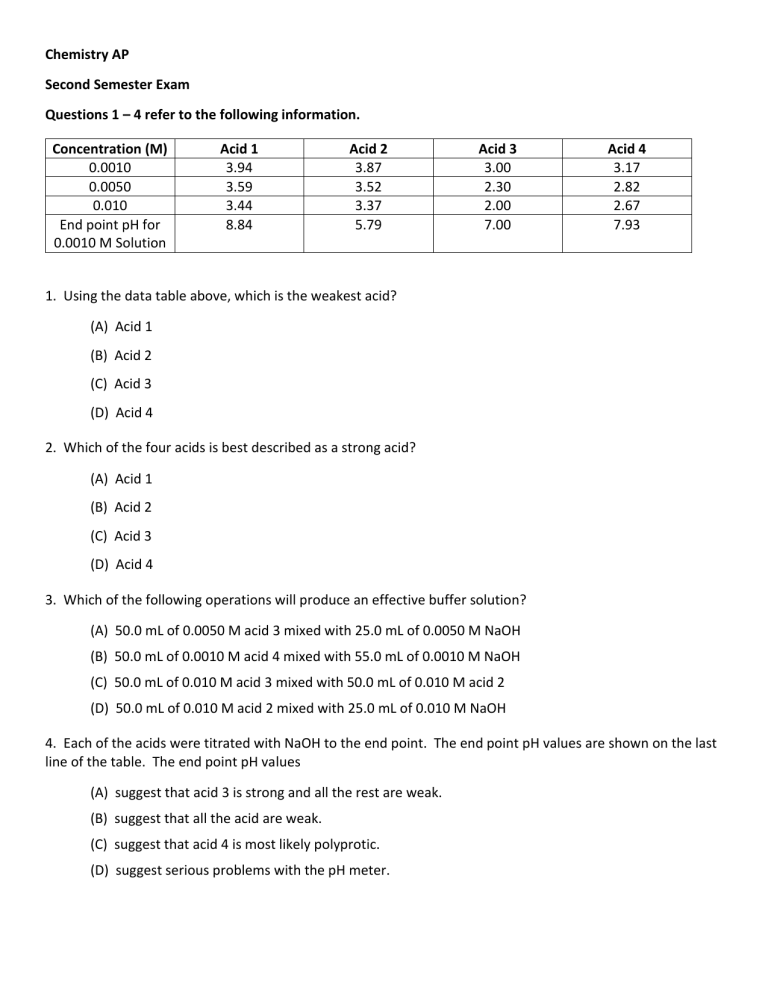
Chemistry AP Second Semester Exam Questions 1 – 4 refer to the following information. Concentration (M) 0.0010 0.0050 0.010 End point pH for 0.0010 M Solution Acid 1 3.94 3.59 3.44 8.84 Acid 2 3.87 3.52 3.37 5.79 Acid 3 3.00 2.30 2.00 7.00 Acid 4 3.17 2.82 2.67 7.93 1. Using the data table above, which is the weakest acid? (A) Acid 1 (B) Acid 2 (C) Acid 3 (D) Acid 4 2. Which of the four acids is best described as a strong acid? (A) Acid 1 (B) Acid 2 (C) Acid 3 (D) Acid 4 3. Which of the following operations will produce an effective buffer solution? (A) 50.0 mL of 0.0050 M acid 3 mixed with 25.0 mL of 0.0050 M NaOH (B) 50.0 mL of 0.0010 M acid 4 mixed with 55.0 mL of 0.0010 M NaOH (C) 50.0 mL of 0.010 M acid 3 mixed with 50.0 mL of 0.010 M acid 2 (D) 50.0 mL of 0.010 M acid 2 mixed with 25.0 mL of 0.010 M NaOH 4. Each of the acids were titrated with NaOH to the end point. The end point pH values are shown on the last line of the table. The end point pH values (A) suggest that acid 3 is strong and all the rest are weak. (B) suggest that all the acid are weak. (C) suggest that acid 4 is most likely polyprotic. (D) suggest serious problems with the pH meter. 5. Which substance is most likely to be soluble in a nonpolar solvent? (A) glucose (C6H12O6) (B) graphite (C) lithium fluoride (D) sulfur 6. An experiment was performed to determine the moles of hydrogen gas formed (collected over water) when an acid reacts with magnesium metal. To do this, a piece of dry magnesium was weighed. Then 100 mL of hydrogen was collected. Next the Mg was dried to remove about 0.20 mL of water and weighed again to see how much Mg had reacted. The volume of hydrogen was measured and converted into moles hydrogen. Which mistake will give the largest error in the result? (A) Failing to convert °C to K. (B) Reading the gas-collecting container to ±40 mL. (C) Forgetting to dry the magnesium before both weighings. (D) Failing to take the vapor pressure of water (23 torr at 25 °C) into account. 7. In the diagram above, which labeled arrow is pointing toward a covalent bond and which is pointing toward a hydrogen bond? Hydrogen Bond Covalent Bond (A) 3 4 (B) 2 1 (C) 1 2 (D) 4 3 S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) 8. The equation for the reaction between sulfur and oxygen, written in equation form above, can be interpreted in all of the following ways except (A) one mole of sulfur atoms reacts with one mole of oxygen molecules to yield one mole of sulfur dioxide molecules. (B) this reaction goes to completion. (C) adding S(s) will change the equilibrium constant. (D) one atom of S reacts with one molecule of O2 to yield one molecule of SO2. The structure of Morphine is shown below. Morphine is the focus of problems number 9 and 10. 