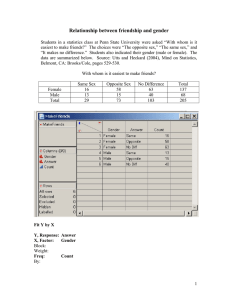
lOMoARcPSD|10133946 Final Exam Test Bank CP102 15e Information Processing with Microcomputer Systems (Wilfrid Laurier University) StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 1 The Impact of Technology in a Changing World 1) ________ tools gather information from sources such as e-mails, text messages, and tweets and make the information instantly and publicly available for use in emergencies. A) Social networking B) Crowdsourcing C) Crisis-mapping D) Affective computing Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 1.01 Describe various technological tools being used to impact national and global issues. 2) ________ tools enable people to connect and exchange ideas. A) Affective computing B) Social media C) Debugging D) Computer forensics Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 1.01 Describe various technological tools being used to impact national and global issues. 3) The gap in ease of access to the Internet and technology is known as the ________ divide. A) web B) Internet C) digital D) technology Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 1.02 Describe various global social issues that are being affected by technology. 4) The Next Einstein Initiative and the ________ Institute for Mathematical Sciences bring bright young learners and the best lecturers in the world together using TED and Google Project 10^100 to make technological changes in that continent. A) African B) Asian C) South American D) Australian Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 1.02 Describe various global social issues that are being affected by technology. 1 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) ________ results when leisure time and available tools allow us to engage in creative acts. A) Crowdsourcing B) Social networking C) Cognitive surplus D) Affective computing Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 1.03 Describe how technology is changing how and why we connect and collaborate with others. 6) ________is a nickname for social media tools which allows users to contribute content easily and to easily connect to each other. A) Cognitive surplus B) QR codes C) Web 2.0 D) Instant Messaging Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 1.03 Describe how technology is changing how and why we connect and collaborate with others. 7) Using the Internet to get small donations from many people to start a business is called ________. A) kickstarting B) crowdfunding C) crowdsourcing D) collaborating Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 1.03 Describe how technology is changing how and why we connect and collaborate with others. 8) QR or ________ codes let any piece of print host a link to online information. A) quick retention B) quick response C) quality response D) quality retention Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 1.04 Summarize how technology has impacted the way we choose and consume products and services. 2 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 9) ________ solicits online input such as product ratings from consumers. A) A quick response code B) Computer forensics C) Crowdsourcing D) Crowdfunding Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 1.04 Summarize how technology has impacted the way we choose and consume products and services. 10) ________ is joining together as a group to use a specific product more efficiently. A) Collaborative consumption B) Crowdfunding C) Crowdsourcing D) Social networking Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 1.04 Summarize how technology has impacted the way we choose and consume products and services. 11) Skype is a ________. A) crowdfunding app B) Voice over IP service C) Social network D) Wi-fi hotspot Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 12) The term computer ________ is used to describe someone who is familiar enough with computers to understand their capabilities and limitations. A) master B) webmaster C) literate D) hacker Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 3 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 13) ________ provides the instructions that tell a computer what to do. A) Software B) Hardware C) Spam D) Data mining Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 14) Unwanted or junk e-mail is called ________. A) spam B) spyware C) adware D) malware Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 15) All of the following are examples of being computer literate, EXCEPT ________. A) knowing how to avoid hackers and viruses B) knowing how to maintain and troubleshoot your computer C) knowing how to use the web efficiently D) knowing how to build and program computers Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 16) Teaching Siri or the Google Assistant how to recognize your voice by reading to it is an example of ________. A) perception B) planning C) unsupervised learning D) supervised learning Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 1.06 Describe artificial intelligence systems and explain their main goals. 17) All of the following are main areas of research in artificial intelligence, EXCEPT ________. A) data mining B) natural language processing C) perception D) problem solving Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 1.06 Describe artificial intelligence systems and explain their main goals. 4 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 18) Processes information using a bottom-up approach, learning by examples rather than rote rules, similar to humans. A) Artificial neural networks B) Cloud computing C) Expert systems D) Rules-based systems Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 1.06 Describe artificial intelligence systems and explain their main goals. 19) ________ analyzes patterns in data, then uses the patterns to draw conclusions and adjust the actions of the AI system accordingly. A) Machine learning B) Big data C) Deep learning D) Cloud Computing Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 1.06 Describe artificial intelligence systems and explain their main goals. 20) Which of the following is an example of a recommendation engine? A) An Excel spreadsheet listing all employees and their annual salaries in a random order B) Amazon providing you a list of products similar to others you've viewed C) Raw data from marketing questionnaires D) A printout of all sales taken from the register at the end of the day Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 21) The Turing test consists of a person asking written questions of a person and a computer. If the questioner can't tell which one of the respondents is a computer, then the computer has attained ________. A) mastery B) intelligence C) independence D) Turing Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 5 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 22) A robot which moves and acts much like a human is a(n) ________. A) empathetic agent B) intelligent personal assistant C) turing machine D) embodied agent Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 23) Course management software often includes intelligent personal assistants to manage ________. A) paperwork B) student interactions C) learning plans D) AI Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 24) ________ reality is the addition of digital information directly into our reality, either to add more detail or to remove unwanted visual effects. A) Augmentative B) Alternate C) Assisted D) Altruistic Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 25) In medicine, 3D printing allows more stylish and less expensive designs for ________. A) medicines B) patient simulators C) prosthetic limbs D) clothing Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 6 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 26) ________ replaces perceived reality with a different world. A) Variable reality B) Augmentative reality C) Virtual reality D) Alternate reality Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 27) Analyzing computer systems to gather potential legal evidence is computer ________. A) detective work B) forensics C) analysis D) enforcement Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 28) ________ behavior is NOT conforming to a set of approved standards of behavior. A) Unethical B) Amoral C) Illegal D) Dogmatic Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 1.08 Define ethics and examine various ethical systems. 29) Which of these is NOT a system of ethics? A) Humanism B) Relativism C) Divine Command Theory D) Utilitarianism Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 1.08 Define ethics and examine various ethical systems. 30) A set of formal or informal ethical principles an individual uses to make decisions is ________. A) personal ethics B) ethical system C) relativism D) societal ethics Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 1.09 Describe influences on the development of your personal ethics. 7 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 31) ________ property is work that is the result of someone's creativity and knowledge. A) Intellectual B) Personal C) Collective D) Public Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 1.10 Present examples of how technology creates ethical challenges. 32) The gap in access to the Internet and technical tools among people around the world is known as the ________. Answer: digital divide Diff: 1 Objective: 1.02 Describe various global social issues that are being affected by technology. 33) The Witness Project hopes to stop ________ abuses throughout the world. Answer: Human Rights Diff: 2 Objective: 1.02 Describe various global social issues that are being affected by technology. 34) ________ asks for small donations from a large number of people to fund a business or project. Answer: Crowdfunding; Crowd-funding Diff: 2 Objective: 1.03 Describe how technology is changing how and why we connect and collaborate with others. 35) Using a smartphone app to rent a bike at a kiosk or schedule a ride are examples of ________. Answer: collaborative consumption Diff: 3 Objective: 1.04 Summarize how technology has impacted the way we choose and consume products and services. 36) ________ is obtaining the opinions of many people on the quality of products or services. Answer: Crowdsourcing; Crowd-sourcing Diff: 2 Objective: 1.04 Summarize how technology has impacted the way we choose and consume products and services. 37) ________ means that people have the combination of leisure time and the tools to be creative. Answer: Cognitive surplus Diff: 2 Objective: 1.03 Describe how technology is changing how and why we connect and collaborate with others. 8 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 38) Scanning a product's ________ code with a smartphone can take you to online information and video content. Answer: quick response, QR Diff: 2 Objective: 1.04 Summarize how technology has impacted the way we choose and consume products and services. 39) Skype, Google Hangouts and Facetime are ________ services to make free phone or video conference calls over the Internet. Answer: Voice over IP; VoIP; voice over internet protocol Diff: 1 Objective: 1.04 Summarize how technology has impacted the way we choose and consume products and services. 40) The term ________ literate means being familiar enough with computers to understand their capabilities and limitations and knowing how to use them. Answer: computer Diff: 1 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 41) ________ programs are the instructions that tell the computer what to do. Answer: Software Diff: 1 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 42) Electronic junk mail is known as ________. Answer: spam Diff: 1 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 43) Using data collected at register terminals to determine consumer buying patterns is an example of ________. Answer: data mining Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 44) ________ focuses on creating computer systems which perform tasks that are usually associated with human intelligence. Answer: AI, Artificial Intelligence Diff: 2 Objective: 1.06 Describe artificial intelligence systems and explain their main goals. 9 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 45) ________ is a type of AI system that understands written and spoken words and can interact with humans using language. Answer: NLP, Natural Language Processing, Natural Language Processor, Natural Language Processors Diff: 2 Objective: 1.06 Describe artificial intelligence systems and explain their main goals. 46) ________ analyzes computer systems using techniques to gather legal evidence. Answer: Computer forensics Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 47) ________ computing relates to recognizing and simulating human emotions. Answer: Affective Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 48) ________ enables production of more inexpensive and better fitting prosthetics than traditional manufacturing methods. Answer: 3-D printing; 3D printing Diff: 3 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 49) Understanding your ________ will make it easier to handle situations which require ethical action. Answer: personal ethics Diff: 3 Objective: 1.09 Describe influences on the development of your personal ethics. 50) ________ is the result of someone's creativity and knowledge and usually is protected by copyrights. Answer: Intellectual property, IP Diff: 3 Objective: 1.10 Present examples of how technology creates ethical challenges. 51) A hackathon is a group of people who get together to develop a computer virus. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.01 Describe various technological tools being used to impact national and global issues. 10 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 52) Civic hacking groups like Random Hacks of Kindness use technology to improve humanity. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.01 Describe various technological tools being used to impact national and global issues. 53) Crisis-mapping tools collect and analyze data from social media and create instantly available information to respond to a crisis. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.01 Describe various technological tools being used to impact national and global issues. 54) The digital divide is the difference between careers which depend on technology and those that depend on human intuition and analysis. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 1.02 Describe various global social issues that are being affected by technology. 55) Crowdfunding is asking for large donations from a few people. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.03 Describe how technology is changing how and why we connect and collaborate with others. 56) Car sharing services like Zipcar are examples of individual ownership. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 1.04 Summarize how technology has impacted the way we choose and consume products and services. 57) The AT&T Mark the Spot mobile app enables customers to report locations where there are gaps in service is an example of crowdsourcing. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.04 Summarize how technology has impacted the way we choose and consume products and services. 58) A computer virus is electronic junk mail. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 11 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 59) You cannot be computer literate unless you have knowledge of higher-level computer skills, such as computer programming. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 60) Hardware refers to the programs that give instructions to the computer. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.05 Characterize computer literacy and explain why it is important to be computer literate. 61) Computer vision is that ability for a computer to interpret visual data as humans do. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.06 Describe artificial intelligence systems and explain their main goals. 62) Rules-based AI systems are expert systems which use preprogrammed algorithms to make human-like decisions. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 1.06 Describe artificial intelligence systems and explain their main goals. 63) Affective computing is a field of study focused on the managing, processing, and automatic retrieval of information. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 64) Computer forensics analyzes computer systems to gather potential legal evidence. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 65) Information technology is the study of managing, processing, and retrieving information. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 12 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 66) Examples of information technology careers are telecommunications and software development. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 67) Big Data is generated by how we use technology, today. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 68) The National Center for the Analysis of Violent Crime database enables detectives to analyze information about similarities between crimes. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 69) Data warehousing is the process of searching large datasets to find patterns. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.07 Describe how artificial intelligence and other information technologies are providing career opportunities. 70) Deontology focuses on adherence to moral duties and morals should apply to everyone, equally. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.08 Define ethics and examine various ethical systems. 71) Your personal ethics are NOT influenced by your culture and religion. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.09 Describe influences on the development of your personal ethics. 72) Copyrights govern ownership of real property. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 1.10 Present examples of how technology creates ethical challenges. 13 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 73) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. augmentative reality data mining information technology spam cognitive surplus A. electronic junk mail B. combination of leisure time and the tools to be creative C. combination of our normal sense of the world and digital information D. field of study focusing on the management, processing, and retrieval of information E. searching for patterns within large amounts of data Answer: C, E, D, A, B Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 74) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. computer forensics computer literacy QR code affective computing collaborative consumption A. computing that simulates emotion B. using computer systems to gather legal evidence C. understanding the capabilities and limitations of computers D. hosts a link to online information and video content in printed form E. sharing a service or product rather than owning it outright Answer: B, C, D, A, E Diff: 1 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 14 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 75) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. crowdsourcing crowdfunding digital divide social media crisis-mapping tools A. facilitates exchange of ideas B. gap between those with access to technology and those without C. collect electronic information and instantly make the information publicly available D. solicits small donations from a large number of people E. used by marketers to solicit online consumer input Answer: E, D, B, A, C Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 2 Looking at Computers: Understanding the Parts 1) What is the difference between data and information? A) Data represents a fact. Information is data that has been organized. B) They are essentially the same thing. C) Data is numbers. Information is words. D) Data represents a process. Information is the stored data. Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 2.01 Describe the four main functions of a computer system and how they interact with data and information. 2) Computers use a ________ language consisting of 0s and 1s. A) symbol B) binary C) byte D) system Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 2.02 Define bits and bytes, and describe how they are measured, used, and processed. 3) In binary language, each letter of the alphabet, each number, and each special symbol is made up of a unique combination of eight ________. A) bytes B) kilobytes C) characters D) bits Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 2.02 Define bits and bytes, and describe how they are measured, used, and processed. 15 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 4) Which of the following is the smallest unit of measure? A) Megabyte B) Gigabyte C) Petabyte D) Terabyte Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 2.02 Define bits and bytes, and describe how they are measured, used, and processed. 16 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) Apple's macOS and Microsoft Windows are examples of ________ software. A) utility B) application C) operating system D) communication Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 2.02 Define bits and bytes, and describe how they are measured, used, and processed. 6) An Apple iPad and an Amazon Fire are examples of ________ computers. A) tablet B) netbook C) desktop D) laptop Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 2.03 List common types of computers, and discuss their main features. 7) Which of the following computers is large, expensive, and is designed to execute a few programs as fast as possible? A) Desktop computer B) Supercomputer C) Mainframe computer D) Embedded computer Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 2.03 List common types of computers, and discuss their main features. 8) ________ computers are specially designed computer chips that reside inside other devices, such as a car. A) Tablet B) Desktop C) Embedded D) Netbook Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 2.03 List common types of computers, and discuss their main features. 9) A keyboard and touch screen are the most common of ________ devices. A) output B) processing C) input D) storage Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 2.04 Identify the main types of keyboards and touch screens. 17 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 10) A(n) ________ is an input device that looks like a pen. A) joystick B) e-rod C) pointer D) stylus Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 2.04 Identify the main types of keyboards and touch screens. 11) Each of these is a basic type of a touch screen, EXCEPT ________. A) resistive B) reflective C) capacitive D) surface acoustic wave Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 2.04 Identify the main types of keyboards and touch screens. 12) The number of pixels displayed on the screen is known as ________. A) contrast ratio B) aspect ratio C) brightness resolution D) screen resolution Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 2.07 Describe options for outputting images and audio from computing devices. 13) The most common type of monitor for laptops and desktop computers is a(n) ________. A) liquid crystal display (LCD) B) light-emitting diode (LED) C) organic light-emitting diode (OLED) D) cathode ray tube (CRT) Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 2.07 Describe options for outputting images and audio from computing devices. 14) The two main categories of home and office printers are ________ and laser printers. A) inkjet B) large format C) cloud-based D) thermal Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 2.08 Describe various types of printers, and explain when you would use them. 18 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 15) ________ printers use static electricity, toner, and heat to set an image on a page very quickly. A) Inkjet B) Thermal C) Nonimpact D) Laser Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 2.08 Describe various types of printers, and explain when you would use them. 16) The ________ contains the central electronic components of the computer. A) motherboard B) arithmetic/logic unit C) peripheral unit D) input unit Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 2.09 Describe the functions of the motherboard and RAM. 17) A ________ enables your computer to connect to other computers or to the Internet. A) video card B) network interface card (NIC) C) sound card D) controller card Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 2.09 Describe the functions of the motherboard and RAM. 18) The computer stores currently used programs and data in ________. A) ROM B) CPU C) RAM D) USB Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 2.09 Describe the functions of the motherboard and RAM. 19) RAM is a ________ storage location. A) permanent B) peripheral C) volatile D) nonvolatile Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 2.09 Describe the functions of the motherboard and RAM. 19 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 20) The area that holds all the startup instructions the computer needs to start is ________. A) RAM B) ROM C) USB D) CPU Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 2.09 Describe the functions of the motherboard and RAM. 21) A(n) ________ CPU has two processing paths, allowing it to process more than one instruction at a time. A) all-in-one B) bimodal C) dual-core D) dual-mode Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 2.10 Explain the main functions of the CPU. 22) Which of the following is NOT an example of nonvolatile storage? A) Hard drive B) DVD C) RAM D) Flash drive Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 2.11 Describe the various means of storing data and information with computing devices. 23) Dropbox is an example of ________. A) SSD technology B) cloud storage C) optical storage D) Bluetooth technology Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 2.11 Describe the various means of storing data and information with computing devices. 24) Flash drives plug into a(n) ________. A) USB port B) serial port C) expansion slot D) drive bay Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 2.11 Describe the various means of storing data and information with computing devices. 20 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 25) Which of the following optical storage media has the greatest storage capacity? A) DVD DL B) DVD C) CD D) Blu-ray Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 2.11 Describe the various means of storing data and information with computing devices. 26) Which port is the most common port used to connect input and output devices to a computer? A) Universal serial bus (USB) B) Parallel C) FireWire D) Ethernet Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 2.12 Describe common types of ports used today. 27) To connect a peripheral device to a computer to exchange data, find the appropriate ________ for the device. A) port B) drive C) slot D) expansion bus Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 2.12 Describe common types of ports used today. 28) Which computer port transmits audio and video without the need for compression? A) VGA B) USB C) HDMI D) RGA Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 2.12 Describe common types of ports used today. 21 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 29) Which of the following is NOT a goal of green IT? A) Cleaning waterways with repurposed computers B) Reduce use of electricity C) Use technology to reduce travel D) Use technology as long as possible Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 2.11 Describe the various means of storing data and information with computing devices. 30) All of the following are ways to avoid injuries when working on computers EXCEPT ________. A) placing a monitor at least 12" from the eyes B) purchasing an adjustable chair C) ensuring proper lighting D) taking breaks Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 2.14 Define ergonomics, and discuss the ideal physical setup for using computing devices. 31) The ________ is the biggest power consumer on a computing device. A) display B) hard drive C) memory module D) CPU Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 2.13 Describe how to manage power consumption on computing devices. 32) ________ is concerned with the design and arrangement of machines and furniture to avoid uncomfortable or unsafe experiences. A) Ergonomics B) Positioning C) Occupational safety D) Repetitive strain prevention Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 2.14 Define ergonomics, and discuss the ideal physical setup for using computing devices. 33) ________ is a representation of a fact, a figure, or an idea and can be a number, a word, a picture, or even a recording of sound. Answer: Data Diff: 1 Objective: 2.01 Describe the four main functions of a computer system and how they interact with data and information. 22 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 34) ________ is the set of computer programs that allows the hardware to perform different tasks. Answer: Software Diff: 1 Objective: 2.02 Define bits and bytes, and describe how they are measured, used, and processed. 35) A(n) ________ is a computer that is designed to execute a few programs extremely rapidly. Answer: supercomputer Diff: 2 Objective: 2.03 List common types of computers, and discuss their main features. 36) A(n) ________ device is a component, such as a keyboard, that connects to the computer. Answer: peripheral Diff: 2 Objective: 2.03 List common types of computers, and discuss their main features. 37) A ________ is approximately 1000 bytes. Answer: kilobyte; KB Diff: 3 Objective: 2.02 Define bits and bytes, and describe how they are measured, used, and processed. 38) Microphones and scanners are examples of ________ devices. Answer: input; peripheral Diff: 1 Objective: 2.06 Explain how images, sounds, and sensor data are input into computing devices. 39) ________ is a wireless transmission standard that lets you connect mobile computing devices to peripheral devices over short distances. Answer: Bluetooth; Bluetooth technology; WiFi; wireless; wi-fi; wi fi Diff: 2 Objective: 2.04 Identify the main types of keyboards and touch screens. 40) Display screens that respond to commands initiated with your finger or a stylus are called ________ screens. Answer: touch Diff: 1 Objective: 2.04 Identify the main types of keyboards and touch screens. 41) A desktop computer's ________ is the case that houses the main components of the computer and where peripheral devices connect. Answer: system unit; tower Diff: 2 Objective: 2.03 List common types of computers, and discuss their main features. 23 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 42) The ________ keyboard layout gets its name from the first six letters in the top-left row of alphabetic keys on the keyboard and is the most common English-language keyboard layout. Answer: QWERTY Diff: 2 Objective: 2.04 Identify the main types of keyboards and touch screens. 43) Joysticks and steering wheels are examples of ________ controllers. Answer: game Diff: 1 Objective: 2.05 Describe the main types of mice and pointing devices. 44) A(n) ________ is a small video camera that sits on top of a monitor or is built into a computing device and can be used to transmit live video. Answer: webcam Diff: 2 Objective: 2.06 Explain how images, sounds, and sensor data are input into computing devices. 45) A(n) ________ microphone picks up sounds coming from all directions at once and is well suited for conference calls. Answer: omnidirectional Diff: 3 Objective: 2.06 Explain how images, sounds, and sensor data are input into computing devices. 46) The width-to-height proportion of a monitor is known as the ________. Answer: aspect ratio Diff: 2 Objective: 2.07 Describe options for outputting images and audio from computing devices. 47) Monitors display images by using a grid made up of millions of tiny dots, called ________. Answer: pixels Diff: 2 Objective: 2.07 Describe options for outputting images and audio from computing devices. 48) The length of time it takes for a processor to request, locate, open and deliver information stored in RAM is measured in ________. Answer: nanoseconds; billionths of a second Diff: 2 Objective: 2.09 Describe the functions of the motherboard and RAM. 49) Each pixel on the newest 4K resolution TVs and monitors is actually made up of four yellow, red, blue, and green ________. Answer: subpixels; sub pixels; sub-pixels Diff: 3 Objective: 2.07 Describe options for outputting images and audio from computing devices. 24 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 50) A(n) ________ is a device that combines the functions of a printer, scanner, copier, and fax machine into one unit. Answer: all-in-one printer; all in one printer Diff: 2 Objective: 2.08 Describe various types of printers, and explain when you would use them. 51) The "brains" of the computer is the ________. Answer: CPU; central processing unit; processor; microprocessor Diff: 2 Objective: 2.10 Explain the main functions of the CPU. 52) An SD card is an example of a(n) ________ card. Answer: flash memory; memory; secure digital Diff: 2 Objective: 2.11 Describe the various means of storing data and information with computing devices. 