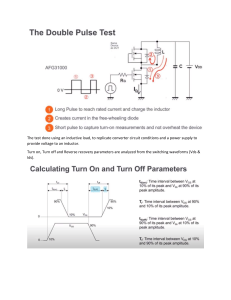
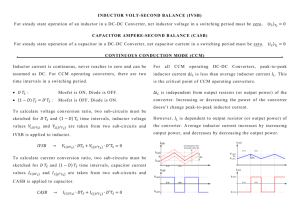
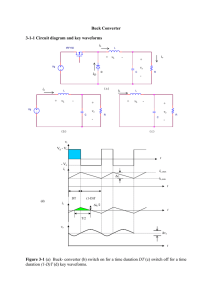
Power Electronics Topics for the oral exam Academic Year 2021/22 Power semiconductor switches, drive and protection circuits Schottky barrier diode. Reverse blocking. 2. Schottky barrier diode: forward conduction. The "limit of silicon" in unipolar conduction. 3. P-i-n diodes: reverse blocking. NPT design. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. R AF T 1. P-i-n diodes: forward conduction. Conductivity modulation. Forward voltage drop. Switching characteristics of p-i-n diodes. Reverse recovery: recovery softness factor. On-state resistance: comparison between unipolar and bipolar conduction. Power MOSFET transistors: device structures, I-V characteristics, on-resistance. Power MOSFETs: trade-off between on-resistance and breakdown voltage. Power MOSFETs: absolute maximum ratings. 10. Power MOSFETs: impact of parasitic capacitances on switching characteristics. 11. Gate charge curve: calculation of switching times and losses. 12. High-side switch drivers: bootstrap. 13. Power MOSFETs: UIS. Overvoltage protection circuits. 14. Power MOSFETs: current-sense strategies, overcurrent protection circuits. Switch-mode DC-DC converters 15. SM DC-DC converters: CCM vs. DCM operation mode. DC voltage transfer function. 16. SM DC-DC converters: effect of parasitic components on the DC voltage transfer function. Efficiency. 17. SM DC-DC converters: modulation techniques, pulse-width modulator. D 18. Dynamic modeling of non-isolated DC–DC converters under CCM operation. 19. PWM switch: average and small signal model. 20. Small signal model of the pulse-width modulator. Sampling effect. 21. Control-to-output transfer function: effect of a RHP zero. 22. Voltage control mode: key design guidelines for the control loop. Loop shaping. 23. Type I, type II and type III compensators. Compensator design techniques. 24. k-factor design method. 25. CCM boost converter: compensation; RHPZ bandwidth limitation. 26. Feedforward control of switching regulators. 27. Current-mode control: principle of operation, slope compensation. 28. Buck converter: key guidelines for filter inductor selection. 29. Filter inductor: core selection procedure; area product. 30. Filter inductor: gapped vs. distributed magnetic cores. 31. Filter inductor: high-frequency copper losses; proximity effects. 32. Buck converter: selection of the input and output filter capacitors. 33. Soft-start circuits. 34. Flyback converter: CCM vs DCM operation. 35. Flyback converter: transformer design for DCM operation. 36. Flyback converter: impact of leakage inductance; winding interleaving. Thermal management R AF T 37. Packaging of power devices. Junction-to-case thermal resistance. Power dissipation and continuous current ratings. Derating. 38. Steady-state heat transfer: guidelines for the design and selection of heat sinks. 39. Transient operation: thermal impedance. Thermal RC model: Foster and Cauer networks. D 40. Transient thermal analysis: single pulse and periodic pulses.