9. Morphine, C17H19NO3 (shown above), has a Kb = 8.0 x 10-7. If a 0.10 M solution of morphine is prepared, the expected pH will be in which one of the following pH ranges? (A) 5 to 7 (B) 7 to 9 (C) 9 to 11 (D) 11 to 13 10. What is the pKa of morphine hydrochloride, C17H20NO3+/Cl-1, where C17H20NO3+ is the conjugate acid of the morphine in the previous question? (A) log(1.0 x 10-14/8.0 x 10-7) (B) – log(1.0 x 10-14/8.0 x 10-7) (C) log (8.0 x 10-7) (D) – log (8.0 x 10-7) 11. A solution of which substance can best be used as both a titrant and its own indicator in an oxidationreduction titration? (A) I2 (B) NaOCl (C) NaOH (D) KMnO4 12. Use the arrangement of atoms suggested in the skeleton structure above to construct the Lewis structure for the SO3 molecule. Which of the following statements about this molecule is incorrect? (A) Sulfur trioxide has a planar triangle shape. (B) Sulfur trioxide has three resonance structures. (C) Sulfur trioxide is polar. (D) the S – O bond order is 4/3. Questions 13 and 14 refer to the following table information. Vessel A B C Molar Mass 302 g/mole 174 g/mole 95 g/mole Pressure 0.2 atm 0.4 atm 0.2 atm Temperature 500 °C 500 °C 600 °C Note that the gases are held in separate, identical, rigid vessels. 13. Which sample has the highest density? (A) Vessel A (B) Vessel B (C) Vessel C (D) All have the same density since the volumes are all the same. 14. The average kinetic energy (A) is greatest in vessel A. (B) is greatest in vessel B. (C) is greatest in vessel C. (D) is the same in all vessels since the volumes are all the same. The following equations all contribute to the synthesis of magnesium oxide from its elements. Use them to answer questions number 15 and 16. 15. Using Hess’s Law, which of the following combinations gives the enthalpy change for the following reaction? 2O-2(g) → O2(g) + 4eA. B. C. D. ∆H = ∆H(3) + 2∆H(4) ∆H = −∆H(4) - ∆H(3) ∆H = −2∆H(4) + ∆H(3) ∆H = −∆H(3) - 2∆H(4) 16. Which of the steps in the table above are endothermic? A. ∆H(1) and ∆H(2) B. ∆H(2) and ∆H(3) C. ∆H(1), ∆H(2), and ∆H(3) D. ∆H(1), ∆H(2), ∆H(3), and ∆H(4) 17. Noting that the reaction goes to completion, producing MgO from the elements, and using the overall chemical equation to estimate the entropy changes for this process, which of the following statements is correct? A. The reaction is unfavorable because of the enthalpy and entropy changes. B. The reaction is favorable and is driven by the enthalpy change since the entropy decreases. C. The reaction is unfavorable since the entropy change is a large negative value. D. The reaction is favorable and is driven by both enthalpy and entropy changes. Questions 18 and 19 refer to the table below. Galvanic Cell Cell Diagram Cell Voltage 1 Fe │ Fe+2 (1.0 M) ║ Hg+2 (1.0 M) │ Hg 1.26 V 2 Ti │ Ti+2 (1.0 M) ║ Hg+2 (1.0 M) │Hg 2.48 V 3 Fe │ Fe+2 (1.0 M) ║ Ti+2 (1.0 M) │Ti ? 