53) CDs, DVDs, and ________ discs are examples of optical storage. Answer: Blu-ray; BD; bluray Diff: 2 Objective: 2.11 Describe the various means of storing data and information with computing devices. 54) ________ is a technology most frequently used for credit and debit card processing Answer: Near field communication; NFC Diff: 2 Objective: 2.07 Describe options for outputting images and audio from computing devices. 55) ________ mode puts the computer in low power usage, but keeps programs in RAM. Answer: Sleep Diff: 2 Objective: 2.13 Describe how to manage power consumption on computing devices. 56) ________ is a power-saving mode that stores data to a computer's hard drive instead of to its memory. Answer: Hibernate Diff: 2 Objective: 2.13 Describe how to manage power consumption on computing devices. 57) Information is data that has been organized or presented in a meaningful fashion. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 2.01 Describe the four main functions of a computer system and how they interact with data and information. 25 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 58) A smartphone is a type of computer. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 2.03 List common types of computers, and discuss their main features. 59) The operating system controls how your computer functions. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 2.02 Define bits and bytes, and describe how they are measured, used, and processed. 60) The terms data and information can be used interchangeably. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 2.01 Describe the four main functions of a computer system and how they interact with data and information. 61) Processing is manipulating, calculating, or organizing data into information. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 2.01 Describe the four main functions of a computer system and how they interact with data and information. 62) On a keyboard, Num Lock and Caps Lock are both toggle keys. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 2.04 Identify the main types of keyboards and touch screens. 63) Laser printers are usually faster at printing in black and white than inkjet printers. Answer: TRUE Diff: 3 Objective: 2.08 Describe various types of printers, and explain when you would use them. 64) All printers can print from smartphones and tablets. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Objective: 2.08 Describe various types of printers, and explain when you would use them. 65) Game controllers are output devices. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 2.05 Describe the main types of mice and pointing devices. 66) Keyboards that display on-screen when text input is required are known as virtual keyboards. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 2.04 Identify the main types of keyboards and touch screens. 26 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 67) Starting a computer when it is powered off is called a warm boot. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 2.13 Describe how to manage power consumption on computing devices. 68) The area that holds all of the instructions the computer needs to start up is called RAM. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 2.09 Describe the functions of the motherboard and RAM. 69) Today's CPUs run at speeds measured in kilohertz. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 2.10 Explain the main functions of the CPU. 70) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. CPU OLED QWERTY ROM RAM A. holds start up instructions needed when the computer is powered on B. standard keyboard layout C. processes commands issued by software instructions D. more energy efficient than LCD monitors E. stores programs and data the computer is currently using Answer: C, D, B, A, E Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 27 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 71) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. data processing information software hardware A. represents a fact, figure, or idea B. data organized in a meaningful way C. physical components of a computer D. turning data into information E. computer programs Answer: A, D, B, E, C Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 72) Rank the following from smallest capacity to largest capacity: I. II. III. IV. V. terabyte gigabyte kilobyte megabyte petabyte A. largest B. second largest C. third largest D. fourth largest E. fifth largest Answer: B, C, E, D, A Diff: 2 Objective: 2.02 Define bits and bytes, and describe how they are measured, used, and processed. 28 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 73) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. input device peripheral device output device motherboard system unit A. case that houses the electronic components, power source, and storage devices of a desktop computer B. main circuit board containing the central electronic components of a computer C. used to enter data D. external device that exchanges data with the computer through ports E. displays processed data Answer: C, D, E, B, A Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 74) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. pixel hertz bit ppm dpi A. measurement of printing speed B. unit of measure for processor speed C. tiny dot that creates an image on the computer monitor D. measurement of printer resolution E. 0 or 1 Answer: C, B, E, A, D Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 3 Using the Internet: Making the Most of the Web's Resources 1) The Internet is ________. A) an internal communication system for businesses B) a communication system for the U.S. navy C) the same as the web D) a large network of networks Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 3.01 Describe how the Internet got its start. 2) The concept of the Internet was developed by the U.S. Department of Defense as a network 29 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 that ________ in event of an attack. A) provides point to point connections B) allows commerce to continue C) would not be disrupted easily D) would not be easily hacked Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 3.01 Describe how the Internet got its start. 3) The World Wide Web was based on a protocol developed by ________. A) CERN B) Ray Tomlinson C) Tim Berners-Lee D) Vinton Cerf Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 3.01 Describe how the Internet got its start. 4) The "fathers of the Internet" are Vinton Cerf and ________. A) Robert Cailliau B) Tim Berners-Lee C) Bill Gates D) Robert Kahn Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 3.01 Describe how the Internet got its start. 30 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) Software that enables you to display and interact with text and other media on the web is a web ________. A) client B) server C) agent D) browser Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 3.01 Describe how the Internet got its start. 6) The web is based on the ________ Protocol. A) Hypertext Transfer B) Hypertext Trade C) Hypertext Transmit D) Hypertext Translate Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 3.01 Describe how the Internet got its start. 7) A computer connected to the Internet that asks for data is a(n) ________. A) server B) client C) surrogate D) aggregator Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 3.02 Explain how data travels on the Internet. 8) The unique identification number assigned to your computer when you connect to the Internet is known as all of the following EXCEPT a(n) ________. A) dotted quad B) path C) dotted decimal D) IP address Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 3.02 Explain how data travels on the Internet. 9) ________ is a professional, business-oriented social networking site. A) Flickr B) Pinterest C) Twitter D) LinkedIn Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 31 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 10) Which of the following is NOT a social networking site? A) Facebook B) YouTube C) LinkedIn D) iTunes Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 11) A ________ allows users to add, remove, or edit its content. A) wiki B) podcast C) blog D) chat Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 12) Which of the following are personal video journal entries posted on the web? A) Podcasts B) Newsgroups C) Vlogs D) Blogs Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 13) A(n) ________ is usually a live broadcast of audio or video content. A) podcast B) wiki C) instant message D) webcast Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 14) A ________ is a personal journal posted on the web. A) blog B) podcast C) wiki D) webcast Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 32 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 15) Podcasts enable you to ________. A) deliver audio/video files via RSS B) post journal entries on the web C) communicate with friends in real time D) edit video files over the web Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 16) All of the following are tips for professional e-mail etiquette EXCEPT ________. A) be concise and to the point B) use spell-checker and proofread before sending C) use abbreviations such as "u," "r," and "BRB" to keep the e-mail message shorter D) include a meaningful subject line Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 3.04 Summarize the technologies used to communicate over the web. 17) Which of the following is a universal instant messaging service? A) Skype B) WhatsApp C) Google Hangouts D) Yahoo! Messenger Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 3.04 Summarize the technologies used to communicate over the web. 18) ________ is installed on your computer, and when the program is opened, your e-mail downloads to your computer. A) Web-based e-mail program B) E-mail client software C) E-mail host package D) E-mail server Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 3.04 Summarize the technologies used to communicate over the web. 19) All of the following are types of e-commerce business EXCEPT ________. A) B2C B) B2B C) C2C D) C2B Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 3.05 Describe how business is conducted using the Internet. 33 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 20) Microsoft ________ is a cloud storage and file sharing service. A) iCloud B) Dropbox C) OneDrive D) Drive Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 3.05 Describe how business is conducted using the Internet. 21) A subset of e-commerce that uses social networks to assist in marketing and purchasing products is known as ________ commerce. A) crowd B) source C) friend D) social Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 3.05 Describe how business is conducted using the Internet. 22) Which of the following is NOT a precaution to take when shopping online? A) Pay with a debit card, not a credit card. B) Shop at well-known, reputable sites. C) Avoid making online transactions on a public computer. D) When placing an order, make sure you receive a confirmation number. Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 3.06 Summarize precautions you should take when doing business online. 23) The "s" in "https" stands for ________ socket layer. A) semantic B) secure C) server D) social Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 3.06 Summarize precautions you should take when doing business online. 24) Which of the following is NOT a feature of the most popular web browsers? A) Pinned tabs B) Session restore C) Tacked browsing D) Thumbnail preview Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 3.07 Explain what web browsers are, and describe their common features. 34 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 25) The browser feature which enables tabs to work independently from one another so if one crashes, the others may continue to work is known as ________. A) pinned tabs B) tab isolation C) free tabs D) privacy browsing Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 3.07 Explain what web browsers are, and describe their common features. 26) The unique address for a particular website is the ________. A) protocol B) domain section C) client D) URL Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 3.08 Explain what a URL is, and discuss its main parts. 27) In the URL: http://www.microsoft.com/surface, the portion labeled ".com" is the ________. A) subdirectory B) host C) top-level domain D) protocol Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 3.08 Explain what a URL is, and discuss its main parts. 28) In the URL: http://www.microsoft.com/surface, the portion labeled "surface" is the ________. A) protocol B) domain name C) subdirectory D) top-level domain Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 3.08 Explain what a URL is, and discuss its main parts. 29) In the URL: http://www.microsoft.com/surface, the portion labeled "http" is the ________. A) protocol B) domain name C) path D) top-level domain Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 3.08 Explain what a URL is, and discuss its main parts. 35 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 30) Which of the following top-level domains identifies a degree-granting institution? A) .gov B) .net C) .edu D) .info Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 3.08 Explain what a URL is, and discuss its main parts. 31) A(n) ________ is a navigation aid that shows the path you have taken to get to a web page or where the page is located within the website. A) index B) navigation bar C) breadcrumb trail D) cookie trail Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 3.09 Describe tools used to navigate the web. 32) AND, OR, and NOT are examples of ________ operators. A) Boolean B) Jacobean C) relational D) keyword Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 3.10 Describe the types of tools used to search the web, and summarize strategies used to refine search results. 33) Which of the following is a supporting argument for geolocation devices posing a threat to privacy? A) Businesses are responsible to educate consumers about how they use geolocation data. B) The social norm has shifted and people have become comfortable with sharing more information, including their location. C) Many businesses incorporate geolocation as a primary marketing strategy; the loss of privacy is outweighed by the benefit to consumers. D) Society may need to reevaluate its expectations as to the amount of privacy in people's digital lives. Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 3.13 Demonstrate an understanding of the ethical issues regarding location tracking applications and devices. 36 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 34) Catfishing is ________. A) creating fake profiles on a dating site and developing a fabricated online and phone relationship B) posting inflammatory remarks to solicit angry and negative responses C) bombarding someone with harassing messages D) posting embarrassing pictures, rumors, or videos via social media Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 3.13 Demonstrate an understanding of the ethical issues regarding location tracking applications and devices. 35) An Internet connected computer that receives a request and returns data is a(n) ________. Answer: server Diff: 2 Objective: 3.02 Explain how data travels on the Internet. 36) Facebook and Twitter are popular examples of ________ networks. Answer: social Diff: 1 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 37) E-mail is ________ communication, which means users do not have to communicate at the same time. Answer: asynchronous Diff: 2 Objective: 3.04 Summarize the technologies used to communicate over the web. 38) ________ e-mail is managed by a browser and enables access to e-mail from anywhere that has Internet access. Answer: Web-based, web based, webbased Diff: 1 Objective: 3.04 Summarize the technologies used to communicate over the web. 39) E-mail ________ are software programs such as Microsoft Outlook that run on your computer and download messages to your computer. Answer: clients Diff: 2 Objective: 3.04 Summarize the technologies used to communicate over the web. 40) Feedspot and iTunes are examples of RSS ________ which locate and download RSS series to which you have subscribed. Answer: aggregators Diff: 3 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 37 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 41) A(n) ________ consists of a series of audio or video content that are distributed over the Internet. Answer: podcast; webcast Diff: 2 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 42) A(n) ________ is usually a live broadcast of audio and video content over the Internet. Answer: webcast Diff: 2 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 43) ________ describes the use of hashtags and posts to raise awareness and foster discussion about specific issues and causes via social media. Answer: Digital activism Diff: 2 Objective: 3.12 Demonstrate an understanding of the ethical issues regarding digital activism. 44) A web browser's ________ feature makes it easy to return to a specific web page. Answer: Favorites; Bookmarks Diff: 2 Objective: 3.09 Describe tools used to navigate the web. 45) The top-level domain suffix used by not-for-profit groups such as the American Diabetes Association is ________. Answer: .org Diff: 3 Objective: 3.08 Explain what a URL is, and discuss its main parts. 46) ________ refers to storing data, files, and applications on the web and being able to access and manipulate these files and applications from any Internet-connected device. Answer: Cloud computing Diff: 1 Objective: 3.05 Describe how business is conducted using the Internet. 47) In B2B commerce, businesses buy and sell goods and services with ________. Answer: businesses Diff: 2 Objective: 3.05 Describe how business is conducted using the Internet. 48) URL stands for ________. Answer: Uniform Resource Locator Diff: 1 Objective: 3.08 Explain what a URL is, and discuss its main parts. 38 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 49) .jp, .ca, .de, and .uk are examples of ________. Answer: top-level domains; country codes; country specific domains; country-specific domains; top level domains Diff: 2 Objective: 3.08 Explain what a URL is, and discuss its main parts. 50) The ________ list shows all of the websites and pages you have visited over a certain period of time. Answer: history Diff: 2 Objective: 3.09 Describe tools used to navigate the web. 51) Another term for social bookmarking is ________. Answer: tagging Diff: 2 Objective: 3.09 Describe tools used to navigate the web. 52) When performing searches, the asterisk (*) is used as a(n) ________. Answer: wild card; wildcard Diff: 3 Objective: 3.10 Describe the types of tools used to search the web, and summarize strategies used to refine search results. 53) The Internet was developed to ensure faster delivery of communications such as e-mail. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 3.01 Describe how the Internet got its start. 54) All popular social networking sites have privacy policies, but you still need to follow certain precautions when using their sites. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. 55) E-mails are completely private. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 3.04 Summarize the technologies used to communicate over the web. 56) With a client-based e-mail account, you are able to view your e-mail only from the computer on which the client program is installed. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.04 Summarize the technologies used to communicate over the web. 39 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 57) A universal chat client enables you to chat with users who use a different IM service than you use. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.04 Summarize the technologies used to communicate over the web. 58) When shopping on the web, it is better to pay for your purchase with a debit card rather than a credit card. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.06 Summarize precautions you should take when doing business online. 59) A browser's bookmark feature makes it easy to return to a specific web page. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 3.09 Describe tools used to navigate the web. 60) Using the browser feature called tab isolation, you can drag an open tab away from its current window and open it in a new window. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.07 Explain what web browsers are, and describe their common features. 61) The semantic web uses metadata with text data to make it more easily processed by computers. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 3.11 Describe how to evaluate a website to ensure it is appropriate to use for research purposes. 62) Wikipedia is a good reference for a research paper. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.11 Describe how to evaluate a website to ensure it is appropriate to use for research purposes. 63) When evaluating the relevance of a website, it is important to evaluate the date of publication. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.11 Describe how to evaluate a website to ensure it is appropriate to use for research purposes. 64) A criticism of hashtag activism is that it fosters a false sense of involvement. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.12 Demonstrate an understanding of the ethical issues regarding digital activism. 40 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 65) Geolocation is a GPS enabled feature on a smartphone that provides your location to apps like Uber. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.13 Demonstrate an understanding of the ethical issues regarding location tracking applications and devices. 66) One method of cyberbullying involves spreading rumors about another person. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.13 Demonstrate an understanding of the ethical issues regarding location tracking applications and devices. 67) A metasearch engine searches other search engines instead of individual websites. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.10 Describe the types of tools used to search the web, and summarize strategies used to refine search results. 68) Cyberbullying is essentially the same thing as cyberstalking, but the parties involved in cyber bullying are children or adolescents. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.13 Demonstrate an understanding of the ethical issues regarding location tracking applications and devices. 69) There are federal laws against cyberstalking. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.13 Demonstrate an understanding of the ethical issues regarding location tracking applications and devices. 70) Websites selling a product are often the most accurate and appropriate for research. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.11 Describe how to evaluate a website to ensure it is appropriate to use for research purposes. 71) Current search engines function by recognizing keywords. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 3.10 Describe the types of tools used to search the web, and summarize strategies used to refine search results. 41 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 72) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. browser Internet search engine host e-mail A. large network of networks B. tool used to locate information on the web C. location that maintains the computers that store the website files D. application program used to view the web E. asynchronous electronic communication Answer: D, A, B, C, E Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 73) Match each of the following domains to the site that would use it: I. II. III. IV. V. .com .gov .edu .ca .org A. White House B. Red Cross C. Stanford University D. Apple E. Ontario Government Answer: D, A, C, E, B Diff: 3 Objective: 3.08 Explain what a URL is, and discuss its main parts. 42 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 74) Match each of the following browsers to a defining feature of it: I. II. III. IV. V. Firefox Safari Mosaic Microsoft Edge Chrome A. Apple's web browser B. the first browser to display graphics as well as text C. available only for Windows 10 D. runs on any platform E. open source Answer: E, A, B, C, D Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 75) Match each of the following terms to a definition of it: I. II. III. IV. V. HTTP C2C FTP B2C URL A. protocol that allows files to be transferred from a web server B. transactions between two individuals C. transactions between a company and its customers D. website address E. protocol that allows files to be transferred over the Internet Answer: E, B, A, C, D Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 43 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 76) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. IM podcast blog webcast wiki A. personal journal posted on the web B. program that enables you to communicate in real time with others online C. uses RSS to deliver an audio or video file D. live streamed broadcast E. website that allows site visitors to change its content Answer: B, C, A, D, E Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 77) Match each of the following social networking sites to its specialty: I. II. III. IV. V. Facebook Pinterest LinkedIn Uber PayPal A. Social Commerce B. Social Travel C. Social Communication D. Business Networking E. Media Sharing Answer: C, E, D, B, A Diff: 2 Objective: 3.03 Evaluate the tools and technologies used to collaborate on the web. Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 4 Application Software: Programs That Let You Work and Play 1) ________ software helps run the computer and coordinates instructions between other software and the hardware devices. A) Application B) Recovery C) Productivity D) System Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 4.01 Compare application software and system software. 2) ________ applications are software in which the vendor hosts the software online over the 44 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 Internet and you do not to install the software on your computer. A) Open Source as a Service B) Platform as a Service C) Software as a Service D) Infrastructure as a Service Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 4.02 Explain the differences between commercial software and open source software, and describe models for software distribution. 3) Using applications on smartphones and tablets to buy and sell products is known as ________ commerce. A) smart B) remote C) mobile D) web Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 4.03 Explain the different options for purchasing software. 4) Which of these is NOT a factor to consider when upgrading software? A) What patches are applied to your current version? B) Do you use the software frequently enough? C) Is the new upgrade stable? D) Is the upgrade sufficiently different? Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 4.05 Explain the considerations around the decision to upgrade your software. 45 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) LibreOffice is an example of a(n) ________ productivity software package. A) open source B) system C) online D) proprietary Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 6) Which of the following is NOT a type of a productivity software application? A) Image editing B) Word processing C) Personal information management D) Spreadsheet Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 7) Which is TRUE about web-based application software? A) It is always free. B) It is installed by the computer manufacturer. C) It is stored completely on a web server instead of your hard drive. D) It does not need an Internet connection. Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 8) The appropriate software to use for writing and editing research papers is ________ software. A) spreadsheet B) presentation C) word processing D) database Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 46 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 9) ________ software lets you perform calculations and numerical analyses. A) Presentation B) Personal information manager C) Word processing D) Spreadsheet Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 10) When using a spreadsheet, the expression =D8-D17 is called a ________. A) function B) range C) formula D) cell Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 11) When using a spreadsheet, SUM in the expression =SUM(B10:B16), is called a(n) ________. A) function B) operator C) formula D) operand Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 12) The box formed by the intersection of a row and column in a spreadsheet program is known as a ________. A) label B) formula C) function D) cell Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 47 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 13) All of the following are tips for a great presentation EXCEPT ________. A) limit bullet points per slide to 4-6 B) use images to convey a thought or illustrate a point C) use a variety of animations on most slides to keep your audience's attention D) keep the font size large enough to be read from the back of the room Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 14) In databases, a data category is called a ________. A) table B) record C) worksheet D) field Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 15) All of the following are examples of database software EXCEPT ________. A) Oracle B) OneNote C) MySQL D) Microsoft Access Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 16) ________ software helps you manage e-mail, contacts, calendars, and tasks in the same application. A) Note-taking B) Personal information manager C) Spreadsheet D) Presentation Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 48 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 17) Adobe InDesign is an example of ________ software. A) image-editing B) presentation C) desktop publishing D) video-editing Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 4.08 Summarize the types of software that large and small businesses use. 18) QuickBooks is an example of ________ software. A) educational B) accounting C) course management D) gaming Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 4.08 Summarize the types of software that large and small businesses use. 19) Dreamweaver is an example of ________ software. A) desktop publishing B) accounting C) course management D) web authoring Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 4.08 Summarize the types of software that large and small businesses use. 20) Software that manages "back office" functions such as billing, production, inventory management, and human resources management is called ________ software. A) accounting B) enterprise resource planning C) project management D) customer relationship management Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 4.08 Summarize the types of software that large and small businesses use. 21) All of the following are types of multimedia and educational software EXCEPT ________. A) digital audio editing software B) digital video editing software C) drawing software D) productivity software Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 4.09 Describe the uses and features of digital multimedia software. 49 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 22) Computer-aided design software is used by ________. A) architects and engineers to create virtual models B) web designers to create websites C) project managers to track tasks D) game makers to create games Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 4.08 Summarize the types of software that large and small businesses use. 23) Software designed specifically for managing real estate is an example of ________ software. A) e-commerce B) general business C) project management D) vertical market Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 4.08 Summarize the types of software that large and small businesses use. 24) Multimedia software includes all of the following EXCEPT ________. A) image-editing software B) animation software C) utility software D) audio-editing software Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 4.09 Describe the uses and features of digital multimedia software. 25) To remove red eye from a digital image, you would use software such as ________. A) Adobe Photoshop B) Adobe Acrobat C) Microsoft PowerPoint D) Apple Keynote Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 4.09 Describe the uses and features of digital multimedia software. 