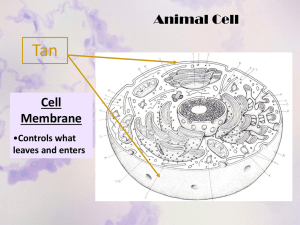
The Plant Cell Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Membrane – thin, flexible barrier around the cell. It regulates what enters and leaves the cell. – it contains ribosomes and it coordinates protein synthesis. Chromatin - it contains most of the genetic material (DNA) of the cell. Nucleolus - produces ribosomes. Nucleus - it is the center of cellular activity and it controls cellular reproduction. Cytoplasm – a jelly-like substance inside the cell that holds all organelles in place. Cell Wall - give the cell strength and structure, and to filter molecules that pass in and out of the cell. Golgi Complex - it produces lysosomes, packages proteins for the cell and releases them into the cytoplasm. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria – serve as the powerhouse of the cell. They provide energy for cellular respiration. Chloroplasts – unlike the rough ER, it lacks ribosomes. It specializes in lipid synthesis, steroid hormone production, and detoxification. -serve as the site of photosynthesis. Central Vacuole Plasmodesmata – small tubes that connect plant cells to each other, providing living bridges between cells. Lysosomes – they breaks down food molecules and dead or injured cells. - Aside from water storage, its main role is to maintain turgor pressure against the cell wall. Ribosomes Cytoskeleton - it provides structure and shape for a cell and it helps the cell move. -assemble amino acids to create proteins. The Animal Cell Nucleus -it is the center of cellular activity and it controls cellular reproduction. Chromatin - it contains most of the genetic material (DNA) of the cell. Nucleolus - produces ribosomes. Mitochondria -serve as the powerhouse of the cell. They provide energy for cellular respiration. Cell Membrane -a thin, flexible barrier around the cell and it regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Cytoplasm – a jelly-like substance inside the cell that holds all organelles in place. Lysosomes - they breaks down food molecules and dead or injured cells. Golgi Apparatus – it produces lysosomes, packages proteins for the cell and releases them into the cytoplasm. Vesicles - transport materials that an organism needs to survive and recycle waste materials. Golgi Apparatus – unlike the rough ER, it lacks ribosomes. It specializes in lipid synthesis, steroid hormone production, and detoxification. Ribosomes – they assemble amino acids to create proteins. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoskeleton – it contains ribosomes and it coordinates protein synthesis. - it provides structure and shape for a cell and it helps the cell move. Centrioles – they help to arrange the microtubules that move chromosomes during cell division. Significance of the Project This project is aimed to remind every student on the acquired knowledge about the basic structures and functions of cells. The collaboration is satisfactory despite the limitations of physical interaction during the currently ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The project was achieved through innovative ideas collaborated together that will benefit every individual to slowly and ferociously understand the complexity of life that we came to appreciate, in a fun learning strategy. Rubrics: • Visual Appeal • Completeness of Parts • Correctness • Collaboration • Timeliness Total: Members: Earl Owen D. Esquivel Jedric C. Tuquero Larah Jerlie L. Limos Yram Lezahnie C. Millet ___/30 ___/20 ___/20 ___/20 ___/10 ___/100 Rating: 10 Rating: 10 Rating: 10 Rating: 10