18. What is the chemical reaction under study in galvanic cell 3? A. Fe + Fe+2 → Hg+2 + Hg B. Fe + Fe+2 → Ti+2 + Ti C. Fe + Ti+2 → Fe+2 + Ti D. Fe + Ti → Fe+2 + Ti+2 19. Rank the three metals from the metal that is easiest to oxidize to the metal that is the most difficult to oxidize. A. Ti > Fe > Hg B. Fe > Hg > Ti C. Ti > Hg > Fe D. Hg > Fe > Ti 20. Dissolving one mole of each of the oxoacids HClO2, HNO2, HNO3, and H3PO4 in 2.0 L of distilled water results in solutions with different pH values. Arrange these acid solutions from the one with the highest pH to the one with the lowest pH. A. HNO2 > H3PO4 > HClO2 > HNO3 B. HNO3 > HNO2 > H3PO4 > HClO2 C. HNO2 > HNO3 > HClO2 > H3PO4 D. HNO2 > HClO2 > HNO3 > H3PO4 Compound Formula Normal Boiling Point, K Propane CH3CH2CH3 231 Propanol CH3CH2CH2OH 370 Propanal CH3CH2CHO 323 Propanoic acid CH3CH2CO2H 414 21. Based on the data table above, which of the following substances has the lowest vapor pressure at any given temperature? A. propane B. propanol C. propanal D. propanoic acid 22. Which of the reactions below will become thermodynamically favored only at high temperatures? ∆H° (kJ/mol) Reaction ∆S° (J/mol•K) A. CO(NH2)2 + H2O → CO2 + 2NH3 +119.2 +354.8 B. C2H2 + 5N2O → CO2 + H2O + 5N2 −437.4 +272.6 C. C2H5OH + O2 → HC2H3O2 + H2O −534.3 +131 D. 2Fe + 3CO2 → Fe2O3 + 3CO +26.7 +15.7 23. During the complete combustion of methane, CH4, what change in hybridization does the carbon atom undergo? (A) sp3 to sp (B) sp2 to sp (C) sp3 to sp2 (D) sp2 to sp3 24. Which diatomic species has the greatest bond length? (A) N2 (B) CO (C) O2 (D) Cl2 25. What is the total number of valence electrons in the peroxydisulfate ion, S2O8-2? (A) 58 (B) 60 (C) 62 (D) 64 Please continue on the next page 26. Which of the following particulate diagrams best represents the reaction of carbon with oxygen to form carbon dioxide? A. B. C. D. 27. To prepare a buffer, all of the following can be used except A. an acid with a pKa close to the desired pH B. a weak acid with an equal mole amount of strong base C. a weak base with its conjugate acid D. an acidic salt along with its conjugate base 28. 29. A compound with the formula X2O5 contains 34.8% oxygen by mass. Identify element X (A) arsenic (B) carbon (C) phosphorus (D) samarium 30. (A) I only (B) III only (C) II and III only (D) I, II, and III