26) Which of the following is the most common audio compression format? A) WAV B) AU C) MP3 D) WMA Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 4.10 Describe the uses and features of digital audio software. 50 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 27) Blackboard is an example of ________ software. A) utility B) drawing C) course management D) gaming Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 4.12 Categorize educational and reference software and explain their features. 28) A(n) ________ software installation copies all the most commonly used files to your computer's hard drive. A) full B) upgrade C) custom D) beta Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 4.04 Describe how to install and uninstall software. 29) A(n) ________ software installation enables you to decide which features you want to install on the hard drive. A) full B) partial C) custom D) upgrade Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 4.04 Describe how to install and uninstall software. 30) Unwanted or unneeded software included by manufacturers on new computers is called ________. A) adware B) bloatware C) malware D) shareware Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 4.04 Describe how to install and uninstall software. 31) Microsoft Office Online is an example of a(n) ________ productivity packages. Answer: web-based; web based; online; on-line Diff: 3 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 51 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 32) The two main types of software are system software and ________ software. Answer: application Diff: 1 Objective: 4.01 Compare application software and system software. 33) Another name for commercial software is ________ software. Answer: proprietary Diff: 2 Objective: 4.02 Explain the differences between commercial software and open source software, and describe models for software distribution. 34) Apple iWork Pages is an example of ________ software which is used to create documents such as résumés, letters and research papers. Answer: word processing; word-processing Diff: 1 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 35) Writer is the ________ program in LibreOffice package. Answer: word processing; word-processing Diff: 1 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 36) iWork is the ________ package made especially for Apple computers. Answer: productivity; proprietary Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 37) Automatic ________ lets you immediately see the effects of changing values in your spreadsheet. Answer: recalculation Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 38) Microsoft Excel is a(n) ________ software program. Answer: spreadsheet Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 39) Spreadsheet equations that use functions are called ________. Answer: formulas Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 52 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 40) To organize and query large, complicated groups of data, you should use ________ software. Answer: database Diff: 1 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 41) In traditional databases, data is organized into fields, records, and ________. Answer: tables Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 42) In a database, a group of related fields is a(n) ________. Answer: record Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 43) In a database, a group of related records is a(n) ________. Answer: table Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 44) You would use ________ software to create a slide show. Answer: presentation Diff: 1 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 45) In most productivity software packages, a(n) ________ guides you through the steps necessary to finish a complicated task. Answer: wizard Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 46) In most productivity software packages, ________ are predefined forms that include specific designs, special formatting, and styles relevant to a particular document. Answer: templates Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 53 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 47) You could use a(n) ________ to combine a series of commands so that they will run as a single command in most productivity software packages. Answer: macro Diff: 3 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 48) Software that helps manage a checkbook or prepare taxes is called ________ software. Answer: financial planning; personal finance; personal financial planning; tax preparation Diff: 1 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 49) ________ software includes image-editing, video-editing, and audio-editing software. Answer: Multimedia Diff: 2 Objective: 4.09 Describe the uses and features of digital multimedia software. 50) ________ programs allow you to experience a real situation through a virtual environment. Answer: Simulation; Training; Simulated training Diff: 2 Objective: 4.12 Categorize educational and reference software and explain their features. 51) Drawing software is also known as ________ software. Answer: illustration Diff: 2 Objective: 4.09 Describe the uses and features of digital multimedia software. 52) A(n) ________ version is a software application that is still under development. Answer: beta Diff: 2 Objective: 4.03 Explain the different options for purchasing software. 53) If you make more copies of software than your license permits, you are committing software ________. Answer: piracy Diff: 1 Objective: 4.06 Explain how software licenses function. 54) Before installing any software, it's always important to back up your system and to create a(n) ________, which enables you to go back to your computer's previous settings if anything goes wrong during a new software installation. Answer: restore point Diff: 2 Objective: 4.04 Describe how to install and uninstall software. 54 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 55) EULA stands for ________. Answer: End User License Agreement Diff: 3 Objective: 4.06 Explain how software licenses function. 56) To create an app for a mobile device yourself, you would use ________ software like Swift, Corona or Scratch. Answer: app creation Diff: 2 Objective: 4.11 Describe the features of app creation software. 57) Application software helps run the computer and coordinates instructions with the hardware. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 4.01 Compare application software and system software. 58) Software as a Service (SaaS) hosts online applications. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.02 Explain the differences between commercial software and open source software, and describe models for software distribution. 59) All online word processing applications are as fully featured as installed versions. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.02 Explain the differences between commercial software and open source software, and describe models for software distribution. 60) LibreOffice is an example of open source software. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 61) All files created by newer versions of software are readable by older versions. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 4.05 Explain the considerations around the decision to upgrade your software. 62) Most word processing programs come with a find-and-replace tool that enables you to locate and replace specific text. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 55 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 63) In a database, a table can be defined as a data category. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 64) You can use PowerPoint to trim video clips without having to use a separate video-editing program. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 65) A CD stores the same number of songs in uncompressed format as in MP3 format. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.10 Describe the uses and features of digital audio software. 66) An installation wizard walks you through completing a complicated tasks during software installation. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.07 Categorize the types of application software used to enhance productivity, and describe their uses and features. 67) Blackboard is an example of gaming software. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.12 Categorize educational and reference software and explain their features. 68) Programmers create all apps using high end Software Development Kits like Corona SDK. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.11 Describe the features of app creation software. 69) Adobe Photoshop is a drawing software application used by graphic artists. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.09 Describe the uses and features of digital multimedia software. 70) Desktop publishing software enables you to create newsletters and annual reports. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.08 Summarize the types of software that large and small businesses use. 56 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 71) A full software installation enables you to choose which program features you want installed on your hard drive. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 4.04 Describe how to install and uninstall software. 72) Match each of the following software categories to its purpose: I. II. III. IV. V. computer-aided design course management desktop publishing tax preparation image-editing A. to design buildings B. modifying pictures C. to create newsletters D. used in personal finance E. used by instructors and students Answer: A, E, C, D, B Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 73) Match each of the following software categories to its purpose: I. II. III. IV. V. vertical market software application software commercial software software suite system software A. bundled group of software programs B. runs the computer C. another term for proprietary software D. designed for a specific industry E. used to perform tasks Answer: D, E, C, A, B Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 57 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 74) Match each of the following software categories to its primary use: I. II. III. IV. V. entertainment enterprise resource planning database video-editing word processing A. manage back end business functions B. write and edit documents C. play games D. edit movies E. keep track of clients Answer: C, A, E, D, B Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 75) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. web-based open source project management personal information manager proprietary A. software used to keep track of appointments B. software that is hosted on a website C. software used to track tasks and coordinate resources D. software which must be purchased E. software code that is freely available Answer: B, E, C, A, D Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 5 System Software: The Operating System, Utility Programs, and File Management 1) The two major types of system software programs are utility programs and the ________. A) supervisor programs B) application software C) user interface D) operating system Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 5.01 Discuss the functions of the operating system. 2) The ________ of the operating system enables users to communicate with the computer 58 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 system. A) window B) modem C) network adapter card D) user interface Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 5.01 Discuss the functions of the operating system. 3) MacOS is the operating system developed by ________. A) Apple B) Microsoft C) Google D) Linux Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 5.01 Discuss the functions of the operating system. 4) Which of the following two operating systems are used most frequently on tablets? A) Windows and iOS B) Windows and Android C) Android and iOS D) BlackBerry and Windows Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 5.02 Explain the most common operating systems for personal use. 5) Most smartphones use operating systems developed by ________. A) Google and Apple B) Apple and Microsoft C) Microsoft and Google D) Symbian and Apple Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 5.02 Explain the most common operating systems for personal use. 6) Which of the following is a proprietary OS for desktop and laptop computers? A) Windows B) iOS C) Android D) Linux Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 5.02 Explain the most common operating systems for personal use. 7) All of the following are examples of network operating systems EXCEPT ________. A) Windows 10 B) Linux 59 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 C) macOS D) MS-DOS Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 5.03 Explain the different kinds of operating systems for machines, networks, and business. 8) Which of the following is NOT a capability of UNIX? A) It is multiuser. B) It is multitasking. C) It is a network OS. D) It is only for supercomputers. Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 5.03 Explain the different kinds of operating systems for machines, networks, and business. 9) Most supercomputers use the ________ operating system. A) UNIX B) Linux C) Windows D) iOS Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 5.03 Explain the different kinds of operating systems for machines, networks, and business. 10) Which of the following is the online storage system affiliated with a Microsoft account? A) iCloud B) Chrome C) OneDrive D) iOS Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 5.02 Explain the most common operating systems for personal use. 60 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 11) Which of the following is NOT a type of user interface? A) Command-driven B) Application programming interface (API) C) Menu-driven D) Graphical user interface (GUI) Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 5.04 Explain how the operating system provides a means for users to interact with the computer. 12) Using hard disk space to temporarily store data or instructions from RAM is referred to as the ________. A) spool B) interrupt sequencer C) compressor D) virtual memory Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 5.05 Explain how the operating system helps manage hardware such as the processor, memory, storage, and peripheral devices. 13) An application programming interface (API) is ________. A) the code the application software needs in order to interact with the CPU B) the code to interface between an application and a peripheral like a printer C) the currently active part of an application D) the code to interface between an application and RAM Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 5.06 Explain how the operating system interacts with application software. 14) Each device attached to your computer has a special program called a(n) ________ that enables the device and operating system to communicate with each other. A) device driver B) translator C) interpreter D) device configurator Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 5.05 Explain how the operating system helps manage hardware such as the processor, memory, storage, and peripheral devices. 61 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 15) Which of the following is the first step in the boot process? A) The BIOS is activated. B) The BIOS checks that all devices are operational. C) The OS is loaded into RAM. D) Configuration and customization settings are checked. Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 5.07 Discuss the process the operating system uses to start up the computer and how errors in the boot process are handled. 16) The basic input/output system (BIOS) is stored on a ________ chip. A) ROM B) CPU C) RAM D) CMOS Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 5.07 Discuss the process the operating system uses to start up the computer and how errors in the boot process are handled. 17) All of the following are terms related to part of the boot process EXCEPT ________. A) ROM B) CMOS C) RAM D) USB Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 5.07 Discuss the process the operating system uses to start up the computer and how errors in the boot process are handled. 18) C: denotes a(n) ________ directory that is at the top of the filing structure of a computer. A) sub B) cluster C) root D) domain Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 19) When using Windows File Explorer, which view provides the most information at a glance? A) List B) Content C) Tiles D) Details Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and 62 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 manages files and folders. 20) The location of a file is specified by its ________. A) domain B) file path C) file type D) file extension Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 21) C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\protocol is an example of a file ________. A) extension B) type C) path D) list Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 22) Which of the following is the name of a Microsoft Excel file? A) inventory.xlsx B) inventory.wpd C) inventory.accdb D) inventory.pdf Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 23) Deleted files on a Mac computer are moved to the ________. A) Garbage Can B) Recycle Bin C) Trash D) Wastepaper Basket Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 63 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 24) Which of the following Windows utility programs arranges pieces of files on your hard drive to allow for faster access? A) Disk Cleanup B) Defragment and Optimize Drives C) Error-checking D) Task Manager Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 25) Which of the following is NOT a Windows utility program? A) Disk Cleanup B) Desktop Cleanup C) Defragment and Optimize Drives D) System Restore Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 26) Which utility temporarily removes redundancies in a file to reduce the file size? A) Disk Cleanup B) File Compression C) Error-checking D) Defragment and Optimize Drives Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 27) Use the Windows ________ to check on a nonresponsive program. A) System Restore B) Backup utility C) Error-checking D) Task Manager Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 64 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 28) The ________ utility automatically creates duplicates of your libraries, desktops, contacts, and favorites to another storage location. A) System Restore B) Time Capsules C) File History D) Carbonite Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 29) The ________ is a group of programs that controls how your computer functions. Answer: operating system; OS Diff: 1 Objective: 5.01 Discuss the functions of the operating system. 30) iOS was developed by ________ as the operating system for its tablets and smartphones. Answer: Apple Diff: 1 Objective: 5.01 Discuss the functions of the operating system. 31) The fuel-injection system in a car engine uses a(n) ________. Answer: real-time operating system; real time operating system; RTOS; Embedded system Diff: 2 Objective: 5.03 Explain the different kinds of operating systems for machines, networks, and business. 32) Most supercomputers use the ________ operating system. Answer: Linux Diff: 3 Objective: 5.03 Explain the different kinds of operating systems for machines, networks, and business. 33) The vast majority of smartphones use the ________ or ________ operating systems. Answer: Android, iOS; iOS, Android Diff: 3 Objective: 5.02 Explain the most common operating systems for personal use. 34) Linux download packages are called distributions or ________. Answer: distros Diff: 3 Objective: 5.02 Explain the most common operating systems for personal use. 35) MS-DOS used a(n) ________ interface. Answer: command-driven; command driven Diff: 1 Objective: 5.04 Explain how the operating system provides a means for users to interact with the computer. 65 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 36) A unique signal by a device to let the operating system know that it needs attention is called a(n) ________. Answer: interrupt Diff: 2 Objective: 5.05 Explain how the operating system helps manage hardware such as the processor, memory, storage, and peripheral devices. 37) If your computer is thrashing, increase ________ to solve the problem. Answer: RAM; Random-Access Memory; Random Access Memory Diff: 2 Objective: 5.05 Explain how the operating system helps manage hardware such as the processor, memory, storage, and peripheral devices. 38) ________is the feature that enables you to use a new device without first installing a device driver. Answer: Plug and Play; PnP Diff: 2 Objective: 5.05 Explain how the operating system helps manage hardware such as the processor, memory, storage, and peripheral devices. 39) The Windows feature that removes a newly installed, improperly working driver and replaces it with the last one that worked is called ________. Answer: Roll Back Driver Diff: 2 Objective: 5.05 Explain how the operating system helps manage hardware such as the processor, memory, storage, and peripheral devices. 40) During the boot process, the ________ is responsible for loading the operating system from the hard drive into RAM. Answer: BIOS; basic input/output system; basic input output system Diff: 2 Objective: 5.07 Discuss the process the operating system uses to start up the computer and how errors in the boot process are handled. 41) Natural language processing is a field of ________that uses software to analyze, understand, and generate human languages naturally. Answer: artificial intelligence; AI Diff: 2 Objective: 5.06 Explain how the operating system interacts with application software. 42) When a computer is booted, the process called ________ checks the computer's components. Answer: power-on self-test (POST); power-on self-test; POST Diff: 2 Objective: 5.07 Discuss the process the operating system uses to start up the computer and how errors in the boot process are handled. 66 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 43) The Windows ________ displays open and favorite applications for easy access at the bottom of the display by default. Answer: taskbar Diff: 2 Objective: 5.08 Describe the main features of the Windows interface. 44) File ________ manages files stored in a hierarchical structure of directories in Windows. Answer: Explorer Diff: 2 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 45) The ________ is a Windows tool that enables you to capture all or a portion of a screen display. Answer: Snipping Tool Diff: 3 Objective: 5.08 Describe the main features of the Windows interface. 46) In the Windows operating system, the C:\ drive is commonly referred to as the ________ directory. Answer: root Diff: 1 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 47) When using a Windows PC, ________ is the main tool for finding, viewing, and managing files. Answer: File Explorer Diff: 2 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 48) The Windows path separator is the ________ character. Answer: backslash; \ Diff: 2 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 49) In the file name, Resume.docx, docx is the ________, indicating the file type. Answer: extension; file extension Diff: 2 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 50) Disk ________ realigns separated data so that related file pieces are unified. Answer: defragmentation; defrag; defragmenter Diff: 2 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide 67 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 accessibility. 51) The Windows utility program that removes unnecessary files from the hard drive is called ________. Answer: Disk Cleanup Diff: 2 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 52) Tracks on hard disk drives are broken down into pie shaped wedges called ________. Answer: sectors Diff: 2 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 53) Scattered pieces of files on the hard drive can be regrouped into sequential order using the ________ utility. Answer: Disk defragmenter; disk defragmenting; disk defragmentation; defrag; disk defrag Diff: 2 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 54) Windows includes ________ settings, which provide a centralized location for assistive technology and tools. Answer: accessibility Diff: 2 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 55) Every computer has an operating system. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 5.01 Discuss the functions of the operating system. 56) Gaming consoles, such as Xbox One and PlayStation 4, do not need an operating system. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 5.01 Discuss the functions of the operating system. 57) A system restore point is a snapshot of your entire computer system's settings. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 58) A personal computer can only have one operating system installed on it. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 68 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 Objective: 5.02 Explain the most common operating systems for personal use. 59) Most desktop and laptop computers run some version of Windows, Linux or macOS. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 5.02 Explain the most common operating systems for personal use. 60) Windows 10 is the planned final operating system release by Microsoft. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 5.02 Explain the most common operating systems for personal use. 61) Android is an open source operating system for network servers. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 5.02 Explain the most common operating systems for personal use. 62) When your computer runs out of RAM, the operating system borrows space from the CPU. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 5.05 Explain how the operating system helps manage hardware such as the processor, memory, storage, and peripheral devices. 63) Installing a device driver can sometimes cause system instability. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 5.05 Explain how the operating system helps manage hardware such as the processor, memory, storage, and peripheral devices. 64) CMOS is a special kind of memory that uses a great deal of power. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 5.07 Discuss the process the operating system uses to start up the computer and how errors in the boot process are handled. 65) Preemptive multitasking is the term used when the operating system processes higherpriority tasks before lower-priority tasks. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 5.05 Explain how the operating system helps manage hardware such as the processor, memory, storage, and peripheral devices. 66) File Explorer is Windows's main program to find, manage and view files. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 69 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 67) You can use System Restore to return your system's settings back to a specific date when everything was working properly. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 5.10 Outline the tools used to enhance system productivity, back up files, and provide accessibility. 68) Match each of the following terms to its file type (extension): I. II. III. IV. V. .zip .jpg .pdf .accdb .html A. Microsoft Access B. compressed files C. portable document format D. image E. web page Answer: B, D, C, A, E Diff: 2 Objective: 5.09 Summarize how the operating system helps keep your computer organized and manages files and folders. 69) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. folder track sector platter taskbar A. displays open and favorite applications B. storage location for a collection of files C. pie-shaped wedge on the hard drive D. round, thin plate of metal that makes up a hard drive E. concentric circle on the hard drive Answer: B, E, C, D, A Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 70 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 70) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. GUI II. thrashing III. Desktop IV. pin V. POST A. checks hardware at startup B. primary work area C. place an application tile on the Start screen or icon on the taskbar D. type of user interface in macOS and Microsoft Windows 10 E. the condition of excessive paging Answer: D, E, B, C, A Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 71) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. Defragment and Optimize Drives Task Manager System Restore File History, File Recovery Disk Cleanup A. brings system back to a previously stable state B. regroups related pieces of files on the hard disk C. lists all the programs being used and indicates their status D. backs up important files, makes a complete mirror image of your current computer setup E. removes unnecessary files from the hard drive Answer: B, C, A, D, E Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 71 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 72) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. virtual memory paging kernel swap file spooler A. process of optimizing RAM storage by using hard drive space B. operating system supervisor program C. coordinates print jobs D. temporary storage area on the hard drive E. swapping data between RAM and a hard drive Answer: A, E, B, D, C Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 6 Understanding and Assessing Hardware: Evaluating Your System 1) The rule of thumb that predicts that the number of transistors on a CPU will double every two years is called ________ Law. A) Charles' B) Moore's C) Intel's D) Boyle's Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 6.01 Describe the changes in CPU performance over the past several decades. 2) Which of the following is the lightest computer? A) Laptop B) Ultrabook C) Smartphones D) Desktop Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 6.02 Compare and contrast a variety of computing devices. 3) The processor market for desktop and laptop computers is dominated by ________. A) IBM B) Microsoft C) Intel D) Apple Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 72 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 4) Which of the following does NOT determine a CPU's processing power? A) Clock speed B) Number of cores C) Amount of cache memory D) Speed of the motherboard Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 73 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) Which of the following activities is carried out by the ALU? A) Moves read/write heads B) Performs arithmetic calculations C) Creates virtual memory D) Renders video images Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 6) All of the following are part of the machine cycle EXCEPT ________. A) fetch B) encode C) execute D) store Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 7) The CPU consists of which two parts? A) The arithmetic logic unit and the front side bus B) The control unit and the arithmetic logic unit C) The control unit and the front side bus D) Cache memory and SSD storage Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 8) The control unit is one component of the ________. A) CPU B) cache C) front side bus D) clock Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 9) Running the CPU at a faster speed than the manufacturer recommends is called ________. A) fetching B) latency C) overclocking D) hyperthreading Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 74 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 10) Cache memory levels are based on proximity to ________. A) the hard drive B) RAM C) the processor D) the video card Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 11) ________ provides high-speed information processing by enabling a new set of instructions to start before the previous set is finished. A) Multitasking B) Cache memory C) Hyperthreading D) Overclocking Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 12) Some of the cache memory of a CPU is ________. A) inside the CPU, itself B) on the hard disk drive C) on a nearby SSD D) in cloud storage Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 13) RAM is an example of ________ storage. A) volatile B) nonvolatile C) permanent D) mobile Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 6.05 Discuss how RAM is used in a computer system. 14) The amount of RAM storage is measured in ________. A) gigabytes B) gigahertz C) gigabits D) machine cycles Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 6.05 Discuss how RAM is used in a computer system. 75 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 15) Windows uses a memory-management technique known as ________ to monitor which applications you use most frequently an d then preloads them into your system memory. A) SuperGet B) SuperFetch C) SuperTake D) SuperRetrieve Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 6.05 Discuss how RAM is used in a computer system. 