white; right or wrong; from bad to worse; the long and short. In future, I shall charge you for medical advice. In short, we know nothing. The negotiations were carried on in secret. I shall see you before long. All rights reserved to: Gobindo Deb, Lecturer, Department of English, Hamdard University Bangladesh and Language Trainer, Language Connect. Before long, he will be appointed to a higher post. At present, he is in pecuniary difficulties. I do not want any more at present. He has left India for good. At best he is a clever versifier: but a poet he is certainly not. It must be said to his credit that he stood by his friend through thick and thin. I must have your teams down in black and white. Right or wrong, my country. I am afraid the young man is going from bad to worse. The long and short of it is that I distrust you. Position of Adjectives Adjective Gi cÖKvi‡f` Abyhvqx Adjective `yB Ae¯’v‡b em‡Z cv‡i| 1. Attributive (before noun) 2. Predicative (After noun and after linking verb) King Francis was a hearty king, and loved a royal sport. (Attributive) Where are you going, my pretty maid, with your rosy cheeks and golden hair? (Attributive) There dwelt a miller hale and bold. (Predicative) The King, fearless and resolute, at once advanced. (Predicative) Franklin had a great genius, original, sagacious, and inventive. (Predicative) He was a man fertile in resource. (Predicative) A Sikh, taller than any of his comrades, rushed forward. (Predicative) G Qvov Adjective Gi Ae¯’vb cwieZ©b Ki‡j A‡_©iI cwieZ©b N‡U| wb‡Pi evK¨ `ywU †`Lyb(i) a great nobleman's son, and (ii) a nobleman's great son. KweZvq cÖvq mgqB †`Lv hvq Gi c‡i e¨eüZ n‡q‡Q| Children dear, was it yesterday. We heard the sweet bells over the bay man with sisters dear! GQvovI wKQz phrases Av‡Q †h¸‡jv‡Z Adjective memgq noun Gi c‡i e‡m| Heir apparent time immemorial lord paramount viceroy elect notary public body politic God Almighty Secretary General Court Martial President elect Attorney General Poet Laureate Nouns as adjectives Bus stand, television program, the garage door, night club, apple trees, etc. All rights reserved to: Gobindo Deb, Lecturer, Department of English, Hamdard University Bangladesh and Language Trainer, Language Connect. Formation Adjectives: Noun Adjective Noun Boy boyish Man Fool foolish Sense Dirt dirty Envy Storm stormy Shame Gift gifted Glory Care careful Trouble Pardon pardonable Courage Gold golden Venture King kingly Outrage Silk silken Hope Play playful Health Time Timely Wealth Heaven Heavenly Hill Room Roomy Greed Pain Painful Doubt Wonder Wonderful Peace Child Childish Prince Mountain Mountainous Ridicule Picture Picturesque Labor Wood Wooden Pomp Artist Artistic Slave Contempt Contemptuous Tempest Sense Sensible Quarrel Thought Thoughtful Friend Noun + ly = Adjective: Motherly, friendly, fatherly, lovely, lively, likely Adjective manly senseless envious shameless glorious troublesome courageous venturesome outrageous hopeful Healthy Wealthy Hilly Greed Doubtful Peaceful Princely Ridiculous Laborious Pomp Slavish Tempestuous Quarrelsome Friendly Verb Tire Cease Talk Move Need Cost Hope Love Laugh Progress Adjective tireless ceaseless talkative moveable Needy Costly Hopefully Lovely laughable Progressive Adjective Tragically Wholesome Threefold Blackish Whitish Sickly Adjective Tragic Whole Three Black White Sick