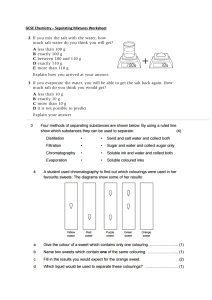
Chap 4: Mixtures 4.1 Q1- What is a Mixture? A mixture is made up of two or more elements and/or compound which are not chemically combined. Many substances around us are mixtures. Mixtures are not pure substances, that is, they are not made up of only one type of element or compound. Mixtures may consists of elements, compound or both. A salt solution, for example, is a mixture of two compounds- salt and water. The constituents of a mixture may be solid, liquid or gas. Q2- Why is a salt solution not a compound? The breaking down and formation of compounds involves chemical reactions. However, no chemical reaction takes place when salt is mixed in water to form a salt solution. The salt in the solution can be separated from water by a physical process such as evaporation. Therefore, a salt solution is not a compound. It is a mixture. Q3- Write some examples of Mixtures? - Air: Air is a Mixture of gases. The gasses include nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and noble gases. - Mineral Water: Mineral Water is mixture of minerals such as calcium, magnesium, potassium and sodium in water. - Alloys: Steel, brass and bronze are mixtures called alloys. They are formed by mixing metals with small amounts of other metals or non-metals to make them stronger and harder than the pure metals. Steel, for example, is an alloy of iron mixed with a little carbon and other metals. Steel is stronger and harder than pure iron. Q4- Write down some properties of Mixtures. 1. No chemical reaction takes place during the formation of mixtures. 2. No energy is exchanged with the surrounding when mixtures are formed. 3. Mixtures have properties of their constituents. 4. The constituents of mixtures can combine in any proportion by mass. 5. Mixtures can be separated into their constituents by physical process. 4.2 Q5- Are the boiling and melting points of mixtures fixed? No, unlike compounds mixtures have a range of melting and boiling points depending on their compositions. The melting point of sodium chloride solution is slightly less than the melting point of pure water (0°C). Its boiling point is slightly higher than that of pure water (100°C). Elements and compound are pure substances which have specific melting and boiling points, densities and electrical and heat conductivities. Mixtures, However, have a range of melting and boiling point, densities and electrical and heat conductivities depending on their compositions. 4.3 Q6- What are some separation techniques? Also explain them. Here are the processes: Filtration; using a piece of filter paper we can remove the solute from the solvent, as the solute cannot pass through the filter paper, but the solvent can. The solute is left as residue on the filter paper while the solvent is collected as the filtrate in the beaker or flask. Evaporation; when common salt dissolves in pure water, both the salt and the water go through the filter paper. To obtain salt from the solution, evaporation is used instead. When a solution is heated, the liquid or solvent evaporates, leaving the solid solute behind as residue. Distillation; is the process In which you obtain the liquid from the Solution when being separated or it also can be the separation of two different boiling points mixtures what happens in the process is that the solution is evaporated and up to a thermometer with the help of a condenser pours out the water in another bowl. Fractional distillation; is when more than two different boiling point liquids are to be separated it is quite similar to distillation but in this process a fractional column or tower is used for the separation. Chromatography; is used to separate, analyze and identify different components in mixtures such as inks, urine, food coloring and fruit juices.