16) Select the best way to determine your RAM allocation. A) List all programs you would run simultaneously and the amount of RAM each needs and add together. B) Count the number of available slots on the motherboard. C) Divide the number of used memory slots by the number of total memory slots. D) Monitor RAM usage in performance monitor and calculate an average of RAM used over 10 random periods. Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 6.06 Evaluate whether adding RAM to a system is desirable. 17) When referring to hard drives, access time is measured in ________. A) megahertz B) bits per second C) milliseconds D) kilobytes Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 18) A ________ uses electronic memory and has no motors or moving parts. A) mechanical hard drive B) solid-state drive C) Bluray disc D) digital video disc Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 19) How do optical discs store data? A) A laser burns tiny pits onto a disc. B) A magnet aligns iron particles on a platter. C) Electronic memory records data on chips. D) A digital spectrometer leaves grooves in a platter. Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 76 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 20) Which of the following is NOT a permanent storage option? A) Optical drive B) Random access memory C) Internal hard drive D) SSD Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 21) Which of the following storage devices has the largest potential capacity? A) Compact disc B) Thumb drive C) Bluray disc D) Mechanical hard drive Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 22) Which of the following ports is NOT considered to be exclusively a video port? A) HDMI B) DVI C) USB D) DisplayPort Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 6.09 Describe the features of video cards. 23) To speed up the display of graphics, a(n) ________ is integrated into most video cards. A) GPU B) CPU C) ALU D) SSD Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 6.09 Describe the features of video cards. 24) A(n) ________ enables the computer to drive the speaker system. A) GPU port B) display port C) sound card D) PCI bus Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 6.10 Describe the features of sound cards. 77 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 25) How many channels are in a Dolby 7.1 surround sound system? A) 7 B) 8 C) 6 D) 12 Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 6.10 Describe the features of sound cards. 26) Running the Disk Defragmenter utility will ________. A) detect and remove spyware B) mark bad memory cells C) make the hard drive work more efficiently D) clean out your Startup folder Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 6.11 Describe steps you can take to optimize your system's reliability. 27) Running the Disk Cleanup utility is a quick way to ________. A) defrag your hard drive B) remove spyware programs C) clear out unnecessary files D) uninstall unwanted apps Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 6.11 Describe steps you can take to optimize your system's reliability. 28) The Windows ________ utility returns your computer to the state it was in when it came from the factory. A) Backup B) Erase C) Restore D) Refresh Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 6.11 Describe steps you can take to optimize your system's reliability. 29) Which statement pertaining to system reliability is FALSE? A) Having the latest version of software products can make your system more reliable. B) An accumulation of temporary Internet files has no effect on your computer's overall performance. C) Removing unnecessary programs from your Startup folder can improve system reliability. D) When you defrag your hard drive, it works more efficiently. Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 6.11 Describe steps you can take to optimize your system's reliability. 78 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 30) To securely erase data, the U.S. Department of Defense suggests that data be ________. A) overwritten seven times B) deleted C) encoded D) refactored Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 6.12 Discuss how to recycle, donate, or dispose of an older computer. 31) ________ Law predicts that the number of transistors in a CPU will double about every two years. Answer: Moore's Diff: 1 Objective: 6.01 Describe the changes in CPU performance over the past several decades. 32) The CPU is located on the ________. Answer: motherboard; system motherboard; mother board; system board Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 33) A CPU's processing power is determined by the combination of the clock speed, the number of cores, and the amount of ________ memory. Answer: cache Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 34) The ________ of a CPU dictates how many instructions the CPU can process each second. Answer: clock speed Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 35) The CPU is composed of two units, the control unit and the ________. Answer: arithmetic logic unit; ALU Diff: 1 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 36) The process the CPU performs for each program instruction is called the ________. Answer: machine cycle Diff: 1 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 37) ________ is a feature of a CPU that allows it to begin to fetch the next instruction before it has finished executing the current one. Answer: Hyperthreading Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 79 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 38) Running the CPU at a faster speed than the manufacturer recommends is called ________. Answer: overclocking Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 39) ________ is the type of RAM memory used most often in today's lower-end computers. Answer: DDR3; Double data rate 3; DDR3 memory modules; Double data rate 3 memory modules Diff: 3 Objective: 6.05 Discuss how RAM is used in a computer system. 40) The CPU's ________ memory is a form of RAM that gets data to the CPU for processing much faster than bringing the data in from the computer's RAM. Answer: cache Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 41) RAM is an example of ________ storage because when the power is turned off, RAM is cleared out. Answer: volatile; temporary Diff: 1 Objective: 6.05 Discuss how RAM is used in a computer system. 42) The time it takes a storage device to locate stored data and make it available for processing is called ________ time. Answer: access Diff: 3 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 43) The ________ has the largest potential capacity of any storage device. Answer: mechanical hard drive; hard drive; hard disk drive Diff: 1 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 44) ________ drives are 100 times faster than mechanical hard drives. Answer: Solid-state; Solid state; SSD Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 45) ________ drives run with no noise and very little heat, and require very little power. Answer: Solid-state; Solid state; SSD Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 46) Optical drives use a(n) ________ to read and write data. Answer: laser; high speed laser; high-speed laser Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 80 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 47) A(n) ________ moves over the spinning platters to retrieve data from a mechanical hard disk. Answer: read/write head Diff: 3 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 48) A stoppage of a mechanical hard drive that often results in data loss is called a(n) ________. Answer: head crash Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 49) ________ improves disk writing performance because data is written across two drives. Answer: RAID 0 Diff: 2 Objective: 6.08 Evaluate the amount and type of storage needed for a system. 50) ________ automatically duplicates your data and saves it on two identical drives. Answer: RAID 1 Diff: 2 Objective: 6.08 Evaluate the amount and type of storage needed for a system. 51) A video card can deliver output to multiple ________. Answer: monitors; displays Diff: 2 Objective: 6.09 Describe the features of video cards. 52) In a video card, GPU stands for ________. Answer: graphics processing unit Diff: 3 Objective: 6.09 Describe the features of video cards. 53) ________ sound is a type of audio system where the listener hears the sound as if it were coming from multiple speakers. Answer: Surround Diff: 1 Objective: 6.10 Describe the features of sound cards. 54) The audio subsystem consists of the speakers, microphone, and a(n) ________. Answer: sound card Diff: 1 Objective: 6.10 Describe the features of sound cards. 55) macOS X uses ________ software to automatically backup and restore data. Answer: Time Machine Diff: 3 Objective: 6.11 Describe steps you can take to optimize your system's reliability. 81 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 56) Many computer manufacturers offer ________ programs to reduce the number of computers disposed in landfills. Answer: recycling Diff: 2 Objective: 6.12 Discuss how to recycle, donate, or dispose of an older computer. 57) Windows has tools to monitor CPU utilization in Task Manager. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.04 Describe tools used to measure and evaluate CPU performance. 58) Solid state hybrid drives are a combination of a mechanical hard drive and an SSD drive. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 59) Desktop computer systems are less reliable than laptop computers. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.02 Compare and contrast a variety of computing devices. 60) Level 3 cache memory is faster than Level 1 and Level 2 cache. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 61) The use of multiple cores on one CPU chip allows the execution of two or more sets of instructions at the same time. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 62) Cache memory is a form of ROM. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 63) Level 1 cache usually contains the least amount of storage of the cache memory levels. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 6.03 Describe how a CPU is designed and how it operates. 64) Accessing data from the hard drive to send to the CPU is faster than accessing data from RAM. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.05 Discuss how RAM is used in a computer system. 82 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 65) The heads of a mechanical hard disk drive touch the surface of the platter to read or write the data. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 66) RAM prices tend to be very stable. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.06 Evaluate whether adding RAM to a system is desirable. 67) Optical discs store data using tiny pits and grooves burned by a laser. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 68) Video cards are designed with their own RAM storage. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 6.09 Describe the features of video cards. 69) When using multiple monitors, you must have multiple video cards. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.09 Describe the features of video cards. 70) 3D sound is different from surround-sound. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.10 Describe the features of sound cards. 71) Dolby Digital 7.1 requires a total of eight speakers. Answer: TRUE Diff: 3 Objective: 6.10 Describe the features of sound cards. 72) RAID 0 automatically duplicates your data and saves it on two identical drives. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.08 Evaluate the amount and type of storage needed for a system. 73) If you reformat the hard drive on a computer, it erases all personal information from your computer and makes it safe to donate. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 6.12 Discuss how to recycle, donate, or dispose of an older computer. 83 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 74) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. latency sectors tracks seek time platters A. time required for the read/write head to move to the correct track B. round, thin plates of metal within a mechanical hard drive C. time needed for correct sector to spin to the read/write head D. concentric circles on a hard drive E. pie-shaped wedges on the surface of a hard drive Answer: C, E, D, A, B Diff: 2 Objective: 6.07 Classify and describe the major types of nonvolatile storage drives. 75) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. RAM hyperthreading clock speed quad-core processor ROM A. a CPU with 4 cores B. volatile storage C. measure of CPU speed D. permanent storage E. simultaneous execution of more than one instruction Answer: B, E, C, A, D Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 84 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 76) Match each of the following terms to its purpose: I. II. III. IV. V. virtual memory physical memory random access memory cache memory video memory A. volatile storage space B. found on a video card C. space on the hard drive for data that doesn't fit in RAM D. can be accessed more quickly than regular RAM E. the amount of RAM contained on memory modules Answer: C, E, A, D, B Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 77) Match each of the following terms to its function: I. II. III. IV. V. CPU ALU cache RAID SSD A. closest memory to the CPU B. processor C. uses electronic memory and has no moving parts D. strategy for using more than one storage drive in a system E. performs arithmetic calculations Answer: B, E, A, D, C Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 7 Networking: Connecting Computing Devices 1) A computer ________ is two or more computers connected using software and hardware so that they can communicate with each other. A) network B) switch C) broadband D) node Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 7.01 Describe computer networks and their pros and cons. 2) A ________ is any device connected to a network such as a computer, printer, or game 85 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 console. A) packet B) node C) NOS D) NIC Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 7.01 Describe computer networks and their pros and cons. 3) ________ is the actual speed of data transfer that is achieved between two nodes on a network and is always less than or equal to the data transfer rate. A) Benchmark B) Broadband C) Bandwidth D) Throughput Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 7.01 Describe computer networks and their pros and cons. 4) Some of the responsibilities of ________ are installing new hardware and software on the network and monitoring performance. A) security engineer B) IT managers C) computer technicians D) network administrators Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 7.01 Describe computer networks and their pros and cons. 86 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) Which of the following is NOT a common network architecture type? A) Local area network (LAN) B) Home area network (HAN) C) Intraoffice area network (IAN) D) Personal area network (PAN) Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 6) You can find out which network adapters are installed in your system by using the Windows ________ Manager utility. A) Network B) Device C) Setup D) Hardware Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 7.08 Explain what should be considered before creating a home network. 7) When setting up a home network, make sure each node has ________. A) a NOS installed B) the proper software installed on each node C) a network adapter D) the proper security protocols in place Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 7.10 Summarize how to configure home network software. 8) The network architecture that spans the largest physical distance is called a ________. A) MAN B) LAN C) PAN D) WAN Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 9) A large network designed to provide access to a specific geographic area, such as a large city, is a ________. A) MAN B) PAN C) LAN D) WAN Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 87 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 10) Which transmission medium transmits data the fastest? A) Twisted-pair cable B) Coaxial cable C) Wireless D) Fiber-optic cable Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 7.03 Describe the types of transmission media used in networks. 11) What transmission media is used for normal telephone service? A) Fiber-optic cable B) Twisted-pair cable C) Coaxial cable D) Ethernet cable Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 7.03 Describe the types of transmission media used in networks. 12) A client/server network is an example of ________ administration. A) local B) wide area C) central D) remote Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 13) A peer-to-peer (P2P) network is an example of ________ administration. A) local B) wide area C) central D) corporate Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 14) Which of the following is NOT a standard for wireless Ethernet networks? A) 802.11n B) 802.11g C) 802.11ab D) 802.11ac Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 88 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 15) Which of the following is NOT a type of cable used in wired networks? A) Unshielded twisted-pair B) Coaxial C) Fiber-optic D) Unshielded coaxial Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 7.03 Describe the types of transmission media used in networks. 16) Which of the following is NOT a type of UTP cable you would use in a wired Ethernet network? A) Cat 5E B) Cat 6 C) Cat 6A D) Cat 7B Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 7.03 Describe the types of transmission media used in networks. 17) If you are going to attach more than 15 devices to your wireless network, you should make sure your router supports which standard? A) 802.11bc B) 802.11n C) 802.11ac D) 802.3ac Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 7.08 Explain what should be considered before creating a home network. 18) Wireless network devices use ________ to communicate with each other. A) fiber optics B) satellites C) radio waves D) DSL Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 7.03 Describe the types of transmission media used in networks. 19) For the nodes on a network to communicate with each other and access the network, each node needs a ________. A) DSL modem B) network adapter C) hub D) router Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 7.04 Describe the basic hardware devices necessary for networks. 89 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 20) On a network, a(n) ________ helps prevent data packets from colliding with each other. A) access point B) hub C) adapter D) switch Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 7.04 Describe the basic hardware devices necessary for networks. 21) Which hardware device connects your network to the Internet? A) Modem B) Router C) Firewall D) Switch Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 7.04 Describe the basic hardware devices necessary for networks. 22) To transfer data packets between two or more networks, a ________ is used. A) router B) hub C) modem D) switch Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 7.04 Describe the basic hardware devices necessary for networks. 23) Data are sent through a network in bundles called ________. A) packages B) pouches C) packets D) nodes Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 7.04 Describe the basic hardware devices necessary for networks. 24) Which of the following is NOT a home operating system that supports P2P networking? A) Windows B) macOS C) Unix D) Linux Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 7.05 Describe the type of software necessary for networks. 90 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 25) Client/server networks are controlled by a central server that runs specialized software called a(n) ________. A) multipersonnel operating system (MPOS) B) network operating system (NOS) C) central operating system (COS) D) central server operating system (CCOS) Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 7.05 Describe the type of software necessary for networks. 26) Which of the following is NOT a wired broadband Internet connection option? A) Cable B) Dial-up C) DSL D) Fiber-optic Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 7.06 Summarize the broadband options available to access the Internet. 27) A(n) ________ device facilitates file sharing and data backup. A) NAS B) WAN C) UTP D) NOS Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 7.09 Describe how to set up a home network. 28) Using a wireless network without the network owner's permission is known as ________. A) hijacking B) spamming C) piggybacking D) phishing Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 29) All of the following are extra precautions you can take to secure a wireless network EXCEPT ________. A) change your network name (SSID) B) enable SSID broadcast C) turn on security protocols D) create a passphrase Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 91 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 30) The unique number assigned to a network adapter by the manufacturer is referred to as the ________ address. A) MAC B) IP C) SSID D) network Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 31) The term network ________ is the same as the network design. Answer: architecture Diff: 1 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 32) A(n) ________ network is one in which each computer can communicate directly with the others. Answer: peer-to-peer; P2P Diff: 2 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 33) A computer lab is an example of a(n) ________ type of network. Answer: LAN; local area network Diff: 1 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 34) A network used to communicate among devices close to one person is called a(n) ________. Answer: PAN; personal area network Diff: 1 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 35) Many cities in the United States now provide a(n) ________ type of network to allow Internet access to residents and tourists. Answer: metropolitan area network; MAN Diff: 2 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 36) ________ cable is composed of four pairs of wires that are wrapped around each other with no external casing. Answer: Unshielded twisted-pair; UTP Diff: 2 Objective: 7.03 Describe the types of transmission media used in networks. 37) ________ cable consists of a single copper wire surrounded by layers of plastic and is used to connect cable TV. Answer: Coaxial Diff: 2 Objective: 7.03 Describe the types of transmission media used in networks. 92 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 38) The capability of current devices to use earlier standards, in addition to the current standard, is known as ________. Answer: backward compatibility Diff: 2 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 39) ________ are devices that transfer packets of data between two or more networks. Answer: Routers Diff: 2 Objective: 7.04 Describe the basic hardware devices necessary for networks. 40) A(n) ________ is a device that receives data packets and sends them to their intended nodes on the same network while preventing data collisions. Answer: switch Diff: 2 Objective: 7.04 Describe the basic hardware devices necessary for networks. 41) The server on a client/server network has specialized ________ software installed. Answer: network operating system; NOS Diff: 2 Objective: 7.05 Describe the type of software necessary for networks. 42) ________ is often referred to as "high-speed Internet." Answer: Broadband Diff: 2 Objective: 7.06 Summarize the broadband options available to access the Internet. 43) DSL broadband service uses ________ cable. Answer: twisted-pair; twisted pair Diff: 3 Objective: 7.06 Summarize the broadband options available to access the Internet. 44) A(n) ________ network uses radio waves as its transmission medium. Answer: wireless Diff: 1 Objective: 7.03 Describe the types of transmission media used in networks. 45) A(n)________ acts like a traffic signal on a network. Answer: switch Diff: 2 Objective: 7.04 Describe the basic hardware devices necessary for networks. 46) In terms of networking, NOS stands for ________. Answer: network operating system Diff: 2 Objective: 7.05 Describe the type of software necessary for networks. 93 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 47) ________ has faster cellular data transfer rates than 3G. Answer: 4G Diff: 2 Objective: 7.07 Summarize how to access the Internet wirelessly. 48) Public places where you can wirelessly connect to the Internet are known as ________. Answer: hotspots; WiFi hotspots; Wi-Fi hotspots; wireless hotspots Diff: 2 Objective: 7.07 Summarize how to access the Internet wirelessly. 49) A(n) ________ is someone who attempts to access your network without your knowledge. Answer: hacker; piggybacker Diff: 1 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 50) When using a wireless connection, the process of ________ translates data into code so that it is protected. Answer: encryption Diff: 2 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 51) SSID stands for ________. Answer: service set identifier; service set ID Diff: 3 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 52) All wireless networks have their own name, referred to as the ________, which is used to identify the network. Answer: service set identifier; SSID; service set ID Diff: 3 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 53) A wireless ________ extender is a wireless network device that repeats your wireless signal. Answer: range Diff: 3 Objective: 7.11 Describe the potential problems with wireless networks and means to avoid them. 54) ________ is a much stronger protocol than WEP for wireless security. Answer: Wi-Fi Protected Access; WPA; WPA2; Wi-Fi Protected Access Version 2 Diff: 3 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 55) A printer connected to a wireless network is considered to be a node on that network. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 7.01 Describe computer networks and their pros and cons. 94 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 56) Sharing files is a benefit of a network. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 7.01 Describe computer networks and their pros and cons. 57) When powering up a home network, make sure all computers and peripherals are turned on before turning on the modem/router. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 7.10 Summarize how to configure home network software. 58) P2P networks are most commonly used in home networks. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 59) The Internet is a WAN. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 60) Current wired Ethernet networks in the United States are based on the IEEE 802.11ac standard. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 61) Wireless network connections are slower than wired broadband connections. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 7.03 Describe the types of transmission media used in networks. 62) An access point connects to the main router wirelessly. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 7.11 Describe the potential problems with wireless networks and means to avoid them. 63) Most computers today come with network adapters already installed. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 7.04 Describe the basic hardware devices necessary for networks. 64) A switch acts like a traffic signal on a network. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 7.04 Describe the basic hardware devices necessary for networks. 95 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 65) A P2P network needs specialized network operating system software installed on every node. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 7.05 Describe the type of software necessary for networks. 66) Wireless networks are more vulnerable to attack than wired networks. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 67) WEP is a stronger form of security than WPA. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 68) Limiting your signal range does not help increase wireless network security. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 7.12 Describe how to secure wireless home networks. 69) Match each of the following network types to its definition: I. HAN II. MAN III. LAN IV. PAN V. WAN A. confined to a small geographic location beyond the home B. services a residence C. used to communicate among devices near an individual D. covers a city E. a network that covers the greatest distance Answer: B, D, A, C, E Diff: 1 Objective: 7.02 Explain the different ways networks are defined. 96 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 70) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. fiber-optic II. twisted-pair III. coaxial cable IV. peer-to-peer V. client/server A. single copper wire surrounded by layers of plastic B. made up of plastic or glass and transmits data at extremely fast speeds C. each node can communicate directly with every other node on the network D. made up of copper wires E. central computer provides information and resources to other computers Answer: B, D, A, C, E Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 71) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. server II. client III. network IV. piggyback V. node A. two or more computers connected together via software and hardware so they can communicate B. a computer, peripheral, or communication device on a network C. computer on which users accomplish specific tasks and make specific requests D. provides information and resources to other computers on a network E. unauthorized connection to a wireless network Answer: D, C, A, E, B Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 97 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 72) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. throughput II. packet III. firmware IV. firewall V. bandwidth A. maximum speed at which data can be transmitted B. the actual speed of data transfer that is achieved on a network C. the format in which data is sent over transmission media D. hardware or software for protecting computers from hackers E. instructions in read-only memory Answer: B, C, E, D, A Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 73) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. NOS II. broadband III. router IV. switch V. NIC A. directs data traffic between networks B. handles data traffic between nodes on the same network C. software used to set up and manage a network D. connects a node to a network E. high-speed Internet connection Answer: C, E, A, B, D Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 8 Managing a Digital Lifestyle: Media and Ethics 1) What does the Digital Living Network Alliance standardize? A) The compilation of available e-texts. B) The codecs used in video compression. C) The sampling rate used to create MP3 files. D) The convergence of devices. Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 8.01 Describe how digital convergence has evolved. 2) The term ________ refers to the use of a single unifying device that handles media, Internet, entertainment, and telephone needs. 98 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 A) multimedia message service B) telephony C) mobile switching center D) digital convergence Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 8.01 Describe how digital convergence has evolved. 3) What kind of e-book reader does Barnes and Noble sell? A) NOOK B) Kindle C) VitalSource D) Fire Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 8.04 Explain how to purchase, borrow, and publish e-texts. 4) What happens after 180 days to e-books rented through VitalSource? A) They are encrypted until you purchase them. B) They show up in your library, but cannot be read. C) They disappear from your device. D) Only the first chapter can be read. Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 8.04 Explain how to purchase, borrow, and publish e-texts. 99 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) What is a system of access control that allows only limited use of material that has been legally purchased? A) DDM B) DRM C) DRR D) MDR Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 8.06 Summarize how to listen to and publish digital music. 6) Google ________ is an online store that can be used for self-publishing books. A) Fun B) Games C) Play D) Sport Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 8.04 Explain how to purchase, borrow, and publish e-texts. 7) A(n) ________ chip converts sound waves from a voice into a digital signal. A) analog-to-digital converter B) digital convergence C) digital signal processor D) telephony Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 8.05 Describe how digital music is created and stored. 