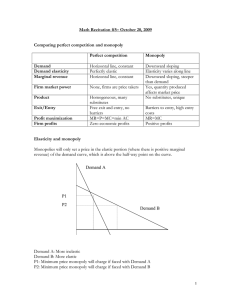
Stephen Seward MICRO EXAM STUDY GUIDE 11/30/2021 Micro Final Exam Study Guide 1. What is Economics, and Why Is It Important? Answer: Economics is the study of how people seek to satisfy their needs and wants by making choices. It is important because it allows people and businesses to make smart decisions in the economy 2. What is Studied in Microeconomics and Macroeconomics? Answer: Microeconomics is the study of how individuals, households, firms, and governments make choices, while macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole 3. What are some of the Requirements for Economic Models? Answer: Models are simplifications of reality that include only essential elements and exclude less relevant details. Economic models include assumptions, hypotheses, and variables. 4. What does a Production Possibilities Curve depict? Answer: The PPF curve shows the specified production level of one commodity that results given the production level of the other. It assumes the maximum possible efficient use of the resources for a maximum possible production of both commodities. The production possibilities curve is a graph that shows all of the different combinations of output that can be produced given current resources and technology. What is the Law of Demand? Answer: The Law of Demand states that other things being constant, an increase in the price of a good lowers the quantity demanded of that good, while a decrease in the price of a good raises the quantity demanded of that good. Price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions. Answer: The Law of Demand Stephen Seward MICRO EXAM STUDY GUIDE 11/30/2021 What components will cause a Shift in the Demand curve? Answer: There are five significant factors that cause a shift in the demand curve: income, trends and tastes, prices of related goods, expectations as well as the size and composition of the population. What components will cause a Shift in the Supply curve? Answer: Factors that can shift the supply curve for goods and services, causing a different quantity to be supplied at any given price, include input prices, natural conditions, changes in technology, and government taxes, regulations, or subsidies. What happens if a market is out of Equilibrium? Answer: There will either be a shortage which means if price is less than equilibrium level. there will be a shortage. Which forces the price up. What does Price Elasticity of Demand Measure? Answer: The price elasticity of demand measures how strongly demanders respond to a change in the price of the good or service. What is the Difference between Fixed Costs, Variable Costs, and Marginal Costs? Answer: Fixed costs is costs that remain the same regardless of level of production or services offered, and Variable costs production costs that change when production levels change. Marginal Costs are the extra cost of producing one additional unit of production. Fixed costs do not affect the marginal cost of production since they do not typically vary with additional units. Stephen Seward MICRO EXAM STUDY GUIDE 11/30/2021 How does one calculate Fixed Costs, Variable Costs, Marginal Costs, and Profits? Answer: 1.) Fixed Costs: First, add up all of your production costs. Make sure to be clear about which costs are fixed and which ones are variable. Take your total cost of production and subtract your variable costs multiplied by the number of units you produced. This will give you your total fixed cost. Fixed costs = Total production costs — (Variable cost per unit * Number of units produced) 1.) Variable Costs: multiply what it costs to make one unit of your product by the total number of products you’ve created. This formula looks like this: Total Variable Costs = Cost Per Unit X Total Number of Units. 2.) Profits are calculated by dividing total revenue by total expenses. All sales are calculated by subtracting direct and indirect costs. Materials and staff wages can be included in direct costs. In addition to rent and utilities, indirect costs include overhead costs. What is meant by Economies and Diseconomies of Scale? Answer: Economies of scale exist when long run average total cost decreases as output increases, diseconomies of scale occur when long run average total cost increases as output increases, and constant returns to scale occur when costs do not change as output increases. Stephen Seward MICRO EXAM STUDY GUIDE 11/30/2021 What is the Difference between predatory pricing, tie-in sales, and bundling? Answer: Predatory pricing is the illegal act of setting prices low to attempt to eliminate the competition. Existing firms use sharp, temporary price cuts to discourage new competition A customer can buy one product only if he buys another. A tie-in sale results from a contractual arrangement between a consumer and a producer whereby the consumer can obtain the desired good (tying good) only if he agrees also to purchase a different good (tied good) from the producer. Bundling is when companies package several of their products or services together as a single combined unit, often for a lower price than they would charge customers to buy each item separately. At what Price should All Firms Produce at? Answer: In order to maximize profit, the firm should produce where its marginal revenue and marginal cost are equal. What should a Firm do for Pricing if it faces Elastic or Inelastic Demand? Answer: For goods with elastic demand, firms should lower prices to increase total revenue by increasing the quantity demanded. For goods with inelastic demand, firms should increase price to raise total revenue. Calculating price elasticity helps a firm make these choices. What is the difference between and Accounting Profit and an Economic Profit? Answer: Accounting profit includes explicit costs, such as raw materials and wages. Economic profit includes explicit and implicit costs, which are implied or imputed costs. Stephen Seward MICRO EXAM STUDY GUIDE 11/30/2021 How does Technology affect the Demand for Labor? Answer: An increase in the availability of certain technologies may increase the demand for labor. Technology that acts as a complement to labor will increase the demand for certain types of labor, resulting in a rightward shift of the demand curve. For example, the increased use of word processing and other software has increased the demand for information technology professionals who can resolve software and hardware issues related to a firm's network. More and better technology will increase demand for skilled workers who know how to use technology to enhance workplace productivity. Those workers who do not adapt to changes in technology will experience a decrease in demand. What is a Natural Monopoly? Answer: A natural monopoly arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market at a smaller cost than could two or more firms. A natural monopoly occurs when there are economies of scale, implying that average total cost falls as the firm's scale becomes larger. What is the Difference between a Natural Monopoly and an Unregulated Monopoly? Answer: A