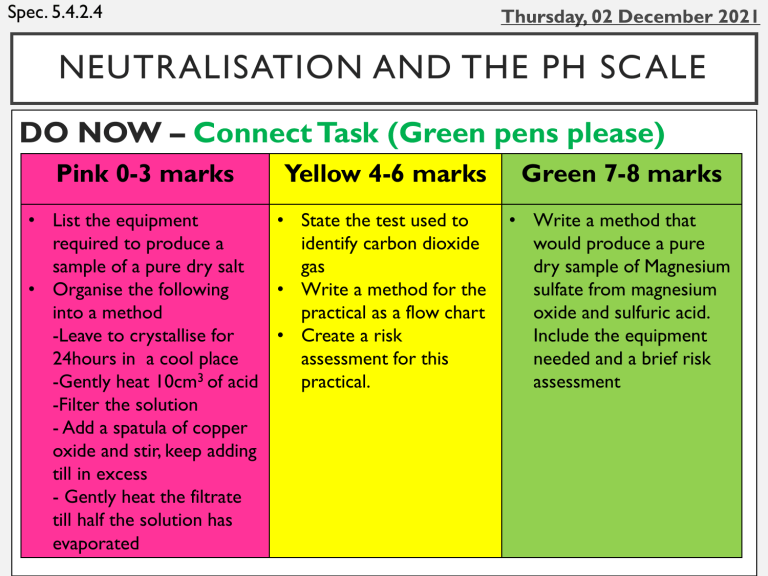
Spec. 5.4.2.4 NEUTRALISATION AND THE PH SCALE DO NOW – Connect Task (Green pens please) Pink 0-3 marks Yellow 4-6 marks • List the equipment • State the test used to required to produce a identify carbon dioxide sample of a pure dry salt gas • Organise the following • Write a method for the into a method practical as a flow chart -Leave to crystallise for • Create a risk 24hours in a cool place assessment for this -Gently heat 10cm3 of acid practical. -Filter the solution - Add a spatula of copper oxide and stir, keep adding till in excess - Gently heat the filtrate till half the solution has evaporated Green 7-8 marks • Write a method that would produce a pure dry sample of Magnesium sulfate from magnesium oxide and sulfuric acid. Include the equipment needed and a brief risk assessment PROGRESS INDICATORS Good progress Outstanding progress Grade 1-3 Use the pH scale to identify acidic or alkaline solutions. Define the following terms: acid, base, alkali, neutral. Describe the use of universal indicator or a wide range indicator to measure the approximate pH of a solution. Grade 4-6 Recall the ionic equation for a neutralisation reaction. Interpret the ionic equation for a neutralisation reaction. WORD CONSCIOUSNESS pH Scale – A scale used to show how acidic/basic a substance is. Neutral - a substance that is not acidic or alkaline e.g. water Neutralisation - a reaction where an acid is reacted with an alkali to produce a salt and water. The products are neutral. PH SCALE Key Facts • Ranges from pH 0-14. Any pH below 7 is an acid, any pH above 7 is an alkali. pH 7 is neutral. • The colours shown above are seen when using universal indicator. • H+ ions make a substance an acid. OH- ions make a substance an alkali. ACTIVITY 1 - DEFINE THE FOLLOWING TERMS: ACID, BASE, ALKALI, NEUTRAL Match the key term to its definition. acid base A substance that forms an aqueous solution with a pH of less than 7 A base that dissolves in water to form a solution greater than 7 alkali neutral Any substance that will react with an acid to form a salt The product when an acid neutralises a base Add these to your word consciousness in your books please ACTIVITY 2 - USE THE PH SCALE TO IDENTIFY ACIDIC OR ALKALINE SOLUTIONS. Substance Colour with universal indictor pH Acid / alkali / neutral Pure water Vinegar Bleach Soap Stomach acid Washing up liquid Normal rain Acid rain Pancreatic juices Caustic soda (drain cleaner) CHALLENGE: Can you distinguish between strong and weak acids and alkalis, if so add it to the last column, e.g. strong acid ACTIVITY 2 ANSWERS Substance Colour with universal indictor pH acid / alkali / neutral Pure water 7 neutral Vinegar 3 (weak) acid Bleach 12 (strong) alkali Soap 11 (weak) alkali Stomach acid 1 (strong) acid Washing up liquid 9 (weak) alkali Normal rain 5 (weak) acid Acid rain 4 (weak) acid Pancreatic juices 10 (weak) alkali Caustic soda (drain cleaner) 14 (strong) alkali SA In red pens please ACTIVITY 3 -DESCRIBE THE USE OF UNIVERSAL INDIC ATOR OR A WIDE RANGE INDIC ATOR TO MEASURE THE APPROXIMATE PH OF A SOLUTION. QUESTIONS 1. Universal indicator is a wide range indicator. What is meant by the term ‘wide range indicator’? 2. Give one advantage of using a wide range indicator. 3. Give one advantage of using a pH probe attached to a pH meter. ACTIVITY 3 ANSWERS QUESTIONS 1. Universal indicator is a wide range indicator. What is meant by the term ‘wide range indicator’? A dye that gradually changes colour over a broad range of pH 2. Give one advantage of using a wide range indicator. Useful for estimating pH of a solution 3. Give one advantage of using a pH probe attached to a pH meter. It is more accurate than an indicator SA In red pens please ACTIVITY 4 -RECALL THE IONIC EQUATION FOR A NEUTRALISATION REACTION Fill in the gaps. hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous Acids produce h_________ solutions. hydroxide ions Aqueous solutions of alkalis contain h__________ (OH-). In neutralisation reactions between an acid and an alkali, hydrogen ions react with hydroxide ions to produce w________. water Using the coloured cards in your planner show red for false, green for true An acid is anything with a pH below 7 An alkali is anything with a pH of 7 or above A substance is acidic due to the H+ ions Neutralisation produces a salt and hydrogen An substance is an alkali because of the OHions pH 2 is an alkaline substance