8) What is NOT an example of a method to stream music? A) Pandora B) Google Tunes C) Spotify D) Apple CarPlay Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 8.06 Summarize how to listen to and publish digital music. 9) ________ property is a product of a person's mind and is usually considered an expression of human creativity? A) Abstract B) Intellectual C) Tangible D) Personal Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 8.09 Describe the various types of intellectual property. 100 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 10) The Apple logo would be considered a(n) ________. A) copyright B) service mark C) patent D) trademark Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 8.09 Describe the various types of intellectual property. 11) To protect a movie, what category of intellectual property would be used? A) Copyright B) Trademark C) Service mark D) Patent Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 8.10 Explain how copyright is obtained and the rights granted to the owners. 12) When does copyright protection begin? A) When the application for the copyright has been approved B) When the application for the copyright has been submitted C) When a work is begun D) When a work is created and fixed into a digital or physical form Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 8.10 Explain how copyright is obtained and the rights granted to the owners. 13) Creative Commons licenses are ________. A) temporary B) irrevocable C) used mostly for software D) used mostly for movies Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 8.10 Explain how copyright is obtained and the rights granted to the owners. 14) A violation of the holder's rights is known as copyright ________. A) violation B) infringement C) defrauding D) abuse Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 8.11 Explain copyright infringement, summarize the potential consequences, and describe situations in which you can legally use copyrighted material. 101 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 15) Which is NOT a reason someone might risk violating a copyright? A) The risk of being caught is very low. B) It is hard to prove the copyright in court. C) Everyone else is doing it. D) I am just one person. Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 8.11 Explain copyright infringement, summarize the potential consequences, and describe situations in which you can legally use copyrighted material. 16) What is the act of copying text or ideas from someone else and claiming them as your own? A) Copyright abuse B) Trademark infringement C) Plagiarism D) Copyleft Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 8.12 Explain plagiarism and strategies for avoiding it. 17) Instead of writing a term paper, some people cheat and purchase one from a(n) ________. A) paper mill B) term paper resource C) academic wholesale house D) academic paper resource Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 8.12 Explain plagiarism and strategies for avoiding it. 18) What is a popular copyleft license used for software? A) Creative Commons (CC) B) General Public License (GNU) C) Software Copy License (SCL) D) NonCommercial (NC) Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 8.10 Explain how copyright is obtained and the rights granted to the owners. 19) What is a website that allows an instructor to upload a paper to check for plagiarism? A) checkit.com B) plagiarism.com C) turnitin.com D) checkthatpaper.com Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 8.12 Explain plagiarism and strategies for avoiding it. 102 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 20) What is a good rule to follow to avoid plagiarism? A) Cite every fact you use. B) Never cite from another source. C) When in doubt, cite your source. D) Cite every comment. Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 8.12 Explain plagiarism and strategies for avoiding it. 21) Works without copyright protection are considered to be in the ________. A) public domain B) free use domain C) trademark zone D) copyleft domain Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 8.10 Explain how copyright is obtained and the rights granted to the owners. 22) Which of the following is NOT true about e-books? A) You can borrow them from the library. B) They are always PDF file format. C) You can annotate them with your own notes. D) Amazon sells more e-books now than printed books. Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 8.03 Describe the different types of e-readers. 23) ________ is digital textual information that can be stored, manipulated, and transmitted by electronic devices. A) Short message service B) SMTP C) E-text D) Digital rights management Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 8.03 Describe the different types of e-readers. 24) How long do current U.S. laws grant copyright protection? A) The life of the author (creator) plus 70 years B) The life of the author (creator) plus 50 years C) 99 years D) 101 years Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 8.10 Explain how copyright is obtained and the rights granted to the owners. 103 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 25) Which of the following is NOT an example of a digital music file format? A) WMA B) MP3 C) AAC D) ACCDB Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 8.05 Describe how digital music is created and stored. 26) ________ allows only limited use of media that has been legally purchased. A) Digital rights management B) Copyright C) Copyleft D) Synchronizing Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 8.06 Summarize how to listen to and publish digital music. 27) Which of the following describes the number of times an analog wave is measured each second during an analog-to-digital conversion? A) Converting rate B) Conversion rate C) Simplifying rate D) Sampling rate Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 8.05 Describe how digital music is created and stored. 28) Which of the following digital formats compress an image file? A) AAC B) RAW C) JPEG D) MPEG Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 8.07 Explain how best to create, print, and share digital photos. 29) Which of the following is NOT a video file extension? A) .jpg B) .mpg C) .avi D) .mov Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 8.08 Describe how to create, edit, and distribute digital video. 104 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 30) A(n) ________ cable carries all audio and video information from one devices to another connected device. A) HDMI B) S component C) Ethernet D) RJ11 Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 8.08 Describe how to create, edit, and distribute digital video. 31) A(n) ________ is anything designed to deceive another person either as a practical joke or for financial gain. Answer: hoax Diff: 1 Objective: 8.13 Describe hoaxes and digital manipulation. 32) When a hoax becomes so well known that it is incorporated into society as a true event, it is known as a(n) ________. Answer: urban legend Diff: 2 Objective: 8.13 Describe hoaxes and digital manipulation. 33) Digital ________ involves altering media so that the images captured are changed from the way they were originally seen by the human eye. Answer: manipulation Diff: 2 Objective: 8.13 Describe hoaxes and digital manipulation. 34) Google ________ is a subscription service that lets you listen to tracks in their catalog. Answer: Play; Play Music Diff: 2 Objective: 8.05 Describe how digital music is created and stored. 35) The tendency of information to remains on the Internet indefinitely is known as ________ of information. Answer: persistence Diff: 2 Objective: 8.14 Describe what comprises your online reputation and how to protect it. 36) Your online ________ consists of the information available about you in cyberspace that can influence people's opinions of you in the real world. Answer: reputation Diff: 1 Objective: 8.14 Describe what comprises your online reputation and how to protect it. 105 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 37) Employment ________ means that unless you're covered by an employment contract or a collective bargaining agreement, employers can fire you at any time for any reason, unless the reason violates a legal statute. Answer: at-will; at will Diff: 3 Objective: 8.14 Describe what comprises your online reputation and how to protect it. 38) You have a constitutional right to ________ speech. Answer: free Diff: 2 Objective: 8.14 Describe what comprises your online reputation and how to protect it. 39) The ________ Machine is a utility that shows you what a website looked like at a previous point in time. Answer: Wayback Diff: 3 Objective: 8.14 Describe what comprises your online reputation and how to protect it. 40) MLA stands for ________ Language Association. Answer: Modern Diff: 2 Objective: 8.12 Explain plagiarism and strategies for avoiding it. 41) Failing to identify a direct quotation with quotation marks is an example of ________. Answer: plagiarism Diff: 2 Objective: 8.12 Explain plagiarism and strategies for avoiding it. 42) Reproduction by a teacher or student of a small part of a work to illustrate a lesson is commonly known as educational ________ use. Answer: fair Diff: 2 Objective: 8.11 Explain copyright infringement, summarize the potential consequences, and describe situations in which you can legally use copyrighted material. 43) Many websites that contain copyrighted material also contain lengthy legal documents that delineate the ________ of use for the material that you download. Answer: terms Diff: 2 Objective: 8.11 Explain copyright infringement, summarize the potential consequences, and describe situations in which you can legally use copyrighted material. 44) Illegally using copyrighted software is known as software ________. Answer: piracy Diff: 2 Objective: 8.11 Explain copyright infringement, summarize the potential consequences, and describe situations in which you can legally use copyrighted material. 106 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 45) Works in the public ________ are considered public property and therefore, anyone can modify, distribute, copy, or sell them for profit. Answer: domain Diff: 2 Objective: 8.10 Explain how copyright is obtained and the rights granted to the owners. 46) The FedEx logo is a ________ mark. Answer: service Diff: 2 Objective: 8.09 Describe the various types of intellectual property. 47) The main grayscale technology for e-text display on the Amazon Kindle Paperwhite and Barnes and Noble NOOK is ________. Answer: E Ink; electronic ink Diff: 2 Objective: 8.03 Describe the different types of e-readers. 48) The ________ is the number of times that an analog wave is measured each second in an analog-to-digital conversion. Answer: sampling rate Diff: 2 Objective: 8.05 Describe how digital music is created and stored. 49) The size of an MP3 file depends on the digital ________ of the song. Answer: sampling Diff: 2 Objective: 8.05 Describe how digital music is created and stored. 50) Digital camera resolution is measured in ________. Answer: megapixels; MP Diff: 1 Objective: 8.07 Explain how best to create, print, and share digital photos. 51) The most common file types supported by digital cameras are raw uncompressed (RAW) data and ________. Answer: Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG); jpg; JPEG Diff: 2 Objective: 8.07 Explain how best to create, print, and share digital photos. 52) The ________ of a digital camera refers to the number of data points recorded for a captured image. Answer: resolution Diff: 2 Objective: 8.07 Explain how best to create, print, and share digital photos. 107 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 53) A(n) ________ is a rule that squeezes the same audio and video information into less space. Answer: codec; compression/decompression Diff: 3 Objective: 8.08 Describe how to create, edit, and distribute digital video. 54) ________ is a term used to refer to various licensing plans that enable copyright holders to grant certain rights to the work while retaining other rights. Answer: Copyleft; Copy left Diff: 2 Objective: 8.10 Explain how copyright is obtained and the rights granted to the owners. 55) A copyright holder cannot loan, rent, or give away the work. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.10 Explain how copyright is obtained and the rights granted to the owners. 56) Facts cannot be copyrighted. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 8.11 Explain copyright infringement, summarize the potential consequences, and describe situations in which you can legally use copyrighted material. 57) Plagiarism is usually considered an academic offense of dishonesty and isn't punishable under U.S. civil law. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 8.12 Explain plagiarism and strategies for avoiding it. 58) Pictures you find on Google image search are considered to be in the public domain. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.09 Describe the various types of intellectual property. 59) YouTube is the entity legally responsible for its content, rather than the person who uploaded the content. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.11 Explain copyright infringement, summarize the potential consequences, and describe situations in which you can legally use copyrighted material. 60) Patents last for a period of 30 years from the date the patent is filed. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.09 Describe the various types of intellectual property. 108 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 61) A trade dress applies to the visual appearance of a product or its packaging. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.09 Describe the various types of intellectual property. 62) A physical music CD is an example of intellectual property. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.09 Describe the various types of intellectual property. 63) DRM-free music can legally be moved from system to system. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.06 Summarize how to listen to and publish digital music. 64) The conversion rate is the number of times per second that the analog signal is measured and converted into a digital value. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.02 Explain the differences between digital and analog signals. 65) When converting analog waves to a series of numerical values, the higher the sampling rate, the more accurately the original wave can be recreated. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.05 Describe how digital music is created and stored. 66) RAW files are larger in size than JPEG files. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.07 Explain how best to create, print, and share digital photos. 67) Real property is considered immoveable, such as land or a home. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 8.09 Describe the various types of intellectual property. 68) Intangible personal property has no value. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 8.09 Describe the various types of intellectual property. 69) In terms of video resolution, HD stands for highly digitized. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 8.08 Describe how to create, edit, and distribute digital video. 109 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 70) Many cameras support wireless connections so you can transfer images without connecting cables. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 8.07 Explain how best to create, print, and share digital photos. 71) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. MP3 AAC ADC WMV SD A. storage card for media B. digital video file format which includes both audio and video C. digital music file format used broadly D. default digital music file format with iTunes E. converts audio signals into digital signals Answer: C, D, E, B, A Diff: 2 Objective: 8.05 Describe how digital music is created and stored. 72) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. resolution digital analog CCD codec A. a rule that squeezes audio and video information into less space B. number of data points used to capture an image C. data encoded as zeros and ones D. electronic sensor used in digital cameras E. continuous sound or light waves Answer: B, C, E, D, A Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 110 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 73) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. NOOK Kindle e-text e-reader E ink A. textual information captured digitally B. sharp grayscale representation of text C. sold by Amazon D. device that displays e-text E. sold by Barnes and Noble Answer: E, C, A, D, B Diff: 2 Objective: 8.03 Describe the different types of e-readers. 74) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. digital-to-analog converter MPEG-4 ripping analog-to-digital converter codec A. changes zeros and ones to a continuous analog wave B. converting a song on a CD to a digital computer file C. changes your voice's sound waves into digital signals D. usually has a .mp4 extension E. rule using hardware or software that compresses audio and video information Answer: A, D, B, C, E Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 111 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 75) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. copyleft sampling rate trademark fair use digital rights management A. granting of certain rights to a work while retaining other rights B. allows only limited use of legally purchased materials C. allows McDonalds to protect its logo D. allows people to use portions of a copyrighted work for specific purposes E. number of times an analog wave is measured Answer: A, E, C, D, B Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 9 Securing Your System: Protecting Your Digital Data and Devices 1) All of the following are top cybercrimes reported to the IC3 EXCEPT ________. A) identity theft B) non-auction scam C) advance fee fraud D) malware fraud Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 9.01 Describe how identity theft is committed and the types of scams identity thieves perpetrate. 2) Which of the following is formally defined as any criminal action perpetrated primarily through the use of a computer? A) Social networking B) Cybercrime C) Phishing D) Hacking Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 9.01 Describe how identity theft is committed and the types of scams identity thieves perpetrate. 3) The Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) is a partnership between the ________. A) FBI and the IRS B) FBI and the CIA C) FBI and National White Collar Crime Center D) NRA and the U.S. Department of Defense Answer: C Diff: 3 112 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 Objective: 9.01 Describe how identity theft is committed and the types of scams identity thieves perpetrate. 4) Government impersonation scams involve ________. A) people pretending to represent official organizations such as the Dept. of Homeland Security or IRS B) running auctions that do not exist C) convincing people to send money as a "good faith" gesture D) collecting funds and not delivering the goods Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 9.01 Describe how identity theft is committed and the types of scams identity thieves perpetrate. 113 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) ________ hackers break into systems legally for non-malicious reasons such as to test system security vulnerabilities. A) Black-hat B) Grey-hat C) White-hat D) Green-hat Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 9.02 Describe the different types of hackers and the tools they use. 6) A packet analyzer is a program that can enable a hacker to do all of the following EXCEPT ________. A) use your debit card information to purchase items illegally B) assume your identity C) steal your logons and passwords for various accounts D) launch a denial of service (DoS) attack on your computer Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 9.02 Describe the different types of hackers and the tools they use. 7) A ________ allows a hacker to gain access to your computer and take almost complete control of it without your knowledge. A) denial of service (DoS) B) zombie C) logic bomb D) rootkit Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 9.02 Describe the different types of hackers and the tools they use. 8) You can block logical ports from invaders and make your computer invisible to others on the Internet by installing ________. A) a packet sniffer B) a firewall C) a packet filter D) antivirus software Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 9.07 Explain what a firewall is and how a firewall protects your computer from hackers. 114 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 9) ________ floods a computer with requests until it shuts down and refuses to answer any requests for information. A) A Trojan horse B) A polymorphic virus C) A DDoS attack D) Pretexting Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 9.02 Describe the different types of hackers and the tools they use. 10) Creating and distributing ________ is one of the most widespread types of cybercrimes. A) spam B) computer viruses C) cookies D) zombies Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 9.03 Explain what a computer virus is, why it is a threat to your security, how a computing device catches a virus, and the symptoms it may display. 11) Which of the following is NOT a virus category? A) Worm B) Logic bomb C) Macro D) Pharming Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 12) All of the following activities may infect your computer with a virus EXCEPT ________. A) sharing flash drives B) downloading video files from peer-to-peer sites C) downloading or running an e-mail attachment file D) printing a document Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 9.03 Explain what a computer virus is, why it is a threat to your security, how a computing device catches a virus, and the symptoms it may display. 13) Which type of virus was the famous Michelangelo virus? A) A worm B) A time bomb C) A script virus D) An e-mail virus Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 115 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 14) A ________ is a virus that is triggered on a certain date. A) worm B) macro C) logic bomb D) time bomb Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 15) A(n) ________ takes advantage of file transport methods, such as e-mail, to spread on its own. A) worm B) script virus C) encryption virus D) macro virus Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 16) A ________ is a virus that is attached to documents. A) script virus B) macro virus C) polymorphic virus D) Trojan horse Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 17) Which of the following classifications of viruses can change its own code to avoid detection? A) Stealth B) Multipartite C) Polymorphic D) Worm Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 18) Viruses, adware, and spyware are referred to collectively as ________. A) bloatware B) grayware C) alertware D) firmware Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 9.05 Explain what malware, spam, and cookies are and how they impact your security. 116 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 19) ________ is a program that gathers information about your surfing habits without your knowledge. A) Adware B) Ghostware C) Shareware D) Spyware Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 9.05 Explain what malware, spam, and cookies are and how they impact your security. 20) Which of the following statements about cookies is NOT true? A) Cookies obtain your personal information by searching your hard drive. B) Cookies are text files. C) Cookies help companies determine the traffic flow through their website. D) Some companies sell the personal information found in cookies to other companies. Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 9.05 Explain what malware, spam, and cookies are and how they impact your security. 21) Social ________ is any technique that uses social skills to generate human interaction that entices individuals to reveal sensitive information. A) engineering B) theft C) pretexting D) pharming Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 9.06 Describe social engineering techniques, and explain strategies to avoid falling prey to them. 22) When malicious code is planted on your computer and alters your browser's ability to find web addresses, it is known as ________. A) phishing B) pharming C) pretexting D) polymorphing Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 9.06 Describe social engineering techniques, and explain strategies to avoid falling prey to them. 117 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 23) Using your computer for non-work activities while you are being paid to work is known as ________. A) cyberloafing B) cybersleeping C) cyberlazing D) cyberbreaking Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 9.06 Describe social engineering techniques, and explain strategies to avoid falling prey to them. 24) In computing, a ________ is named after a housing construction feature that slows the spread of fires from house to house. A) firehouse B) firebreak C) firewall D) fire extinguisher Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 9.07 Explain what a firewall is and how a firewall protects your computer from hackers. 25) Configuring a firewall to ignore all incoming packets that request access to a specific port is known as ________. A) packet filtering B) packet switching C) static addressing D) logical port blocking Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 9.07 Explain what a firewall is and how a firewall protects your computer from hackers. 26) Regarding computer protection, quarantining is defined as ________. A) updating your antivirus software B) placing a found virus in a secure area on the hard drive C) repairing an infected file D) deleting an infected file Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 9.08 Explain how to protect your computer from virus infection. 118 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 27) A(n) ________ is the portion of virus code that is unique to a particular computer virus. A) virus signature B) encryption code C) compression code D) virus pattern Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 9.08 Explain how to protect your computer from virus infection. 28) Rules for creating passwords include all of the following EXCEPT ________. A) keep your password a secret B) change your password frequently C) keep a master password that is the same for all of your accounts D) use letters, numbers, and symbols in your passwords Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 9.09 Describe how passwords and biometric characteristics can be used for user authentication. 29) One type of CAPTCHA is ________. A) antivirus software B) a password method C) the wavy hard-to-read letter and number sequence that you type to prove that you are human to a website D) a rootkit virus Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 9.09 Describe how passwords and biometric characteristics can be used for user authentication. 30) Which is NOT one of the four key pieces of personal information you should protect from identity thieves? A) Social Security number B) Anniversary C) Date of birth D) Street address Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 9.11 Describe the types of information you should never share online. 119 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 31) A(n) ________ backup makes a copy of all changes since the last backup. A) incremental B) full C) image D) data Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 9.12 List the various types of backups you can perform on your computing devices, and explain the various places you can store backup files. 32) A whole-house surge protector is installed ________. A) at the breaker panel B) at the power line from the street C) on each device and appliance D) on computers Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 9.13 Explain the negative effects environment and power surges can have on computing devices. 33) Victims of ________ can spend months, or even years, trying to repair their credit and eliminate fraudulent debts. Answer: identity theft Diff: 1 Objective: 9.01 Describe how identity theft is committed and the types of scams identity thieves perpetrate. 34) A botnet is a group of applications running on ________ computers in a DDoS attack. Answer: zombie Diff: 2 Objective: 9.02 Describe the different types of hackers and the tools they use. 35) For security reasons, you should be extremely wary of opening e-mail ________ such as Word files. Answer: attachments Diff: 1 Objective: 9.03 Explain what a computer virus is, why it is a threat to your security, how a computing device catches a virus, and the symptoms it may display. 36) A(n) ________ virus is a series of commands that is executed without your knowledge. Answer: script Diff: 2 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 120 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 37) A(n) ________ virus runs a program that searches for common types of data files, compresses them, and makes them unusable. Answer: encryption; ransomware Diff: 3 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 38) A(n) ________ virus is designed to infect multiple file types in an effort to fool antivirus software. Answer: multipartite Diff: 2 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 39) A(n) ________ virus temporarily erases its code from the files where it resides, and then hides in the active memory of the computer. Answer: stealth Diff: 1 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 40) A(n) ________-hat hacker illegally penetrates a system simply to demonstrate the hacker's expertise to the system administrator. Answer: grey; gray Diff: 2 Objective: 9.02 Describe the different types of hackers and the tools they use. 41) Another name for a sniffer is a(n) ________ analyzer. Answer: packet Diff: 2 Objective: 9.02 Describe the different types of hackers and the tools they use. 42) A(n) ________ can help block unwanted, unsolicited e-mail. Answer: spam filter Diff: 1 Objective: 9.05 Explain what malware, spam, and cookies are and how they impact your security. 43) Unwanted, unsolicited e-mail is referred to as ________. Answer: spam Diff: 1 Objective: 9.05 Explain what malware, spam, and cookies are and how they impact your security. 44) The most common kind of pretexting in cyberspace is ________. Answer: phishing Diff: 2 Objective: 9.06 Describe social engineering techniques, and explain strategies to avoid falling prey to them. 121 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 45) ________ is malware that tries to convince you that your computer is infected with a virus. Answer: Scareware Diff: 2 Objective: 9.06 Describe social engineering techniques, and explain strategies to avoid falling prey to them. 46) Social ________ is any technique that uses social skills to generate human interaction that entices individuals to reveal sensitive information. Answer: engineering Diff: 2 Objective: 9.06 Describe social engineering techniques, and explain strategies to avoid falling prey to them. 47) ________ is the act of tricking people into revealing sensitive information and is often associated with credit card fraud. Answer: Phishing Diff: 2 Objective: 9.06 Describe social engineering techniques, and explain strategies to avoid falling prey to them. 48) During the process of ________, antivirus software records key attributes about the files on your computer and keeps these statistics in a safe place on your hard drive. Answer: inoculation Diff: 2 Objective: 9.08 Explain how to protect your computer from virus infection. 49) The best defense against viruses is to install ________ software, which is specifically designed to detect viruses and protect your computer and files from harm. Answer: antivirus, anti-virus Diff: 1 Objective: 9.08 Explain how to protect your computer from virus infection. 50) ________ occur when a website downloads harmful software onto your computer. Answer: Drive-by downloads, drive by downloads Diff: 3 Objective: 9.08 Explain how to protect your computer from virus infection. 51) Devices that use a unique personal characteristic, such as a fingerprint, in place of a password are called ________ authentication devices. Answer: biometric Diff: 2 Objective: 9.09 Describe how passwords and biometric characteristics can be used for user authentication. 122 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 52) One way to protect your personal information on Facebook is to change your ________ settings. Answer: privacy Diff: 2 Objective: 9.11 Describe the types of information you should never share online. 