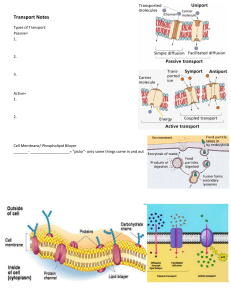
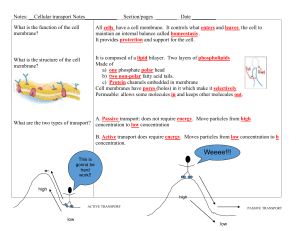
Welcome! CJ • Lesson: Begin 4.1 Cell Membrane Structure • Understand components and chemistry of cell membrane • Calculate surface area to volume ratio • Complete 4.1 In-Class Activity 2020-2021 Do Now • Explain how the structure of a phospholipid is correlated with the structure of the cell membrane • Are phospholipids the only type of molecules found in the cell membrane? If no, what other molecules can be found? Foulds| Biology 8 1 Cellular Exchange with Environment Unit 4 Images Created with BioRender.com Lesson 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure 2020-2021 Foulds | Biology 8 3 Big Picture – Context Going in to Unit 4 • In the last unit, we touched on the idea that the cell membrane separates the highly delicate biochemical environment inside of the cell from the chaos and disorder of nature outside of the cell • But the cell is not a “closed system” – the cell needs to exchange materials with it’s environment in order to maintain homeostasis • Thus the cell must carefully pick and choose what materials can enter and leave the cytoplasm. • Our cells take advantage of physics and chemistry in order to successfully transport materials Cell Membrane Structure • Cell membranes = flexible, doublelayered sheets called a phospholipid bilayer. • Cell membrane contains a variety of different molecules embedded among the many phospholipids Phospholipid The Lipid Bilayer • The lipid bilayer forms spontaneously when phospholipids are in water • This is the most stable configuration of phospholipids in water • Thus, the structure of the membrane itself abides by laws of physics • How does phospholipid structure correlate with membrane structure? Amphipathic – both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts The Lipid Bilayer • Phospholipids = Amphipathic • Hydrophilic head groups point outwards, toward water • Hydrophobic tail groups point inwards, away from water • Middle of the membrane is extremely hydrophobic. It is a hydrophobic barrier • Thus, water and other polar molecules can not pass through directly Amphipathic – both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts Membrane Behavior • Fluid Mosaic Model • • • • The cell membrane is “fluid” Thousands of phospholipids move side-to-side (laterally) in the membrane Proteins also are fluid in membrane, but move more slowly due to big size Note: fluid here does not mean liquid – fluid in this context means the membrane is flexible • “Mosaic” part – there are many different types of molecules embedded in the membrane • Phospholipids, proteins, glycoproteins, glycolipids, cholesterols, etc. • Video: Visualizing Membrane Fluidity Selective = choose carefully Permeable = allow to pass Barrier = obstacle to prevent movement Putting it together The cell membrane is a selectively permeable, hydrophobic barrier • Some substances cross more easily than others • Phospholipid tails keep hydrophilic, polar molecules from passing directly through • So how do polar molecules, like water, enter or leave the cell? • Membrane proteins provide passage for polar molecules to go through the hydrophobic barrier • Recall that proteins are highly specific about what molecules they will interact with. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Why Are Cells So Small? Surface area = 6s2 Volume = s3 • A cell needs to be able to get enough nutrients in and waste out so that the cell can function. • But as a cell increases in size, the volume (inside the cell) increases more rapidly than the surface area (membrane area). • To get around this problem, it is advantageous for cells to maintain a high surface area to volume ratio, by staying small in size. • High surface area, low volume Why Are Cells So Small? s Surface area = 6s2 Volume = s3 Cell Membrane Structure • To summarize, cells can maintain high surface area to volume in 2 ways: • 1: Cells stay small in size (as seen on last page) • 2: Membranes can achieve high surface area by folding in on themselves • Example - The inner membrane of the mitochondria is folded in order to increase its surface area •Allows for surface area to grow without much change in cell volume