natural monopoly arises when average costs are declining over the range of production that satisfies market demand. This typically happens when fixed costs are large relative to variable costs. As a result, one firm is able to supply the total quantity demanded in the market at lower cost than two or more firms—so splitting up the natural monopoly would raise the average cost of production and force customers to pay more In the case of a natural monopoly, market competition will not work well and so, rather than allowing an unregulated monopoly can raise price and quantity and influence the market. Stephen Seward MICRO EXAM STUDY GUIDE 11/30/2021 How does the Government examine Cost-Benefit analysis? Answer: Cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is a tool used by regulatory decision makers to identify the costs and benefits, in financial terms, of a regulation to society as a whole. Persons preparing a CBA attempt to assign a monetary value (also known as monetizing) to all the predicted costs and benefits of a regulation. These include not only the direct costs and benefits, but any tangential effects a regulation may impose on society. In evaluating the effects on society, CBA includes costs and benefits to industry, government, individual citizens, communities, the environment, and the economy at large. This attempts to do for government programs what the forces of the marketplace do for business programs: to measure, and compare in terms of money, the discounted streams of future benefits and future costs associated with a proposed project. If the ratio of benefits to costs is considered satisfactory, the project should be undertaken. What are the three types of Efficiency necessary to achieve Economic Efficiency? Answer: allocative efficiency; productive efficiency; and dynamic efficiency What are some of the Factors Leading to Globalization? Answer: Factors influencing Globalization are as follows: Historical, Economy Resources and Markets, Production Issues, Political, and Industrial Organization Technologies. What are the Characteristics of a Purely Competitive Market? Answer: In an ideal purely competitive market, the products being sold would be identical, which removes the option of one seller offering something different or better than another seller. Because there are so many competitors in the market offering the same product at the same price, one competitor doesn't have an edge over the others. Essentially, all the sellers are equal. New companies can easily enter the market. The price of products is determined solely by what consumers are willing to pay. Stephen Seward MICRO EXAM STUDY GUIDE 11/30/2021 What are the Characteristics of a Monopolistic Competition Market? Answer: -Many buyers and sellers. -Slight differentiated products. -Maximize profits. -Low barriers to entry and exit. -Potential supernormal profits in the short term. -Normal profits in the long-run. -Imperfect information. -Non-price competition. What are the Characteristics of a Oligopoly Market Answer: -A Few Firms with Large Market Share -High Barriers to Entry -Interdependence -Each Firm Has Little Market Power In Its Own Right -Higher Prices than Perfect Competition -More Efficient What are the Characteristics of a Monopoly Market? Answer: A monopoly market is characterized by the profit maximizer, price maker, high barriers to entry, single seller, and price discrimination. Stephen Seward MICRO EXAM STUDY GUIDE 11/30/2021 What are Intellectual Property Rights? Answer: Intellectual property rights are the rights given to persons over the creations of their minds. They usually give the creator an exclusive right over the use of his/her creation for a certain period of time. What is Income Inequality? Answer: Income inequality is how unevenly income is distributed throughout a population. The less equal the distribution, the higher income inequality is. Income inequality is often accompanied by wealth inequality, which is the uneven distribution of wealth. Populations can be divided up in different ways to show different levels and forms of income inequality such as income inequality by gender or race. What is meant by a Poverty Trap? Answer: A poverty trap is a mechanism that makes it very difficult for people to escape poverty. A poverty trap is created when an economic system requires a significant amount of capital in order to earn enough to escape poverty. When individuals lack this capital, they may also find it difficult to acquire it, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of poverty. How are Labor Markets Affected by Discrimination? Answer: Labor market discrimination is defined as a situation where workers or groups of workers are treated differently in terms of recruitment, pay, benefits and promotion from other workers or groups due to their non-economic characteristics, including gender, race, religion and age. This means that while workers may be equally productive, they are not treated the same. Treatment may be positive, where certain groups are favored, or negative, where groups are treated less favorably. What is the Purpose of Unions? Answer: The main purpose of labor unions is to give workers the power to negotiate for more favorable working conditions and other benefits through collective bargaining. Stephen Seward MICRO EXAM STUDY GUIDE 11/30/2021 What are the impacts of Human and Physical Capital in a Global Economy? Answer: Human capital and economic growth have a strong correlation. Human capital affects economic growth and can help to develop an economy by expanding the knowledge and skills of its people. Human capital refers to the knowledge, skill sets, and experience that worker have in an economy. The skills provide economic value since a knowledgeable workforce can lead to increased productivity. The concept of human capital is the realization that not everyone has the same skill sets or knowledge. Also, the quality of work can be improved by investing in people's education. What is the Difference between a Tariff and a Quota? Answer: The tariff is a tax charged on imported goods. The quota is a limit defined by the government on the quantity of goods produced in the foreign country and sold domestically. Tariff results in generating revenue for the country and hence, increase the GDP. As opposed to quota, is imposed on the numerical value of goods, not the amount and so it has no effect. With the effect of the tariff, consumer surplus goes down while the producer’s surplus goes up. On the other hand, quota results in the fall of consumer surplus. Income generated from the collection of the tariff is the revenue of the government. Conversely, in the case of quota, traders will get extra income from the collection. Who are the Winners and Losers from trade Restrictions? Answer: The winners are consumers and workers, managers and owners of firms that produce goods whose demand increases through international trade. The losers are workers, managers and owners of firms whose demand decreases as a result of international trade; that is, firms who produce substitutes for imports.