53) A(n) ________ backup backs up only the files on a computer that have changed since the last time a backup was performed. Answer: incremental; partial Diff: 2 Objective: 9.12 List the various types of backups you can perform on your computing devices, and explain the various places you can store backup files. 54) A(n) ________ protects a computer against power surges. Answer: surge protector Diff: 1 Objective: 9.13 Explain the negative effects environment and power surges can have on computing devices. 55) ________ alarm software is an inexpensive theft deterrent for mobile devices. Answer: Motion Diff: 2 Objective: 9.14 Describe the major concerns when a device is stolen and strategies for solving the problems. 56) Ethical hackers are also known as white-hat hackers. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 9.02 Describe the different types of hackers and the tools they use. 57) A denial-of-service attack can be used to deny hackers access to a computer system. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 9.02 Describe the different types of hackers and the tools they use. 58) Creating and spreading online viruses is a cybercrime. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 9.03 Explain what a computer virus is, why it is a threat to your security, how a computing device catches a virus, and the symptoms it may display. 59) All viruses cause serious destruction of computer data. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 9.03 Explain what a computer virus is, why it is a threat to your security, how a computing device catches a virus, and the symptoms it may display. 123 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 60) A worm does NOT require human interaction to spread to other computers. Answer: TRUE Diff: 3 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 61) A stealth virus is designed to infect multiple file types to fool the antivirus software. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 62) A time bomb virus can be triggered on a certain date. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 63) The terms virus and worm mean the same thing. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 64) An encryption virus replicates itself onto a hard drive's master boot record. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 65) A macro virus is a virus that is attached to a file. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 9.04 List the different categories of computer viruses, and describe their behaviors. 66) A virus signature is a portion of virus code that is unique to a particular computer virus. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 9.08 Explain how to protect your computer from virus infection. 67) Currently, there are no antivirus programs for mobile devices. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 9.08 Explain how to protect your computer from virus infection. 68) To create a secure password, you should use a mixture of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 9.09 Describe how passwords and biometric characteristics can be used for user authentication. 124 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 69) You should use the same password for each system or website you need to access. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 9.09 Describe how passwords and biometric characteristics can be used for user authentication. 70) Virtual private networks (VPNs) are secure networks that are established without using the public Internet infrastructure. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Objective: 9.10 Describe ways to surf the web anonymously. 71) Since you can always redownload program files, you do not need to include them in backups. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 9.12 List the various types of backups you can perform on your computing devices, and explain the various places you can store backup files. 72) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. Trojan horse pretexting cookie botnet time bomb A. text file for storing personal preferences pertaining to websites B. program that appears to be something useful or desirable C. virus that is triggered by the passage of time or on a certain date D. creating a scenario that sounds legitimate enough that someone will trust you E. programs that run on a large number of zombie computers Answer: B, D, A, E, C Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 125 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 73) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. grey-hat hacker black-hat hacker cyberloafing social engineering white-hat hacker A. techniques used to manipulate people into performing actions or divulging confidential information B. an unethical hacker C. flaunts expertise to the administrator of a system D. an ethical hacker E. using an employer's computer for non-work activities Answer: C, B, E, A, D Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 74) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. packet filtering IP address firewall CAPTCHA biometric authentication device A. program that generates distorted text and requires that it be typed into a box B. reads a unique personal characteristic and converts its pattern to a digital code C. hardware or software for protecting computers from hackers D. a computer's identity on the Internet E. method for selectively allowing certain requests to access ports Answer: E, D, C, A, B Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 126 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 75) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. II. III. IV. V. worm computer virus encryption virus polymorphic virus logic bomb A. virus that is triggered when a file is opened or program is started a certain number of times B. attempts to travel between systems through network connections to spread an infection C. virus that changes its own code to avoid detection D. program that attaches itself to another program and attempts to spread itself to other computers through the exchange of files E. a program that renders your computer files unusable by compressing them Answer: B, D, E, C, A Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 76) Match each of the following terms to its meaning: I. spear phishing II. rootkit III. scareware IV. zombie V. spyware A. program that allows hackers to gain access to your computer without your knowledge B. malware on your computer used to convince you that your computer has a virus C. a computer controlled by a hacker D. sending e-mails to people known to be customers of a company in an effort to get individuals to reveal sensitive data E. transmits information about you, such as your Internet-surfing habits Answer: D, A, B, C, E Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 10 Behind the Scenes: Software Programming 1) What is the first step of the system development life cycle (SDLC)? A) Design B) Analysis C) Problem and Opportunity Identification D) Development Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 10.02 Summarize the stages of the system development life cycle (SDLC). 127 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 2) ________ is the process of translating a task into a series of commands that a computer will use to perform the task. A) Debugging B) Programming C) Analyzing D) Diagramming Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 10.03 Define programming and list the steps in the program development life cycle (PDLC). 3) Which of the following is the final stage of the program development life cycle (PDLC)? A) Making a Plan B) Coding C) Testing and Documentation D) Debugging Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 10.03 Define programming and list the steps in the program development life cycle (PDLC). 4) The set of specific, sequential steps that describe exactly what a computer program must do to complete the work is called a(n) ________. A) Beta code B) structure chart C) algorithm D) working plan Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 10.03 Define programming and list the steps in the program development life cycle (PDLC). 128 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) Translating an algorithm into a programming language is called ________. A) interpreting B) coding C) compiling D) executing Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 10.03 Define programming and list the steps in the program development life cycle (PDLC). 6) A clearly stated objective of how a program should work and how it responds to errors is called the ________. A) SDLC B) problem statement C) compilation D) execution Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 10.04 Describe how programmers construct a problem statement from a description of a task. 7) Which of the following provides a visual representation of the patterns of an algorithm? A) Flowchart B) Pseudocode C) Gantt chart D) Flow analysis Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 8) The keywords used in programming languages that use decisions to redirect the flow of a program are called ________. A) pseudocode B) control structures C) flowcharts D) operators Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 129 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 9) A loop decision point for an algorithm consists of three features: an initial value, a set of actions to be performed, and a(n) ________. A) class B) operator C) test condition D) documentation plan Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 10) ________ breaks down a problem into a series of high-level tasks and continues to break each task into successively more detailed subtasks. A) Object-oriented analysis B) Top-down design C) Bottom-up design D) Inheritance Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 11) Object-oriented ________ are defined by the information (data) and the actions (methods) associated with them. A) blocks B) classes C) units D) fields Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 12) In object-oriented programming, ________ allows a new class to automatically use all the data and methods of an existing class. A) reusability B) regression C) scalability D) inheritance Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 130 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 13) An example of a first-generation language is ________. A) BASIC B) machine language C) COBOL D) assembly language Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 14) The capability of moving a completed programming solution easily from one type of computer to another is known as ________. A) portability B) scalability C) transferability D) inheritance Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 15) SQL is an example of a ________ category programming language. A) 2GL B) 3GL C) 4GL D) 5GL Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 16) Which statement does NOT describe fifth-generation languages? A) They are the most "natural" of languages. B) They use a set of short, English-based commands (such as ADD) that speak directly to the CPU. C) Problems are presented as a series of facts or constraints rather than as a specific algorithm. D) The system of facts can be queried. Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 131 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 17) The process that converts program code into machine language is called ________. A) documentation B) variable declaration C) compilation D) execution Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 18) ________ is the set of instructions that programmers have written in a higher-level language. A) Executable code B) Base code C) Compiled code D) Source code Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 19) An integrated development environment (IDE) is a ________. A) program that helps interpret code B) tool that converts one programming language into a different programming language C) collection of tools that helps programmers write and test their programs D) program that translates code into binary 1s and 0s and ignores comments Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 20) Division by zero is a ________ error that is caught when the program executes. A) compiler B) runtime C) syntax D) logical Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 10.07 Identify the role of debugging in program development. 21) Before its final commercial release, a(n) ________ version of software may be offered to certain test sites or to interested users free or at a reduced cost. A) gamma B) release to manufacturers (RTM) C) beta D) general availability (GA) Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 10.08 Explain the importance of testing and documentation in program development. 132 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 22) Which refers to a text-based approach to documenting an algorithm? A) Syntax B) Pseudocode C) Keywords D) Data types Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 23) Which is NOT a key factor a programmer uses in selecting the language for a project? A) Space available B) Number of inputs required C) Speed required D) Type of target application Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 10.10 Summarize the considerations in identifying an appropriate programming language for a specific setting. 24) ________ is a programming language that can be used to create a wide range of Windows applications. A) Visual Basic B) PHP C) BASIC D) HTML Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 25) Which language is the most popular language for writing Apple macOS applications? A) C++ B) HTML C) Objective C D) Java Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 26) A small Java-based program is called a ________. A) Java class B) JSP C) JavaScript D) Java applet Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 133 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 27) Special symbols called tags are used in which of the following languages? A) C# B) Java C) HTML/XHTML D) C++ Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 28) Which of the following would NOT be used to build websites with interactive capabilities? A) Active Server Pages (ASP) B) PHP (PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor) C) FORTRAN D) Java Server Pages (ISP) Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 29) ________ enables users to define their own data-based tags and facilitates the exchange of information between websites. A) HTML B) XHTML C) XML D) PHP Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 30) Corona and App Inventor can be used to develop ________. A) complex web applications B) apps for mobile devices C) Mac software D) Web pages Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 31) You can automate features by using custom-built miniprograms called ________. Answer: macros Diff: 2 Objective: 10.01 Describe the importance of programming to both software developers and users. 32) The programming term SDLC stands for ________. Answer: system development life cycle Diff: 1 Objective: 10.02 Summarize the stages of the system development life cycle (SDLC). 134 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 33) In a(n) ________ system, each step is dependent on the previous step being completed. Answer: waterfall; "waterfall" Diff: 2 Objective: 10.02 Summarize the stages of the system development life cycle (SDLC). 34) A(n) ________ is a visual diagram of a process that includes any decisions that are made along the way. Answer: flowchart; data-flow diagram Diff: 2 Objective: 10.02 Summarize the stages of the system development life cycle (SDLC). 35) In the ________ phase of the SDLC, exploration of the depth of a problem and development of program specifications take place. Answer: analysis Diff: 2 Objective: 10.02 Summarize the stages of the system development life cycle (SDLC). 36) In the "Making a Plan" step of the PDLC, a(n) ________ is written in natural, ordinary language describing exactly what the computer program is to do. Answer: algorithm Diff: 2 Objective: 10.03 Define programming and list the steps in the program development life cycle (PDLC). 37) ________ is the part of the problem statement that describes what a program should do if the input data is invalid. Answer: Error handling Diff: 2 Objective: 10.04 Describe how programmers construct a problem statement from a description of a task. 38) The flowchart shape for a binary decision is a(n) ________. Answer: diamond Diff: 2 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 39) A(n) ________ is a control structure that continues to be performed while a test condition is true. Answer: loop; repeating loop Diff: 2 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 135 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 40) Scratch and App Inventor are considered ________ programming languages. Answer: visual; top down Diff: 1 Objective: 10.10 Summarize the considerations in identifying an appropriate programming language for a specific setting. 41) In object-oriented terms, an original class is called the ________ class. Answer: base Diff: 2 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 42) In object-oriented terms, a new, modified class is called the ________ class. Answer: derived Diff: 3 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 43) SQL stands for ________. Answer: Structured Query Language Diff: 3 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 44) ________-generation languages use symbols and commands to help programmers tell the computer what to do. Answer: Third; 3rd Diff: 3 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 45) A(n) ________ translates source code into an intermediate form of code, line by line. Answer: interpreter Diff: 3 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 46) A(n) ________ program is the binary sequence that has been translated from source code by a compiler for use by the CPU. Answer: executable Diff: 2 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 136 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 47) A(n) ________ error is caused by not following the strict, precise set of rules for a specific programming language. Answer: syntax Diff: 2 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 48) The programming term IDE stands for ________. Answer: integrated development environment Diff: 3 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 49) The process of running a program over and over to find and repair errors and make sure the program behaves in the way it should is known as ________. Answer: debugging Diff: 1 Objective: 10.07 Identify the role of debugging in program development. 50) ________ and runtime errors are caught only when a program executes. Answer: Logical; Logical errors Diff: 2 Objective: 10.07 Identify the role of debugging in program development. 51) Most browsers can execute Java ________, which are small Java-based programs. Answer: applets Diff: 2 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 52) When a large project begins, a programmer can build a(n) ________, which is a small model of what the final program will look like when it is finished. Answer: prototype Diff: 2 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 53) HTML uses special symbols called ________ to control how information is displayed on the web. Answer: tags Diff: 1 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 54) The MUMPS language is often used to build ________ databases. Answer: clinical; medical Diff: 2 Objective: 10.12 State key principles in the development of future programming languages. 137 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 55) Programming is necessary when the software needed to accomplish a task is not available. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 10.01 Describe the importance of programming to both software developers and users. 56) The program specification is a clear statement of the goals and objectives of the project. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 10.02 Summarize the stages of the system development life cycle (SDLC). 57) Data is the raw input that users have at the start of the job. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 10.04 Describe how programmers construct a problem statement from a description of a task. 58) The standard set of vocabulary for pseudocode is specific and detailed. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 59) A data-flow diagram provides a visual representation of an algorithm. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Objective: 10.02 Summarize the stages of the system development life cycle (SDLC). 60) Bottom-up design is a systematic approach in which a problem is broken into a series of high-level tasks. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 61) When programmers need to create several different examples of a class, each is known as an object. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 138 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 62) Inheritance means that the data and methods of an existing class can be extended and customized to fit a new class. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 10.05 Explain how programmers use flow control and design methodologies when developing algorithms. 63) Prolog is an example of a fourth-generation programming language. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 64) Second-generation languages are also known as assembly languages. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 65) A compiler translates the source code into an intermediate form of code, line by line. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 66) One IDE can often be configured to support many different languages. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 67) During the program debugging stage, the people who will use the program test the software. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 10.07 Identify the role of debugging in program development. 68) Syntax errors are caught only when a program executes. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 69) A Windows application which demands a lot of raw processing power to execute repetitive complex calculations is a good candidate for the object-oriented programming language C/C++. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 10.11 Compare and contrast modern programming languages. 139 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 70) Eventually all programming languages will merge into one universal language. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 10.12 State key principles in the development of future programming languages. 71) Match each of the following generations to its language: I. II. III. IV. V. 1GL 2GL 3GL 4GL 5GL A. assembly language B. SQL C. machine language D. Prolog E. COBOL Answer: C, A, E, B, D Diff: 3 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 72) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. portability reusability inheritance method data A. a new class can automatically pick up data and methods of an existing class B. the capability to move a completed programming solution easily from one type of computer to another C. the ability to apply classes from other projects to a new project D. an object-oriented action or behavior E. raw input Answer: B, C, A, D, E Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 140 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 73) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. source code syntax compiler interpreter operator A. program that translates code into binary 0s and 1s and ignores comments B. agreed-on set of rules defining how the language must be structured C. translates source code line by line into an intermediate form of code D. coding symbol that represents a fundamental action of a language E. programmers' instructions written in a higher-level language Answer: E, B, A, C, D Diff: 3 Objective: 10.06 Discuss the categories of programming languages and the roles of the compiler and the integrated development environment (IDE) in coding. 74) Match each of the following steps of SDLC development to its position in the development process. I. II. III. IV. V. development design analysis testing and installation problem/opportunity identification A. first step B. second step C. third step D. fourth step E. fifth step Answer: D, C, B, E, A Diff: 3 Objective: 10.02 Summarize the stages of the system development life cycle (SDLC). 141 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 75) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. pseudocode error handling source code binary decision variable A. program instructions written in a higher-level language B. text-based approach to documenting an algorithm C. items allocated storage space in RAM D. managing what a program should do if input data is invalid E. can be answered in only two ways (for example, yes/no) Answer: B, D, A, E, C Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 11 Behind the Scenes: Databases and Information Systems 1) A ________ is a collection of related data that can be stored, sorted, organized, and queried. A) database B) document C) memo D) macro Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 11.01 Explain what a database is and why databases are useful. 2) If a school keeps two lists, one for student registration and one for student financial information, both containing name and address information, this is an example of data ________. A) integrity B) redundancy C) completeness D) normalization Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 11.01 Explain what a database is and why databases are useful. 3) Data ________ means that the data contained in a database is accurate and reliable. A) efficiency B) integrity C) redundancy D) consistency Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 11.02 Discuss the benefits of using a database. 142 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 4) Data ________ helps to ensure data integrity by maintaining information in only one place. A) flexibility B) redundancy C) mapping D) centralization Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 11.02 Discuss the benefits of using a database. 143 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) ________ is used to ensure that data is organized most efficiently in a database. A) Consistency checking B) Validation C) Normalization D) Range checking Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 11.02 Discuss the benefits of using a database. 6) ________ databases are the most commonly used electronic databases. A) Relational B) Flat-file C) Multidimensional D) Object-oriented Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 11.03 Describe features of relational databases. 7) A ________ relationship indicates that for each record in a table, there is only a single corresponding record in a related table. A) many-to-one B) one-to-many C) one-to-one D) many-to-many Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 11.03 Describe features of relational databases. 8) Nontraditional data in object-oriented databases such as audio clips, video clips, pictures, and very large documents are called ________ data. A) enterprise B) structured C) unstructured D) multidimensional Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 11.04 Describe features of object-oriented databases. 9) Data in a multidimensional database is organized in a ________ format. A) linear B) modular C) cube D) cellular Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 11.05 Describe features of multidimensional databases. 144 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 10) In a database, the term ________ is synonymous with a category of data. A) field B) record C) row D) table Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 11) In a database, a group of related records is referred to as a(n) ________. A) memo B) field C) object D) table Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 12) In a Microsoft Access database, something like the Gettysburg Address would be stored in a(n) ________ field. A) text B) long text C) short text D) object Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 13) You can set a ________, which is automatically displayed in a field unless the user enters something different. A) default value B) relation C) field type D) numeric check Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 14) Which of the following is a likely primary key in a student information record? A) Last name B) Date of birth C) Student ID number D) First name Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 145 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 15) ________ means that for each value in the foreign key of one table, there is a corresponding value in the primary key of another table. A) Referential integrity B) Normalization C) Database consistency D) Record integrity Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 16) A ________ check would be used in a field to restrict the fines for speeding violations so that they fall between $50 and $250. A) completeness B) range C) consistency D) numeric Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 17) A(n) ________ check determines whether a required field such as LastName was filled in. A) completeness B) range C) consistency D) alphabetic Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 18) A ________ check compares the values of data in two or more fields to see whether those values are reasonable. A) correctness B) range C) consistency D) numeric Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 19) You would use a ________ in a database to temporarily display records of residents for the city of Boston. A) sieve B) filter C) validation rule D) field constraint Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 146 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 20) A(n) ________ is a way of retrieving information from one or more tables that defines a particular subset of data. A) validation rule B) field constraint C) enquiry D) query Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 21) A ________ displays a subset of data from a table (or tables) based on the specified criteria. A) table query B) join query C) select query D) criteria query Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 22) SQL uses ________ to extract records from a database by using English-like expressions that have variables and operations. A) Boolean algebra B) relational algebra C) primary keys D) foreign keys Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 23) ________ involves taking data from your database and putting it into an electronic file in a format that another external application or database can recognize. A) Exporting B) Importing C) Enhancing D) Extracting Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 147 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 24) A data ________ is a large-scale collection of data that contains and organizes all of an organization's data in one place. A) mart B) chain C) warehouse D) storehouse Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 11.08 Explain what data warehouses and data marts are and how they are used. 25) Data staging consists of all of the following steps, EXCEPT ________. A) transforming the data B) mining the data C) storing the data in a warehouse D) extracting the data Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 11.08 Explain what data warehouses and data marts are and how they are used. 26) Big data analytics is usually associated with ________ services. A) office support B) data warehouse C) management information D) decision support Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 11.08 Explain what data warehouses and data marts are and how they are used. 27) In a transaction-processing system (TPS), if the TPS database can be queried and updated while the transaction is taking place, this is called ________ processing. A) direct B) batch C) real-time D) immediate Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 11.10 Describe the main types of business information systems and how they are used by business managers. 148 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 28) Management information systems (MIS) provide ________ reports, which show conditions that are unusual or need attention from users of the system. A) detail B) summary C) exception D) expert Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 11.10 Describe the main types of business information systems and how they are used by business managers. 29) Siri, the personal assistant application on Apple's iPhone is an example of a ________. A) natural language processing (NLP) system B) decision support system (DSS) C) management information system (MIS) D) database management system (DBMS) Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 11.10 Describe the main types of business information systems and how they are used by business managers. 