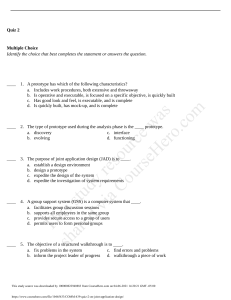
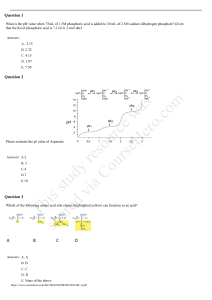
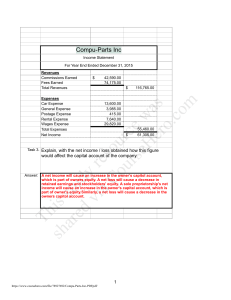
CHAPTER 3: MANAGING AND TAKING GOOD CARE OF YOURSELF Take care of yourself = I want to see you again alive and healthy LESSON 12: BECOMING A BETTER STUDENT LEARNING – involves acquiring CHANGE in the present knowledge, skills,habits, behaviors, or tendencies through experience, practice or formal education. o o Defined as a permanent change in behavior as a result of experience Requires continuity of behavioral change Characteristics of Learning Learning is purposeful Learning is a Result of Experience Learning is Multifaceted Learning is an Active Process What happens during learning? Brain Changes: 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Get organized Prepare your review materials Ask Help Test yourself or ask someone to test you. Allot time to take a break and eliminate stress Create or join a study group Teach what you have learned Study to understand, not to remember LESSON 13: SETTING GOALS FOR SUCCESS Albert Bandura’s social cognitive theory – self efficacy refers to one’s belief in one’s ability to succeed in specific situations or accomplish a task. Self-efficacy- is a belief, faith that “If one has faith, nothing is impossible” Mastery Experiences – refers to the first-hand or direct experiences that a person acquires. New Nerve Cells may grow and new neutral networks will then be formed The strength of existing synaptic connection changes, thus functionally changing the connectivity (and the activity) within the existing neutral networks in response to sensory stimuli New synapses are formed between neurons that were not connected before, thus effectively creating, new networks of neurons that, when active, represent a new memory. Self-regulated learning – refers to the learner’s ability to regulate or control one’s own learning and behavior. Th “If you are not getting better, you are getting worse”Pat Riley sh Outcome-based education – the premise of instruction is based on what the students can do, opposed to what the students know. o WAYS TO DEVELOP GOOD HABITS: is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m 1. 2. 3. 4. Study Habits – refer to the attitudes and behaviors of students when preparing for tests or any learning assessment. Vicarious Experience- emanate from observing people, especially those that one regards as his or her role models. Verbal Persuasion –to motivation coming from influential people such as parents, teachers etc. Emotional and Physiological States – refer to the Emotional and Physiological conditions that a person is in. Carol Dweck – one of the world-renowned researchers in the area of motivation. Fixed Mindset – people believe that basic qualities such as intelligence and talents are fixed traits. Growth Mindset- people believe that talent and intelligence are developed through learning, effort, training and practice. Clarity – being clear and not vague Performance-based and action- based James Spady – father of Outcomes-based education (OBE) Challenge – that a goal must trigger the knowledge, skills, and abilities. Commitment- reflects a person’s dedication towards the attainment of the set goals. This study source was downloaded by 100000812551980 from CourseHero.com on 12-08-2021 20:35:50 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/96350646/UTS-QUIZ-REVIEWER-CHAPTER-3docx/ Feedback- serves as a mechanism to ensure that everyone sharing the same goal is on the right track. as well as in protocols for healing and recovery from diseases. Task Complexity- pushes people to take the extra mile and work hard. Physical Health Responsibility – involves active participation in one’s own health and healing through education and lifestyle changes. Expectancy Theory – focused mainly on the expectations that share a particular behavior in a particular situation. Stress – refers to the reaction of our physiological and psychological self to any kind of demand or threat. o Expectancies – Learning creates cognition. King (2004) – categorized success into mental, spiritual, personal,career, financial, social, physical and family success. Eustress – is a beneficial stress that can be in the form of physical, psychological and biological stimuli. o Mental Success- understanding and accepting one’s intellectual abilities, feelings, and emotions. Eu means good hence the word eustress means good stress. Distress – occurs when there a tension buildup which becomes unbearable and difficult to cope with. is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Spiritual Success – equates to having a sound body and spirit. Also causes aging and cancer Personal Success – comes with overcoming one’s physical and psychological limitations such as overcoming phobia. Career Success – entails achieving milestones in one’s career such as getting one’s dream job. Financial Success- means financial stability. Social Success – reflects the recognition and respect one has from the community. Physical Success – can mean possessing the desired qualities of one’s body. Family Success – is to have a harmonious and happy family. LESSON 14 : TAKING CHARGE OF ONE’S SELF Th Physical Domain – includes coordination, strength, and well-being. Intellectual Domain- includes alertness, analytical functioning, logical analysis etc. sh Emotional Domain- includes creativity, sensitivity, mood, perception and awareness. Steinbrook (2006) – stated that today, more than ever, personal health responsibility or taking charge of one’s own healthy is an essential step in disease prevention Stressor- is any event that compels a person to adjust or change. COMMON STRESSOR 1. 2. 3. 4. Catastrophic events and experiences Life changes and strains Chronic Problems Everyday Hassles Stress tolerance – refers to the ability of an individual to endure stress. Problem-focused coping method – involves an attempt to change or eliminate sources of stress. Ex: confrontation, seeking social support undertaking careful, deliberately problem solving. and Emotion-focused method – is aimed are controlling the negative emotional consequence of stressors. Ex: self-control (keeping feelings to ones self), distancing (not thinking about the stressors) accepting responsibility (attributing the stress as one’s creation) and wishful thinking (thinking that the situation will pass) Self – care – refers to all activities that a person does to maintain and improve his or her physical well-being. This study source was downloaded by 100000812551980 from CourseHero.com on 12-08-2021 20:35:50 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/96350646/UTS-QUIZ-REVIEWER-CHAPTER-3docx/ life-threatening Psychological self - care – includes all activities one does to deal or resolve mental health issues, address both positive and negative emotions. Emotional self care- includes all the activities one does to cope with stress and deal with grief. Social self- care – includes all activities one does to connect with people valuable to him or other. Spiritual Self- care – activities one does to strengthen one’s relationship with his or her beliefs. BENEFITS OF SELF- CARE Enhanced productivity Improved vitality Enhanced self- esteem Increased self- knowledge Mindfulness and compassion is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Self- Compassion – is defined as showing compassion to one’s self. THREE MAIN ELEMENTS OF SELF - COMPASSION SELF- KINDNESS – means not being physically and verbally harsh to one self. o Self – beration – a kind of verbal abused directed to oneself. Involves the act where he blames himself for his actions and decisions. o Self- harm- an act of harming ones self through physical. o Common humanity – acceptance that one is an imperfect being. o Mindfulness – practice of being fully present in the moment. sh Th 1. This study source was downloaded by 100000812551980 from CourseHero.com on 12-08-2021 20:35:50 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/96350646/UTS-QUIZ-REVIEWER-CHAPTER-3docx/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)