Distribution and Spatial Interaction
advertisement
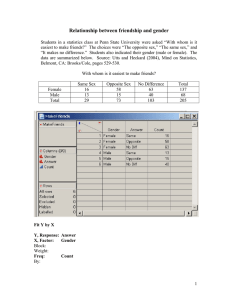
Distribution and Spatial Interaction • Distribution – arrangement of feature in space…properties of distribution… o Density: frequency something occurs • Arithmetic Density: total # of objects in an area (i.e. pop density – 340/sq km) • Physiological Density: # of persons per unit of area suitable agric (i.e. can country feed itself?) World Population Density Distribution (cont’d.) • Concentration: feature’s spread over space o Clustered/agglomerated: objects close together o Dispersed/scattered: objects far apart (see next slide) • Pattern: geometric arrangement of objects in space (square, rectangle, irregular, etc.) Density and Concentration of Baseball Teams, 1952– 2000 The changing distribution of North American baseball teams illustrates the differences between density and concentration. Time Space Convergence • Time-space convergence o The rate at which places move closer together in travel or communication costs o Results from a decrease in the friction of distance as space-adjusting technologies have brought places closer together over time • Global and local • Shrinking of space has important implications Time-Space Convergence • Friction of distance – Tobler’s 1st Law of Geog: everything is related to everything else, but nearer things are more related than distant things (i.e. distance itself hinders interaction). • Leads to distance decay: contact between two places decreases as distance increases Discuss • How much is Distance Decay an issue today? Is this something geographers might have to re-think? Quick Write: Think about where people are spaced in the US. Where are they clustered? Why there? Where is it dispersed? Why? Space-Time Compression 1492–1962 The times required to cross the Atlantic, or orbit the Earth, illustrate how transport improvements have shrunk the world. Spatial Interaction o Complementarity: we need each other • Ex. One area needs houses, other area has the trees for lumber o Transferability: cost involved in moving goods from one place to another • Cost • Ability to bear the costs • Variability • Space-Time Compression (see next slide) o Accessibility: is location accessible? Highways, RR, shipping? Ex: food very expensive in Alaska DIFFUSION • Process in which phenomenon (disease, trends, technology, etc.) spread from one place to another over time o Hearth: place of origination o Diff happens quickly today w/ modern technology, communication, transportation o The “S” Curve Types of Diffusion • 1.) Relocation Diff: spread b/c people move • Languages, Money, Aids • 2.) Expansion Diff: snowball process o A. Hierarchical diff: top down process • Fashion, Music o B. Contagious diff: like a wave without regard to hierarchy • Diseases, Fads o C. Stimulus diff: spread of underlying principle, even though characteristic itself failed to diffuse • Settlers in America – tobacco growers Hierarchical Diffusion Contagious Diffusion Hierarchical and Contagious Stimulus Diffusion