30) ________ is the branch of computer science that attempts to create computers that think like humans. A) Natural language processing B) Expert systems C) Artificial intelligence D) Enterprise resource planning Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 11.10 Describe the main types of business information systems and how they are used by business managers. 31) A database that allows data to be maintained in a single location provides data ________. Answer: centralization Diff: 2 Objective: 11.02 Discuss the benefits of using a database. 32) In a relational database, a(n) ________ relationship indicates that a record that appears only one time in a table, may appear multiple times in a related table. Answer: one-to-many; one to many Diff: 1 Objective: 11.03 Describe features of relational databases. 33) ________ databases are better than relational databases at handling unstructured data such as audio clips, video clips, and pictures. Answer: Object-oriented; Object oriented Diff: 2 Objective: 11.04 Describe features of object-oriented databases. 149 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 34) A(n) ________ database stores data in more than two dimensions, as opposed to relational databases, which store data in two-dimensional tables. Answer: multidimensional; multi-dimensional Diff: 2 Objective: 11.05 Describe features of multidimensional databases. 35) A data dictionary is also referred to as a(n) ________. Answer: database schema Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 36) A group of related records is called a(n) ________. Answer: table; file Diff: 1 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 37) Data that describes other data is called ________. Answer: metadata Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 38) In a database, another term for a table is a(n) ________. Answer: file Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 39) In a Microsoft Access database, an active web page, e-mail address, or existing file is stored as a(n) ________ field. Answer: hyperlink Diff: 3 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 40) When working with a relational database, each record must have a(n) ________ key field, which has a value unique to that record. Answer: primary Diff: 1 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 41) Referential integrity means that for each value in the ________ field of a table, there is a corresponding value in the primary key of the related table. Answer: foreign key Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 150 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 42) A(n) ________ provides a view of data fields to be filled in with appropriate labels to assist a user in entering data into the database. Answer: input form; form; user form Diff: 2 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 43) ________ is the process of ensuring that the data entered into a field meets specified guidelines. Answer: Validation; Data validation Diff: 2 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 44) A field ________ is a property that must be met before an entry can be accepted into the field. Answer: constraint Diff: 2 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 45) To temporarily display records from a single table that match certain criteria, you would use a(n) ________. Answer: filter Diff: 2 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 46) When using SQL, a(n) ________ query is used to extract data from two or more tables. Answer: join Diff: 2 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 47) The data in a data warehouse is ________, meaning it does not all pertain to one period in time. Answer: time-variant; time variant Diff: 2 Objective: 11.08 Explain what data warehouses and data marts are and how they are used. 48) ________ data is information about how users of a company's website move through the web pages. Answer: Clickstream Diff: 2 Objective: 11.08 Explain what data warehouses and data marts are and how they are used. 49) When creating a data warehouse, ________ is the process that extracts data from source databases, reformats the data, and stores them in the warehouse. Answer: data staging Diff: 2 Objective: 11.08 Explain what data warehouses and data marts are and how they are used. 151 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 50) A(n) ________ is created from a large data business warehouse to analyze a single component of the business. Answer: data mart Diff: 3 Objective: 11.08 Explain what data warehouses and data marts are and how they are used. 51) ________ is used to analyze large amounts of data and identify unseen patterns or trends. Answer: Data mining Diff: 2 Objective: 11.09 Describe data mining and how it works. 52) A business that updates its records all at once at the end of the business day uses ________ processing. Answer: batch Diff: 2 Objective: 11.10 Describe the main types of business information systems and how they are used by business managers. 53) A(n) ________ report provides a consolidated picture of detailed data and usually includes some calculation or visual displays of information and is generated by a MIS. Answer: summary Diff: 3 Objective: 11.10 Describe the main types of business information systems and how they are used by business managers. 54) A(n) ________ tries to replicate the decision-making processes of human experts to solve specific problems. Answer: expert system Diff: 1 Objective: 11.10 Describe the main types of business information systems and how they are used by business managers. 55) Data redundancy ensures that the data contained in the database is accurate and reliable. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 11.01 Explain what a database is and why databases are useful. 56) Normalization means that there are no data entry errors in a database. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 11.02 Discuss the benefits of using a database. 57) In a relational database, when two tables have a common field, the link between the tables is known as a hyperlink. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 11.03 Describe features of relational databases. 152 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 58) A street address field is an example of a field that should have a default value. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 59) A group of related records is called a table. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 60) In an employee database, an employee's ID number, last name, first name, company position, address, city, state, and Zip Code make up a record. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 61) When using Access, the text of the Declaration of Independence would be stored in a short text field. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 62) Employees' last name would usually make an appropriate primary key field. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 63) A database schema defines the name, data type, and length of each field in the database. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 11.06 Describe how relational databases organize and define data. 64) Most databases can import electronic data from other software applications. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 65) A filter is limited to extracting data from a single table. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. 66) Small slices of a data mart are called data warehouses. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 11.08 Explain what data warehouses and data marts are and how they are used. 153 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 67) The information in a data mart spans an entire enterprise. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 11.08 Explain what data warehouses and data marts are and how they are used. 68) Data mining analyzes and investigates large amounts of data with the intention of discovering significant patterns or trends. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 11.09 Describe data mining and how it works. 69) Real-time processing means that transactions are updated when they occur. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 11.10 Describe the main types of business information systems and how they are used by business managers. 70) A summary report generated by an MIS provides a list of the transactions that occurred during a specified time period. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 11.10 Describe the main types of business information systems and how they are used by business managers. 71) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. field database record table primary key A. a group of related fields B. a category of information in a database C. a collection of related data that can be stored, sorted, organized, and queried D. a field that has a value unique to each record E. a group of related records Answer: B, C, A, E, D Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 154 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 72) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. data mining expert system data mart artificial intelligence data staging A. small slice of a data warehouse B. includes transforming data to fit into a data warehouse C. process by which great amounts of data are analyzed and investigated D. software that tries to replicate the decision making of human specialists E. attempts to create computers that think like humans Answer: C, D, A, E, B Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 73) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. office support system (OSS) natural language processing (NLP) management information system (MIS) decision support system (DSS) enterprise resource planning (ERP) system A. provides managers with timely and accurate information B. software system that integrates multiple system data sources and ties together the various processes of an organization C. helps managers develop solutions for specific problems D. assists employees in day-to-day tasks and communication E. communicates with computer systems using a natural spoken or written language Answer: D, E, A, C, B Diff: 3 Objective: 11.10 Describe the main types of business information systems and how they are used by business managers. 155 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 74) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. data warehouse batch processing relational database real-time processing data dictionary A. when a database is queried and updated as a transaction is taking place B. organizes data into various tables based on logical groupings C. defines the name, data type, and length of each field in a database D. large-scale collection of data E. transaction data that are processed all at once Answer: D, E, B, A, C Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 75) Match the following data checks to their definition: I. II. III. IV. V. alphabetic numeric completeness consistency range A. ensures data entered into the database fall within a certain set of values B. ensures that all required fields have data entered into them C. confirms that only numbers are entered into a field D. confirms that only textual characters are entered into a field E. compares values in two or more fields to see whether the values are reasonable Answer: D, C, B, E, A Diff: 3 Objective: 11.07 Describe how data is inputted and managed in a database. Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 12 Behind the Scenes: Networking and Security in the Business World 1) A ________ is a group of two or more computers, or nodes, configured to share information and resources. A) router B) bus C) bridge D) network Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 12.01 List the advantages for businesses of installing a network. 2) A ________ network can contain servers as well as individual computers. 156 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 A) client/server B) peer-to-peer C) switch D) bridge Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 12.02 Explain the differences between a client/server network and a peer-to-peer network. 3) In a ________ network, each node connected to the network communicates directly with every other node. A) client/server B) peer-to-peer C) router D) bridge Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 12.02 Explain the differences between a client/server network and a peer-to-peer network. 4) The computers in a lab on a floor of a building would be connected using a ________. A) WAN B) LAN C) MAN D) PAN Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 12.03 Describe the common types of client/server networks as well as other networks businesses use. 157 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) Cars often have ________ connectivity. A) Wi-Fi and Bluetooth B) ROVER-5 and ethernet C) IPv7 and IPv6 D) Exhaust and fuel injection Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 12.03 Describe the common types of client/server networks as well as other networks businesses use. 6) A ________ uses the Internet communications infrastructure to build a secure and private network. A) PAN B) WAN C) VPN D) HAN Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 12.03 Describe the common types of client/server networks as well as other networks businesses use. 7) A(n) ________ server tracks who is logging on to the network as well as which services on the network are available to each user. A) application B) authentication C) dedicated D) file Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 12.04 List the common types of servers found on client/server networks. 8) A(n) ________ server is a server that stores and manages files for network users. A) file B) e-mail C) print D) database Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 12.04 List the common types of servers found on client/server networks. 158 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 9) A print server uses a print ________ as a software holding area for jobs waiting to be printed. A) stack B) spooler C) logger D) heap Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 12.04 List the common types of servers found on client/server networks. 10) Which of the following is NOT a common network topology? A) Star B) Cluster C) Linear bus D) Ring Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 11) A network ________ is a set of rules for how information and communications are exchanged. A) protocol B) token C) frame D) packet Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 12) Ring networks use the ________ method to avoid data collisions. A) packet screening B) active-check C) token D) passive-check Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 159 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 13) The ends of the cable in a bus network use a(n) ________ to absorb signals so that they are not reflected back to network components that have already received the signals. A) endcap B) terminator C) stopper D) block Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 14) In a ________ network, data collisions can occur fairly easily because the network is essentially composed of a single cable. A) star B) bus C) hierarchical D) cluster Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 15) Which of the following is the most commonly used client/server network topology? A) Star B) Cluster C) Ring D) Hierarchical Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 16) In an Ethernet network, the signal that is sent to indicate a signal collision is called a ________ signal. A) hit B) crash C) stop D) jam Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 160 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 17) A ________ topology uses more than one type of topology when building a network. A) hybrid B) multiple-use C) fusion D) crossover Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 18) ________ is the amount of data that can be transmitted across a transmission medium measured in bits per second. A) Data capacity B) Scalability C) Bandwidth D) Infusion Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 19) Which of the following is NOT a major factor to consider when selecting network cabling? A) Cable diameter B) Interference C) Maximum run length D) Bandwidth Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 20) ________ cable is NOT subject to electromagnetic interference or radio frequency interference. A) Twisted-pair B) Fiber-optic C) Polycarbonate D) Coaxial Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 21) For business networks, which of the following is NOT one of the main cable types? A) Twisted-pair B) Polyvinyl C) Coaxial D) Fiber-optic Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 161 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 22) Most wired home networks use ________ cable, which is most susceptible to interference. A) fiber-optic B) unshielded twisted-pair C) Wi-Fi D) coaxial Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 23) ________ is the standard communications protocol used on most client/server networks. A) Ethernet B) NOS C) Mac D) VPN Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 12.07 Describe how network adapters help data move around a network. 24) The physical address assigned to each network adapter is called its ________ address. A) network access control (NAC) B) physical address control (PAC) C) network physical address (NPA) D) media access control (MAC) Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 12.08 Define MAC addresses, and explain how they are used to move data around a network. 25) A(n) ________ address is the address that external entities use when communicating with your network. A) ALU B) MAC C) WAP D) IP Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 12.08 Define MAC addresses, and explain how they are used to move data around a network. 26) A ________ sends data from one collision domain to another. A) switch B) bridge C) link D) router Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 12.09 List the various network navigation devices, and explain how they help route data through networks. 162 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 27) A ________ sends information between two networks. A) repeater B) switch C) bridge D) router Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 12.09 List the various network navigation devices, and explain how they help route data through networks. 28) A ________ keeps your computer safe by determining who is trying to access it. A) gateway B) firewall C) hub D) switch Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 29) Packet ________ is a form of protection for your computer that looks at each packet that comes into your computer network. A) viewing B) examination C) scanning D) screening Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 30) A(n) ________ is a heavily secured server located between a company's secure internal network and its firewall. A) transitional B) iron-clad C) bastion host D) proxy Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 163 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 31) Configuring an account to disable itself after a set number of login attempts using invalid passwords is a method of countering a ________. A) brute force attack B) spammer C) worm D) Trojan horse Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 32) A(n) ________ network is often the type of network that is set up in a home or very small business. Answer: peer-to-peer (P2P); peer-to-peer; P2P Diff: 2 Objective: 12.02 Explain the differences between a client/server network and a peer-to-peer network. 33) ________ means that additional users can easily be added to a network without affecting the performance of the other network nodes. Answer: Scalability Diff: 2 Objective: 12.02 Explain the differences between a client/server network and a peer-to-peer network. 34) A(n) ________ is made up of two or more LANs that are miles apart. Answer: wide area network (WAN); Wide Area Network; WAN Diff: 2 Objective: 12.03 Describe the common types of client/server networks as well as other networks businesses use. 35) A(n) ________ is a private network that is used exclusively by a select group of employees, customers, suppliers, volunteers, or supporters. Answer: intranet Diff: 2 Objective: 12.03 Describe the common types of client/server networks as well as other networks businesses use. 36) ________ technology for a VPN places data packets inside other data packets. Answer: Tunneling Diff: 3 Objective: 12.03 Describe the common types of client/server networks as well as other networks businesses use. 164 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 37) A(n) ________ is an area of an intranet to which only certain external users have access. Answer: extranet Diff: 2 Objective: 12.03 Describe the common types of client/server networks as well as other networks businesses use. 38) A(n) ________ server is maintained by a hosting company and is connected to an internal network using the Internet. Answer: cloud Diff: 2 Objective: 12.04 List the common types of servers found on client/server networks. 39) A(n) ________ server is a server used to fulfill one specific purpose. Answer: dedicated Diff: 1 Objective: 12.04 List the common types of servers found on client/server networks. 40) A library book reservation service is a good example of a use for a(n) ________ server. Answer: database Diff: 2 Objective: 12.04 List the common types of servers found on client/server networks. 41) A(n) ________ server is used to host an Internet site. Answer: web Diff: 1 Objective: 12.04 List the common types of servers found on client/server networks. 42) A ring topology is also known as a(n) ________ topology. Answer: loop; token-ring; token ring Diff: 2 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 43) Because of its centralized design, a(n) ________ topology is the simplest to troubleshoot and repair. Answer: star Diff: 2 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 44) Fluorescent lights and machinery with motors or transformers are common sources of ________ emissions. Answer: electromagnetic interference (EMI); electromagnetic interference; EMI Diff: 3 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 165 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 45) ________ is a type of network interference for cable transmission media that can be caused by nearby television or radio signals. Answer: Radio frequency interference (RFI); Radio frequency interference; RFI Diff: 1 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 46) A(n) ________ network cable contains a glass or plastic core. Answer: fiber-optic; fiber optic Diff: 1 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 47) ________ network cable is the most costly to install. Answer: Fiber-optic; Fiber optic Diff: 2 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 48) A(n) ________ provides wireless devices with a sending and receiving connection point to the network. Answer: wireless access point (WAP); wireless access point; WAP Diff: 1 Objective: 12.07 Describe how network adapters help data move around a network. 49) In networking terminology, NIC stands for ________. Answer: network interface card Diff: 2 Objective: 12.07 Describe how network adapters help data move around a network. 50) A(n) ________ is a container that can hold multiple data packets that are sent together. Answer: frame Diff: 3 Objective: 12.08 Define MAC addresses, and explain how they are used to move data around a network. 51) A(n) ________ is a device that reads information from a magnetic strip on the back of a credit card-like identification card. Answer: access card reader; card reader Diff: 2 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 52) ________ is the process that requires users to prove that they have permission to access a computer network. Answer: Authentication Diff: 2 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 166 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 53) A(n) ________ can often be equipped to act as a hardware firewall. Answer: router Diff: 2 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 54) A(n) ________ server acts as a liaison between an internal network and an external network. Answer: proxy Diff: 2 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 55) Retinal scanning is an example of ________ authentication. Answer: biometric Diff: 1 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 56) Identification badges and smart keys are examples of ________ objects that users carry to identify themselves and that allow them access to a computer system or computer facility. Answer: possessed Diff: 2 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 57) P2P networks become difficult to administer when they have large numbers of users. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 12.02 Explain the differences between a client/server network and a peer-to-peer network. 58) In a client/server network, each network node communicates directly with every other node on the network. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 12.02 Explain the differences between a client/server network and a peer-to-peer network. 59) An international company like Microsoft would use a MAN to connect all of its computers. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 12.03 Describe the common types of client/server networks as well as other networks businesses use. 167 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 60) Data flows in both directions around the ring in a ring network. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 61) In an active topology, each node helps to move data through a network. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 12.05 Describe the common types of network topologies and the advantages and disadvantages of each one. 62) Transmission media comprise the system that data takes to flow between devices on the network. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 63) Since data transmissions can pass through fiber-optic cable in only one direction, at least two fibers are required to enable transmission of data in both directions. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 64) Crosstalk interference is the tendency of signals on one twisted-pair wire to interfere with signals on the wire next to it. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 65) Wireless access points can provide coverage wherever employees are working with portable devices, such as in conference rooms. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 12.06 Describe the types of wired and wireless transmission media used in networks. 66) MAC addresses are restricted to Macintosh computers. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 12.08 Define MAC addresses, and explain how they are used to move data around a network. 67) MAC addresses and IP addresses are the same thing. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 12.08 Define MAC addresses, and explain how they are used to move data around a network. 168 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 68) A bridge sends information between two networks. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 12.09 List the various network navigation devices, and explain how they help route data through networks. 69) A phishing attack is an attempt to access an account by repeatedly trying different passwords. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 70) Worms often try to disguise their origins by using a bogus IP address instead of using an authorized IP address belonging to the network. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 71) A facial-recognition scanner is an example of a biometric authentication device. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 12.11 List major security threats to networks, and explain how network administrators mitigate these threats. 72) Match each of the following dedicated servers to its function: I. II. III. IV. V. authentication web cloud database application A. acts as a repository for application software B. keeps track of user logins to the network and which services are available to each user C. a server not physically located at a company's site but accessed through the Internet D. allows client computers to access a database E. hosts websites that can be accessed via the Internet Answer: B, E, C, D, A Diff: 1 Objective: 12.04 List the common types of servers found on client/server networks. 169 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 73) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. protocol token terminator honey pot frame A. special type of data packet B. computer system designed to attract unauthorized users C. device that absorbs a signal so that it is not reflected back D. set of common rules that control communications among network devices E. holds multiple data packets Answer: D, A, C, B, E Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 74) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. NOS NIC CSMA/CD P2P MAC address A. adapter card that connects a computer to a network B. used for internal identification of nodes on a network C. an operating system for network servers D. method used on Ethernet networks to avoid data collisions E. network in which each node connected to the network communicates directly with every other node Answer: C, A, D, E, B Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 170 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 75) Match each of the following networks to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. WAN LAN MAN PAN HAN A. links users in a specific geographic area (usually a city) B. network of two or more LANs C. a network in a small geographic area D. can be used for a small home-based business E. used by a single individual connecting devices using wireless media Answer: B, C, A, E, D Diff: 3 Objective: 12.03 Describe the common types of client/server networks as well as other networks businesses use. 76) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. switch firewall router bridge packet A. data broken into a small segment with an address to which it is sent B. makes decisions as to where data are to be sent and rebroadcasts them to the appropriate node C. software or hardware that prevents unauthorized entry to a network D. sends data between different collision domains on a single network E. device that sends information between two networks Answer: B, C, E, D, A Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 13 Behind the Scenes: How the Internet Works 1) The ________ is responsible for the Internet's domain name system and the allocation of IP addresses. A) ISOC B) ICANN C) W3C D) IAB Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 13.01 Describe the management of the Internet. 171 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 2) The main path of the Internet along which data travels the fastest is known as the Internet ________. A) protocol B) highway C) backbone D) cache Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: 13.02 Explain how the Internet's networking components interact. 3) High-speed ________ communication lines on the Internet backbone use fiber optics. A) IP B) OC C) DSL D) cable Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 13.02 Explain how the Internet's networking components interact. 4) Individual Internet users connect to ISPs through a(n) ________. A) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) B) T line C) optical carrier (OC) line D) point of presence (POP) Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 13.02 Explain how the Internet's networking components interact. 172 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) The main suite of protocols used for transmitting data on the Internet is ________. A) FTP B) TCP/IP C) SMTP D) POP Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 13.03 List and describe the Internet protocols used for data transmission. 6) ________ uses a dedicated connection between two points with the connection remaining active for the duration of the transmission. A) Packet switching B) An open circuit C) Circuit switching D) A closed circuit Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 13.03 List and describe the Internet protocols used for data transmission. 7) Which of the following information is NOT contained in a packet sent over the Internet? A) The size (in bytes) of the packet B) The address to which the packet is sent C) The address from where the packet originates D) The data that are transmitted Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 13.03 List and describe the Internet protocols used for data transmission. 