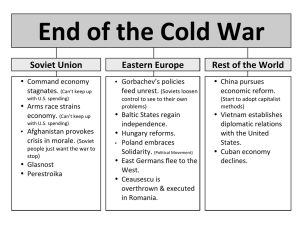
The Cold War Era (1945–1991) The Cold War Ends The Cold War Era (1945–1991) Lesson 5 The Cold War Ends Learning Objectives • • • • Understand why the Soviet Union declined. Identify the reforms introduced by Mikhail Gorbachev. Describe the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union. Evaluate how the end of the Cold War affected the remaining communist nations and the United States. The Cold War Era (1945–1991) Lesson 5 The Cold War Ends Key Terms • • • • • • • Mikhail Gorbachev glasnost perestroika Lech Walesa Solidarity Vaclav Havel Nicolae Ceausescu The Soviet Union Declines • During the Cold War, relations between the Soviet Union and the United States swung back and forth between confrontation and détente (easing of hostility or strained relations, especially between countries). • The superpowers confronted each other over issues such as the Berlin Wall, Soviet intervention in Eastern Europe, and Cuba. However, in the 1970s, Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev pursued détente and disarmament with the United States. The Soviet Union Declines • • • The Soviets in Afghanistan The Command Economy Stagnates Gorbachev Tries Reform The Soviet Union Declines In 1979 the Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan. The war proved costly, and over time, Soviet soldiers grew disillusioned. The Soviet Union Collapses Gorbachev faced a host of problems: His policies brought rapid change that led to economic turmoil. Shortages grew worse, and prices soared. Factories that could not survive without government help closed, throwing thousands out of work. Old-line Communists and bureaucrats whose careers were at stake denounced the reforms. At the same time, other critics demanded even more changes. The Soviet Union Collapses • • The Soviet Empire Crumbles End of the Soviet Union The Soviet Union Collapses Gorbachev struggled at home, but the United States welcomed Soviet reforms. President Ronald Reagan and Mikhail Gorbachev shake hands before a summit near Geneva in 1985. In a 1987 speech near the Berlin Wall, Reagan urged Gorbachev to “tear down this wall!” The Soviet Union Collapses Analyze Maps The Soviet Union officially dissolved in 1991, and many former republics gained independence. Which of the former Soviet republics is the largest? Eastern Europe Transformed During the Cold War, Eastern Europe lay in the Soviet orbit. Efforts to resist Soviet domination were met with harsh repression. Despite the Soviet threat, some nations in Eastern Europe slowly made reforms. After Mikhail Gorbachev announced that the Soviet Union would no longer intervene in Eastern Europe, a “democracy movement” swept the region, and the nations of Eastern Europe were remarkably transformed. Eastern Europe Transformed • Poland Struggles Toward Democracy • Revolution and Freedom • Ethnic Tensions in Eastern Europe • The Breakup of Yugoslavia • Restoring Peace Communism Declines Around the World The collapse of communism in the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe affected other communist nations. Cuba, which had long depended on Soviet aid and support, faced severe difficulties. Its economy suffered, too, from sanctions imposed by the United States decades earlier. Communism Declines Around the World • • Other Communist Nations Adopt Market Reforms Different Paths for Vietnam and North Korea The Post-Cold War World • The Move Toward Market Economies The Post-Cold War World When the Cold War ended in the early 1990s, Americans hoped for a more peaceful world. But as the sole superpower, the United States played a leading role in trying to resolve world conflicts. The United States led coalition forces in several missions around the world. The Post-Cold War World The role of the United States as the sole remaining superpower means that the U.S. military often responds to problems and conflicts all over the world. Essential Question: How should we (usa) handle conflict around the world? Quiz: The Soviet Union Declines In the 1980s, the Soviet economy was strained by A. B. C. D. increased spending on social programs. economic stagnation and increased military spending. increased spending on satellite nations’ populations. a lack of natural resources. Quiz: The Soviet Union Collapses What is the difference between perestroika and glasnost? A. Perestroika refers to changes in the structure of the government; glasnost refers to openness and increased freedoms. B. Perestroika refers to the reforms in Eastern Europe; glasnost refers to those inside the Soviet Union. C. Perestroika refers to the reforms inside the Soviet Union; glasnost refers to those in Eastern Europe. D. Perestroika refers to increased freedoms; glasnost refers to changes in structure of the government. Quiz: Eastern Europe Transformed Most of the communist governments of Eastern Europe fell because A. B. C. D. their citizens staged armed rebellions. the Soviets allowed them to change their command economies to capitalist ones. their citizens staged large protests, and the Soviets did not intervene militarily. the military support promised by the Soviets did not arrive in time. Quiz: Communism Declines Around the World China and Vietnam reacted to the collapse of the Soviet bloc by A. B. C. D. moving toward capitalist economies. becoming more politically liberal. launching a trade war against the Soviet Union. becoming satellites of the United States. Quiz: The Post-Cold War World What was the initial effect of the transition from command to market economies in Eastern Europe? A. B. C. D. People could afford more goods than they could before. People stopped purchasing goods. Unemployment and prices rose. There were fewer consumer goods available for purchase.