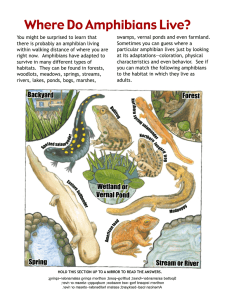
Amphibians IMPORTANCE OF AMPHIBIANS WHAT ARE AMPHIBIANS ? Amphibians are ectothermic, tetrapod vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Example: Frog Salamander Caecilians What is the difference between reptiles and amphibians? Reptiles include snakes, turtles and lizards, while amphibians include toads, frogs and salamanders, according to Mass Audubon. One difference between reptiles and amphibians is their relationship with water. ... Frogs are amphibians. They spend time on land, but in their larval stage, as tadpoles, they live in water. What are amphibians used for? Amphibians evolved as models for a variety of developmental and physiological processes, largely due to their unique ability to undergo metamorphosis. Scientists have used amphibian embryos to evaluate the effects of toxins, mutagens, and teratogens Importance of amphibians Amphibians are an important part of the food chain, providing food resources for numerous animals from snakes to raptors. The skin of amphibians contains a multitude of different peptide forms, providing a number of human diseases with potential medicinal cures. In nature, both as predators and prey, amphibians play an important role. They eat pest insects, which are helpful to the world's agriculture and help reduce the spread of diseases, including malaria. With almost a third species categorized as endangered, world amphibians face an imminent extinction crisis. The loss of freshwater ecosystems is the principal cause of amphibian declines. Many other causes have been identified, which act synergistically; these include pollution, climate change and disease amphibian declines and extinctions are evidence of the harmful effects of humans on human beings Amphibians' skill to regrow limbs is being studied to shed light on how to improve tissue regeneration and growth.