8) A(n) ________ address is a unique number that identifies a computer, server, or device connected to the Internet. A) TCP B) IP C) SMTP D) NetBIOS Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 173 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 9) A(n) ________ address is a temporary IP address that is assigned from an available pool of IP addresses. A) dynamic B) static C) assigned D) transition Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 10) An IP address that does not change and is usually assigned manually by a network administrator or an ISP is called a ________ address. A) dynamic B) static C) fixed D) stationary Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 11) IPv6 was introduced when IPv4 ________. A) became too old B) was eliminated C) no longer had enough unique addresses D) was revoked Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 12) When checking to see whether a particular name is registered on the Internet, your computer accesses a database that is kept on a(n) ________ server. A) DNS B) URL C) FTP D) XML Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 13.05 Discuss how a numeric IP address is changed into a readable name. 174 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 13) An IP address in the form 197.169.100.1 is called a(n) ________. A) sequential access number B) dotted quad C) encryption key D) random number Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 14) In the URL http://www.pearsonhighered.com, which of the following is the top-level domain? A) http B) www C) pearsonhighered D) .com Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 13.05 Discuss how a numeric IP address is changed into a readable name. 15) Which of the following is NOT used in developing websites? A) XML B) KML C) DHTML D) HTML Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 16) Which of the following was created for the transfer of hypertext documents across the Internet? A) SSL B) HTTP C) FTP D) AJAX Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 17) <i> is an example of an HTML ________. A) marker B) tag C) indicator D) key Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 175 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 18) To boldface text in HTML, you would enclose your text in ________. A) <b> and </b> B) /b and b C) *b* and */b* D) HTM.bold.on and HTM.bold.off Answer: A Diff: 3 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 19) ________ describes the website content in terms of the data that is being described rather than how it is to be displayed. A) CGI B) JavaScript C) XML D) HTML Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 20) Which of the following organizations research new Internet technologies to improve its capabilities? A) Internet Architecture Board B) Internet Society C) World Wide Web Consortium D) Internet Engineering Task Force Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 13.01 Describe the management of the Internet. 21) A(n) ________ is a small program that resides on a server and is designed to be downloaded and run on a client computer. A) CGI script B) app C) applet D) JavaScript Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 22) The JavaScript ________ defines items on a web page such as graphics, tables, and headers as objects. A) SSL B) MIME C) JSON D) DOM Answer: D Diff: 3 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 176 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 23) Which protocol is used when sending files as attachments by e-mail? A) Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) B) Post Office Protocol (POP) C) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) D) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: 13.08 Discuss the mechanisms for communicating via e-mail and instant messaging. 24) In public-key encryption, the two keys, one for coding and one for decoding, are known as ________. A) code keys B) linked keys C) key tags D) a key pair Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: 13.09 Explain how data encryption improves security. 25) Which of the following is an example of an instant messaging service? A) LinkedIn B) Monster C) WhatsApp D) Flickr Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: 13.08 Discuss the mechanisms for communicating via e-mail and instant messaging. 26) ________ permits two or more people to communicate over the Internet in real time. A) E-mail B) Snapfish C) Flickr D) Instant messaging Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: 13.08 Discuss the mechanisms for communicating via e-mail and instant messaging. 27) Strong encryption now requires ________-bit keys. A) 40 B) 128 C) 256 D) 512 Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: 13.09 Explain how data encryption improves security. 177 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 28) The ________ is a consortium of organizations that develops web protocols and sets standards. Answer: World Wide Web Consortium (W3C); World Wide Web Consortium; W3C Diff: 2 Objective: 13.01 Describe the management of the Internet. 29) A typical ________ is made up of one or more network switches to which ISPs connect to each other. Answer: Internet exchange point (IXP); Internet exchange point; IXP Diff: 2 Objective: 13.02 Explain how the Internet's networking components interact. 30) ________ servers are computers that host software that enables users to buy goods and services over the web. Answer: Commerce Diff: 2 Objective: 13.02 Explain how the Internet's networking components interact. 31) ________ is the communications methodology where data are broken into smaller chunks to be sent over various routes at the same time. Answer: Packet switching Diff: 2 Objective: 13.03 List and describe the Internet protocols used for data transmission. 32) SMTP stands for ________. Answer: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Diff: 3 Objective: 13.08 Discuss the mechanisms for communicating via e-mail and instant messaging. 33) ________ is a method of communication in which a dedicated connection is formed between two points and the connection remains active during the transmission. Answer: Circuit switching Diff: 2 Objective: 13.03 List and describe the Internet protocols used for data transmission. 34) In the acronym HTTPS, the S stands for ________. Answer: Secure Diff: 3 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 35) The ________ IP addressing scheme uses 128-bit addressing. Answer: IPv6; IP version 6; Internet Protocol version 6; Internet Protocol v6 Diff: 3 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 178 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 36) 197.169.73.63 is an example of a(n) ________. Answer: IP address; Internet Protocol address; dotted decimal number; dotted quad Diff: 1 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 37) Within an URL, .com and .edu are examples of a(n) ________. Answer: top-level domain (TLD); top-level domain; top-level domain; TLD Diff: 2 Objective: 13.05 Discuss how a numeric IP address is changed into a readable name. 38) When using ________ addressing, a computer is assigned a temporary address from a pool of available IP addresses. Answer: dynamic; DHCP; Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Diff: 1 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 39) The IPv4 protocol is beginning to be replaced by the ________ protocol. Answer: IPv6; IP version 6; Internet Protocol version 6; Internet Protocol v6 Diff: 2 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 40) A(n) ________ links a URL to an IP address when a web page is requested. Answer: DNS server; Domain Name System server; Domain Name System (DNS) server Diff: 2 Objective: 13.05 Discuss how a numeric IP address is changed into a readable name. 41) When a(n) ________ address is assigned to a computer, its IP address will NOT change. Answer: static Diff: 1 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 42) In the URL http://example.gov, what is the second-level domain? Answer: example Diff: 2 Objective: 13.05 Discuss how a numeric IP address is changed into a readable name. 43) Transport Layer Security (TLS) and ________ are two protocols that provide data integrity and security for Internet transmission. Answer: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL); Secure Sockets Layer; SSL Diff: 3 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 179 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 44) PHP is a popular choice for coding ________ programs. Answer: server-side; server side Diff: 2 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 45) ________ is a commonly used scripting language for creating DHTML effects. Answer: JavaScript Diff: 2 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 46) DHTML stands for ________. Answer: Dynamic HyperText Markup Language; Dynamic HTML Diff: 3 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 47) <i> is an example of an HTML ________. Answer: tag; italics tag Diff: 2 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 48) ________ combines HTML, cascading style sheets, and JavaScript. Answer: Dynamic HTML; DHTML Diff: 2 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 49) A(n) ________ program is a computer program that runs on the client computer and requires no interaction with a web server. Answer: client-side; client side Diff: 1 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 50) A(n) ________ is a small program that resides on a server, is downloaded to the client, and runs when needed without additional data transfers between the client and server. Answer: applet Diff: 2 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 51) The MIME specification stands for ________. Answer: Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions Diff: 3 Objective: 13.08 Discuss the mechanisms for communicating via e-mail and instant messaging. 180 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 52) ________ is the process of encoding e-mail so that only the person with a corresponding key can decode and read the message. Answer: Encryption; Private-key encryption; Public-key encryption; Private key encryption; Public key encryption Diff: 1 Objective: 13.09 Explain how data encryption improves security. 53) When using ________-key encryption, only the message sender and recipient have the code. Answer: private Diff: 1 Objective: 13.09 Explain how data encryption improves security. 54) In ________- key encryption, two keys, known as a key pair, are created, where one key is used for coding and the other key for decoding. Answer: public Diff: 2 Objective: 13.09 Explain how data encryption improves security. 55) The United States government is the sole country in charge of the Internet. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 13.01 Describe the management of the Internet. 56) FTP enables files to be downloaded or uploaded between computers. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 13.03 List and describe the Internet protocols used for data transmission. 57) When using packet switching, packets are always sent over the same route. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 13.03 List and describe the Internet protocols used for data transmission. 58) File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is used to transmit e-mail messages across the Internet. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 13.03 List and describe the Internet protocols used for data transmission. 59) IPv6 uses six groups of 16-bit numbers. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 181 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 60) Dynamic IP addressing is accomplished using a DHCP server. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 13.04 Explain how each device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique address. 61) Client-side programs run on a web server rather than on your computer. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 62) An applet is a small application that resides on a server but is downloaded to, and run on, the client computer. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 63) Node.js is used to create faster animation. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 64) HTML is an acronym for Highly Textual Markup Language. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 65) The tag <i> informs a browser that the text that follows the tag should be italicized. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 66) XML technologies allow web pages to change after they have been loaded. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 13.06 Compare and contrast a variety of web development languages. 67) Java and JavaScript refer to the same language. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 13.07 Compare and contrast server-side and client-side application software. 68) Most instant messaging services provide a high level of encryption for their messages. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: 13.08 Discuss the mechanisms for communicating via e-mail and instant messaging. 182 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 69) Facebook Connect is one the most popular instant messaging services. Answer: FALSE Diff: 3 Objective: 13.08 Discuss the mechanisms for communicating via e-mail and instant messaging. 70) Match each of the following TCP/IP suite protocols to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. SMTP DHCP HTTP TCP IP A. transfers data from servers to browsers B. prepares data for transmission providing for error checking and resending lost data C. used for transmission of e-mail messages across the Internet D. sends data between computers on the Internet E. protocol that assigns dynamic IP addresses Answer: C, E, A, B, D Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 71) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. circuit switching PGP handshaking packet switching ICANN A. breaks information down into pieces that can take different paths B. a dedicated connection is formed between two communicating parties C. allocates IP addresses D. exchange of control packets between computers E. public-key package Answer: B, E, D, A, C Diff: 3 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 183 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 72) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. IP address key pair computer protocol static address dynamic address A. a set of rules for exchanging electronic information B. used in a common encryption technique C. temporary IP address for a computer that is assigned from a pool of available IP addresses D. IP address for a computer that does not change E. a unique identification number that defines each computer, service, or other device that connects to the Internet Answer: E, B, A, D, C Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 73) Match each of the following terms to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. second-level domain cascading style sheet instant messaging Internet cache private-key A. section of a hard drive that stores web page information B. used to decode an encrypted message C. list of rules that define how to display HTML elements D. communication between two or more people over the Internet in real time E. unique domain within another domain Answer: E, C, D, A, B Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter 184 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 74) Match each of the following servers to its definition: I. II. III. IV. V. DNS DHCP commerce web e-mail A. assigns users IP addresses for the duration of a session B. specifically deals with the SMTP communication method C. delivers HTML documents on request D. translates a domain name into an IP address E. enables users to purchase items over the Internet Answer: D, A, E, C, B Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) Chapter 14 Appendix A - The History of the Personal Computer 1) The first personal computer to come to the market in 1975 was the ________. A) Apple I B) Altair 8800 C) TRS-80 D) IBM PC Jr. Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: A.01 Describe the earliest personal computer ever designed. 2) A major advancement in the Apple II was storing the operating system ________. A) on a cassette tape B) on a floppy disk C) in ROM D) in RAM Answer: C Diff: 1 Objective: A.02 Describe the distinguishing features of the Apple I and Apple II. 3) The ________ was the first portable computer. A) TRS-80 B) Osborne C) IBM PC D) ENIAC Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: A.03 Describe the first portable computer. 4) Prior to the IBM PC, IBM primarily made ________. 185 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 A) networking equipment B) software C) copiers D) mainframe computers Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: A.04 Describe the development of the IBM PC. 186 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) BASIC's main advantage over FORTRAN, COBAL and ALGOL was ________. A) BASIC used a GUI interface B) Beginning programming students could easily learn BASIC C) Earlier programming languages were solely for accounting and statistical applications D) Bill Gates and Paul Allen used BASIC to program the Altair Answer: B Diff: 3 Objective: A.05 Explain why BASIC was an important step in revolutionizing the software industry. 6) The 5.25 floppy disk was a significant advancement because ________. A) it had a hard protective case B) they were readily available C) it facilitated saving programs and development of operating systems D) they were on every personal computer Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: A.06 Explain why the development of the operating system was an important step in PC development. 7) Virtually All PCs with Intel chipsets ran ________ by the early 80s. A) TRS-DOS B) CP/M C) MS-DOS D) Unix Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: A.06 Explain why the development of the operating system was an important step in PC development. 8) Each of the following are examples of Spreadsheet applications, EXCEPT ________. A) Access B) VisiCalc C) Excel D) Lotus 1-2-3 Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: A.07 List early application software that was developed for the PC. 9) ________ was the first computer with a graphical user interface, developed in 1972. A) Apple Lisa B) Xerox Alto C) Apple Macintosh D) Microsoft Windows Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: A.08 Describe the features of the Lisa and Macintosh computers and their predecessor, the Xerox Alto. 187 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 10) Which web browser was the first introduced? A) Mosaic B) Internet Explorer C) Netscape Navigator D) Chrome Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: A.09 List the first successful web browsers. 11) Who invented the first accurate mechanical calculator? A) Katherine Johnson B) Blaise Pascal C) Charles Babbage D) Herman Hollerith Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: A.10 Discuss the features of the Pascalene calculator and the Jacquard loom that inspired modern computer elements. 12) Who translated an Italian description of Babbage's Engine to English and added extensive notes, creating the best description of the machine? A) Joseph Jacquard B) Herman Hollerith C) Ada Lovelace D) Blaise Pascal Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: A.11 Discuss the contributions of Babbage's engines and the Hollerith Tabulating Machine to modern computing. 13) Grace Hopper gets credit for coining a common computing term by ________. A) removing a bug from a computer B) creating a program that translates English to machine language C) creating punch cards to be read by a computer D) removing fragments from a computer Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: A.12 Discuss the features of the Z1, the Atanasoff-Berry Computer, and the Mark I. 188 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 14) What concept introduced in the Turing Machine became the precursor to modern RAM? A) audio cassettes in an infinite loop B) Infinite paper tape which could be written to, erased, and changed C) punch cards arranges in an infinite loop D) reel to reel tapes Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: A.13 Discuss the major features of the Turing Machine, the ENIAC, and the UNIVAC. 15) Which invention replaced vacuum tubes in computers? A) Integrated circuits B) Magnetic tape C) Micro controllers D) Transistors Answer: D Diff: 1 Objective: A.14 Describe the milestones that led to each "generation" of computers. 16) The ________ computer introduced in 1975 had no keyboard or monitor and used switches on the front to enter data and lights on the front to display results. Answer: Altair 8800, Altair, 8800 Diff: 2 Objective: A.01 Describe the earliest personal computer ever designed. 17) Apple Computer was founded by ________ and Steve Wozniak. Answer: Steve Jobs, Jobs Diff: 2 Objective: A.02 Describe the distinguishing features of the Apple I and Apple II. 18) The Osborne was the first ________ computer. Answer: portable Diff: 2 Objective: A.03 Describe the first portable computer. 19) ________ used the term PC to market its first personal computer. Answer: IBM Diff: 2 Objective: A.04 Describe the development of the IBM PC. 20) John Kemeny and Thomas Kurtz revolutionized programming by developing the ________ programming language in 1964. Answer: Beginners All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code, BASIC Diff: 3 Objective: A.05 Explain why BASIC was an important step in revolutionizing the software industry. 189 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 21) Bill Gates developed the ________ operating system for IBM PCs in 1980. Answer: MS-DOS Diff: 2 Objective: A.06 Explain why the development of the operating system was an important step in PC development. 22) VisiCalc was the first ________ application. Answer: spreadsheet, spread sheet Diff: 3 Objective: A.07 List early application software that was developed for the PC. 23) A(n) ________ uses icons and a pointing device to allow users to interact with the computer. Answer: GUI, Graphical User Interface Diff: 3 Objective: A.08 Describe the features of the Lisa and Macintosh computers and their predecessor, the Xerox Alto. 24) Microsoft bundled its ________ browser in Windows 95. Answer: Internet Explorer, IE Diff: 1 Objective: A.09 List the first successful web browsers. 25) The Jacquard loom used holes punched in stiff ________ to make complex designs in fabric. Answer: cards Diff: 2 Objective: A.10 Discuss the features of the Pascalene calculator and the Jacquard loom that inspired modern computer elements. 26) ________ designed the Analytical Engine in 1834. Answer: Charles Babbage, Babbage Diff: 1 Objective: A.11 Discuss the contributions of Babbage's engines and the Hollerith Tabulating Machine to modern computing. 27) The Atanasoff-Berry Computer was the first to use ________ instead of mechanical switches. Answer: vacuum tubes Diff: 2 Objective: A.12 Discuss the features of the Z1, the Atanasoff-Berry Computer, and the Mark I. 28) The ________ was the first computer to use magnetic tape instead of punch cards. Answer: UNIVAC Diff: 2 Objective: A.13 Discuss the major features of the Turing Machine, the ENIAC, and the UNIVAC. 190 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 29) Bell Telephone Laboratories invented the ________, which replaced the vacuum tube. Answer: transistor Diff: 1 Objective: A.14 Describe the milestones that led to each "generation" of computers. 30) Babbage's engine was used for years as a mechanical calculator in odometers. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: A.11 Discuss the contributions of Babbage's engines and the Hollerith Tabulating Machine to modern computing. 31) Howard Aiken and Grace Hopper designed the Mark series of computers used by the U.S. Navy for ballistic and gunnery calculations. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: A.12 Discuss the features of the Z1, the Atanasoff-Berry Computer, and the Mark I. 32) The UNIVAC identified Dwight D. Eisenhower as the winner of the 1952 US Presidential race. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: A.13 Discuss the major features of the Turing Machine, the ENIAC, and the UNIVAC. 33) Bill Gates developed the floppy disk. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: A.06 Explain why the development of the operating system was an important step in PC development. 34) Match each of the following people with their important development: I. Steve Wozniak II. Bill Gates III. Blaise Pascal IV. Herman Hollerith V. Grace Hopper A. mechanical calculator that used gears to count by tens B. punch cards C. floppy disk D. debugging E. MS DOS Answer: C, E, A, B, D Diff: 2 Objective: Multiple Objectives in the Chapter Technology in Action, Complete, 15e (Evans et al.) 191 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 Chapter 15 Appendix B - Careers in IT 1) Jobs leaving the US for workers in other countries is known as ________. A) outsourcing B) offshoring C) outbounding D) offsourcing Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 2) Which of the following is NOT an example of an Enabler IT type career? A) business process analysts B) network administrators C) application developers D) project managers Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 3) A(n) ________ job deals with moving and storing information. A) customer interaction B) infrastructure C) enabler D) application developer Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 4) ________-based jobs involve a lot of travel for short term projects and the ability to work independently. A) Office B) Home C) Project D) Field Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 192 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 5) What type of job involves working at client locations for extended periods of time? A) Field-based B) System-based C) Office-based D) Project-based Answer: D Diff: 2 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 6) IT professionals generally work ________ hours per week and on-call than people in other professions. A) significantly fewer B) significantly more C) about the same D) exactly the same Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: B.02 Explain the various challenges of IT careers. 7) Which of the following is NOT a stressor in IT careers? A) Underrepresentation of women B) Constant change C) Repetitive work D) 24/7 on-call Answer: C Diff: 3 Objective: B.02 Explain the various challenges of IT careers. 8) The paths in the development and integration division of IT in a large corporation are systems development and ________. A) information systems B) support services C) web development D) project management Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: B.03 List and describe the various IT careers for which you can train. 9) Which IT professional primarily gathers information from end users, documents systems, and proposes solutions to solve problems in information systems? A) Systems analyst B) Programmer C) Project manager D) Database developer Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: B.03 List and describe the various IT careers for which you can train. 193 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 10) Which IT professional generates systems documentation for end users and programmers? A) Programmer B) Technical writer C) Network administrator D) Helpdesk analyst Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: B.03 List and describe the various IT careers for which you can train. 11) Which of the following skills are NOT typically necessary for game designers? A) Programming B) Artistic ability C) Special effects D) Video sequencing Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: B.03 List and describe the various IT careers for which you can train. 12) The IT role responsible for generating images for websites are ________. A) network administrators B) graphic designers C) web programmers D) interface designers Answer: B Diff: 2 Objective: B.03 List and describe the various IT careers for which you can train. 13) A good way to gain IT experience while pursuing your degree is ________. A) obtaining certification B) doing an internship C) researching the field and companies D) publishing articles in IT journals Answer: B Diff: 1 Objective: B.04 Explain the various ways you can prepare for a career in IT. 14) Which of the following is NOT a typical degree preparing students for careers in IT? A) Computer Science B) Management Information Systems C) Networking Systems D) Information technology Answer: C Diff: 2 Objective: B.04 Explain the various ways you can prepare for a career in IT. 194 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 15) Which resource for finding a career in IT should be available at all colleges? A) Career resource center B) Professional organizations C) Certification workshops D) CareerBuilder.com Answer: A Diff: 2 Objective: B.05 Explain the various ways you can find a career in IT. 16) You can find very accurate ________ information for your geographical area on the web including averages nationally and locally. Answer: salary Diff: 2 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 17) A business is ________ when they hire a third-party firm to provide business services previously handled by in-house employees. Answer: outsourcing Diff: 2 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 18) Outsourcing to a firm using employees located outside the US is known as ________. Answer: offshoring Diff: 2 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 19) Currently, about 26% of IT jobs are held by ________. Answer: women, females Diff: 2 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 20) A(n) ________ job requires a lot of self-discipline and has a very little supervision or commuting and travel. Answer: home-based, home based, telecommute, telecommuting Diff: 2 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 21) IT skills which move well between industries are considered ________. Answer: transferable Diff: 2 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 195 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 22) ________ time is the hours an employee must be available to work in the event of a problem. Answer: On-call, On call Diff: 3 Objective: B.02 Explain the various challenges of IT careers. 23) A web ________ generates the words and images that appear on a website and has interdisciplinary skills in areas outside of IT, including possibilities of journalism, editing, animation, or graphic design Answer: content creator Diff: 2 Objective: B.03 List and describe the various IT careers for which you can train. 24) ________ managers direct the overall systems development process: assigning staff, budgeting, reporting to management, coaching team members, and ensuring deadlines are met. Answer: Project Diff: 1 Objective: B.03 List and describe the various IT careers for which you can train. 25) ________ install and configure database servers and ensure that the servers provide an adequate level of access to all users. Answer: Database Administrators, DBAs, DBA Diff: 1 Objective: B.03 List and describe the various IT careers for which you can train. 26) To obtain a professional ________, you usually need to pass a written exam on specific IT skills. Answer: certification Diff: 2 Objective: B.04 Explain the various ways you can prepare for a career in IT. 27) Internships often provide valuable ________ in your intended line of work. Answer: experience, job skills, skills Diff: 2 Objective: B.04 Explain the various ways you can prepare for a career in IT. 28) Professional ________ like IEEE and ACM often provide a means to network with other IT professionals. Answer: organizations Diff: 1 Objective: B.05 Explain the various ways you can find a career in IT. 29) IT Jobs are among the slowest growing jobs in the near future. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: B.01 List the reasons why IT fields are attractive to students pursuing bachelor's degrees. 196 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net) lOMoARcPSD|10133946 30) IT skills are NOT transferable if the company you are working for becomes obsolete. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: B.02 Explain the various challenges of IT careers. 31) Professional certifications for IT skills replace a college degree in the eyes of most employers in IT. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Objective: B.04 Explain the various ways you can prepare for a career in IT. 32) Developing relationships with your instructors may help you land a career, because many still work in the industry. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Objective: B.04 Explain the various ways you can prepare for a career in IT. 33) Match each of the following IT roles with their best descriptions: I. network administrator II. programmer III. interface designer IV. helpdesk analyst V. project manager A. create a look and feel of a website B. solve problems for customers or employees C. involved in every stage of network planning and deployment D. supervise, organize, and coach team members E. build the software that solves problems Answer: C, E, A, B, D Diff: 2 Objective: B.03 List and describe the various IT careers for which you can train. 197 Copyright © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. Downloaded by u not getting info hahahha (nodgznspprabtiutyz@mrvpm.net)