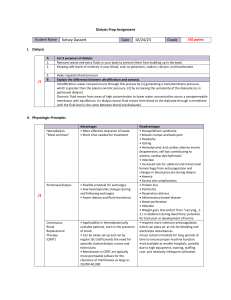
Healthcare Remediation Notes: Head Injuries, ESRD, CHF
advertisement

Exam 4 Remediation Kassem Charafeddine 1. Head injuries: - The most common cause of death from trauma in the United States - Concussion: an alteration in mental status that results from trauma and may or may not involve loss of consciousness treatments involves observing and managing symptoms like headache, dizziness, lethargy, irritability, anxiety, phonophobia, difficulty concentrating and memory difficulties - Contusion: a more severe injury, involving bruising of the brain with possible surface hemorrhage - Diffuse axonal: injury involves widespread damage to axons in the cerebral hemispheres - Epidural hematoma: collection of blood in the space between the skull and the dura - Subdural hematoma: collection of blood between the dura and the brain - Intracerebral hemorrhage: bleeding into the parenchyma of the brain Will cause altered level of consciousness: - Not oriented to name, date, where they are, won’t follow commands, constant simulation to stay awake - State of alertness to coma - Use Glasgow coma scale: assessing eye opening, motor response and verbal responses - A normal GCS score is equal to 15, which indicates a person is fully conscious, less than 8 you intubate 2. Common allergic reactions, such as hay fever, certain types of asthma, and hives are linked to an antibody produced by the body called immunoglobulin E (IgE). Each IgE antibody can be very specific, reacting against certain pollens and other allergens. 3. LHF causes pulmonary congestion and therefore crackles are audible on auscultation of the lungs. Some sever cases are treated with a loop diuretic (potassium wasting) to help eliminate more fluids. One way to check if such treatment is successful the nurse can reassess for absence of crackles and monitor potassium levels closely. 4. End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) is a medical condition in which a person's kidneys cease functioning on a permanent basis leading to the need for a regular course of long-term dialysis or a kidney transplant to maintain life. You may need to make changes to your diet when you have chronic kidney disease (CKD). These changes may include limiting fluids, eating a low-protein diet, limiting salt, potassium, phosphorous, and other electrolytes, and getting enough calories 5. One of the most common issues patients with a dialysis fistula develop is stenosis or narrowing of the veins and/or artery. Changes in the bruit or thrill at the fistula site may indicate stenosis. If you do not feel the thrill or hear the bruit in your access, this could indicate blockade of access. 6. Advantages of Peritoneal Dialysis include greater lifestyle flexibility and independence, a less restricted diet, and longer lasting residual kidney function. 7. For patients with ESRD and on hemodialysis, dialysis is necessary to help regulate potassium. Between dialysis treatments, however, potassium levels rise, and high-potassium foods must be limited. 8. Renal impairment may be evident at any stage of heart failure (CHF). End stage renal disease can be a complication of heart failure and chronic heart disease can be a consequence of ESRD. Patients with such prognosis present with worsening fluid retention and increased shortness of breath, edema, electrolyte abnormalities, high blood pressure, anemia, and Unbalanced calcium-phosphorous levels. Nurses should be encouraged to maximize their knowledge on management of fluid balance, blood pressure control/monitoring, discussion of blood results and reduction of cardiovascular risk factors. Close monitoring and effective management of modifiable cardiac risk factors, such as diabetes and hypertension can reduce onset and slow progression of CKD. Drug therapy, particularly angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and beta-adrenergic receptor blockers, is sometimes used in patients with ESRD and CHF.