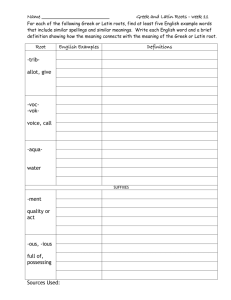
Greek and Latin Roots This lesson will help you build word power by taking words apart. Roots are the building blocks of words, and knowing some common roots will help you to gain vocabulary fluency with unfamiliar words. Prefixes and suffixes modify or alter word meaning. In this lesson, you'll focus on the root words to which prefixes and suffixes are attached. Our English language is a relatively new language in the history of the world, and it's one of the richest and most complicated. Its very newness is responsible for the great variety of English words in the language. Thousands of English words are built upon root words from other languages that have existed for thousands of years. English, as we speak it today, began about 400 or 500 years ago, so we're practically babies in the language game! People who study the history and origin of words and languages are called etymologists. But you don't need to be an etymologist to benefit from knowing how words are formed and re-formed with word roots. As a student, your vocabulary skills will be enhanced (look up enhanced if you don't already know what it means) by learning some common root words. Once you do, you'll be able to use them to help you figure out the meaning of unfamiliar words. The two most common sources for English words are Latin and Greek roots. You have probably learned about these civilizations in school, so you know that Latin was the language spoken in ancient Rome more than 2,000 years ago. Latin spread throughout Europe and eventually developed, by about the seventeenth century, into modern languages spoken today, like French, Italian, Spanish, and Portuguese. A Sample Latin Root and Its Use in Common English Words Look at some of the many English words that have been built from one Latin root, ced/ceed/cess, which can mean “go,” “yield,” and/or “stop.” • • • • • • • antecedent: that which comes before cessation: a stopping, the end of something concede: to admit something is true, to surrender exceed: to extend beyond precede: to come before proceed: to go forward procedure: the act of proceeding, a process You don't have to memorize Latin roots; that would be a huge task and could take years! But a list like the one above should help you see the relationships that exist between words and help you figure out meanings of similar-sounding words. Ancient Greek is the other major original source of many English words. The language spoken in Greece today is descended (look up that word if you don't already know it) from earlier forms of Greek that date back to the thirteenth century B.C. Imagine how fascinating it is for etymologists to trace a modern word in English back through 3000 years of Greek usage! A Sample Greek Root and Its Use in Common English Words Look at some of the many English words that have been built from chron, which is the Greek root for time: • anachronism: something that is out of date or placed in the wrong time • chronic: continuing over a long time, or recurring • chronology: the sequence of events in time • chronicle: a detailed record or description of past events • synchronize: to cause to occur at the same time Greek and Latin Roots Practice Exercise Write the italicized word from each sentence and the best choice to define the word: • The Latin root am means love. An amiable person is talkative. truthful. well educated. friendly, good natured. • The Latin root plac means to please. A complacent person is one who makes frequent mistakes. is argumentative. is self-satisfied. is known to tell frequent lies. • The Latin root luc/lum/lus means light. A lucid argument is very clear and understandable. loosely held together. illogical. one that blames others. • The Latin root qui means quiet. A quiescent place is very isolated. very chaotic. very dangerous. very still and restful. • The Latin root loc/loq/loqu means word, speech. Something that is eloquent is dull and trite. expressed in an effective way. very old-fashioned. equally divided into parts. • The Greek word auto means self. To have autonomy means to have a lot of money. be independent. have courage. have strong opinions. • The Greek root pas/pat/path means feeling, suffering, disease. To have empathy is to give to others. have a love for others. identify with the feelings of others. be similar to others. • The Greek root pseudo means false, fake. The root nom/nym means name. A pseudonym is a false name. an ancient god or deity. a harsh sound. a long and boring speech. • The Greek root dog/dox means opinion. The suffix -ic means having the quality of. A person who is dogmatic is not in touch with reality. intolerant of other opinions. one who asserts opinions in an arrogant way. secretive and ungenerous. • The Greek root phil means love and the root anthro/andro means human. Philanthropy is the love of humankind. a preference for something in particular. using force to control others. spreading unkind rumors. Even if you don't have a clue about what a new word means, look at it closely and see if it sounds similar to another word you know, or if it has parts similar to other words you know. If all else fails, consult a good online dictionary like thefreedictionary.com, which has an auditory feature for correct pronunciation. Words You Should Now Know • amiable • enhance • anachronism • etymologist • autonomy • exceed • cessation • lucid • chronic • philanthropy • chronicle • precede • chronology • procedure • complacent • proceed • concede • pseudonym • dogma • quiescent • eloquent • synchronize • empathy Select ten words from the list above that were not used in the practice exercise, and write a context sentence for each. Write or type your sentences on the same page as your answers to the practice exercise. Sample Sentence: A famous anachronism appears in Shakespeare’s play Julius Caesar, when a character refers to a clock, which did not exist in Roman times.