Measurement & Problem Solving Worksheet
advertisement
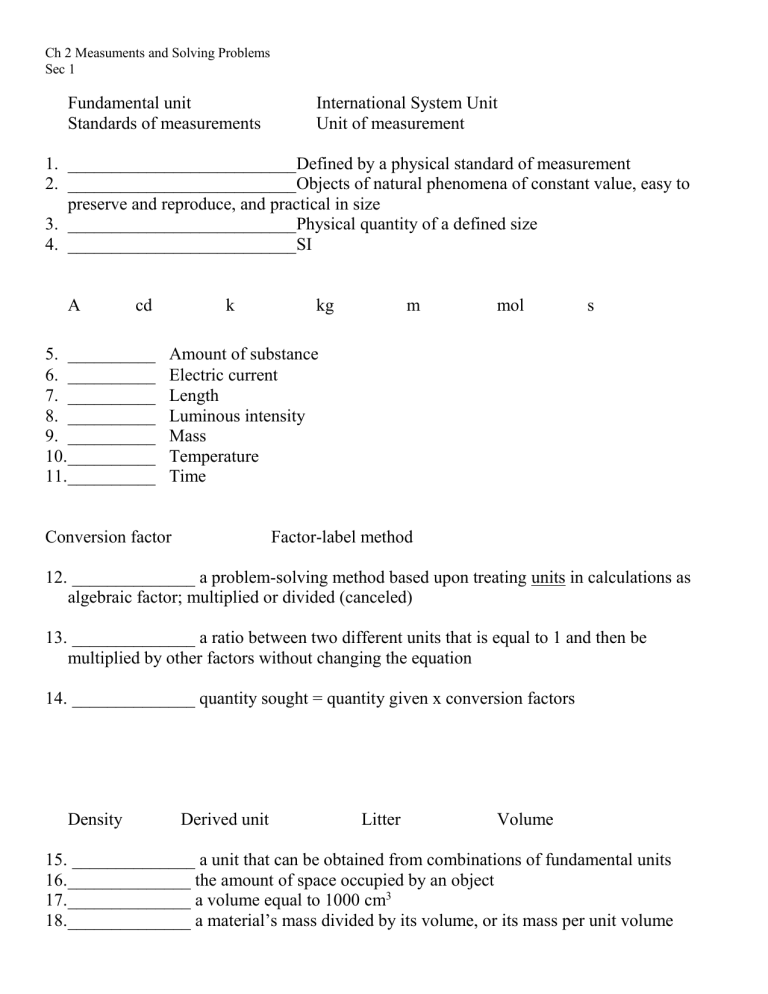
Ch 2 Measuments and Solving Problems Sec 1 Fundamental unit Standards of measurements International System Unit Unit of measurement 1. __________________________Defined by a physical standard of measurement 2. __________________________Objects of natural phenomena of constant value, easy to preserve and reproduce, and practical in size 3. __________________________Physical quantity of a defined size 4. __________________________SI A cd 5. __________ 6. __________ 7. __________ 8. __________ 9. __________ 10.__________ 11.__________ k kg m mol s Amount of substance Electric current Length Luminous intensity Mass Temperature Time Conversion factor Factor-label method 12. ______________ a problem-solving method based upon treating units in calculations as algebraic factor; multiplied or divided (canceled) 13. ______________ a ratio between two different units that is equal to 1 and then be multiplied by other factors without changing the equation 14. ______________ quantity sought = quantity given x conversion factors Density Derived unit Litter Volume 15. ______________ a unit that can be obtained from combinations of fundamental units 16.______________ the amount of space occupied by an object 17.______________ a volume equal to 1000 cm3 18.______________ a material’s mass divided by its volume, or its mass per unit volume Sec 2 Degree Celsius Heat or heat energy Kelvin Temperature 19. ______________ a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter 20. ______________ can be thought of as the sum total of the kinetic energies of the particles in a sample of matter 21. ______________ a unit of temperature on the Celsius scale 22.______________ the unit of temperature on the Kelvin scale and is the fundamental SI unit for temperature Calorie Heat capacity Joule Specific heat 23. ______________ the SI unit of heat energy and all forms of energy 24. ______________ the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water through one Celsius degree, equivalent to 4.184 J 25.______________ the amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of a given sample of matter by one Celsius degree 26.______________ the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by one Celsius degree Sec 3 Accuracy Percent error Precision Significant figures 27.______________ the closeness of a measurement to the true or accepted value of the quantity measured 28.______________ the closeness of a set of measurements to each other, need to be the same quantity, made in the same way 29.______________ Value accepted – Value experimental x 100% Value accepted 30.______________ all digits known with certainty (measured) plus one final digit, which is uncertain (estimated) Addition or subtraction Multiplication or division Scientific notation 31. ______________ the arithmetic result should be rounded off so that the final digit is in he same place as the leftmost uncertain digit 32.______________ the arithmetic product or quotient should be rounded off to the same number of significant figures as in the measurement with the fewest significant figures 33.______________ numbers are written in the form M x 10n Sec 4 Direct proportional Inverse proportional Variable 34.______________ a quantity that can change in value 35.______________ two variables that have constant ratio 36.______________ two variables that have a constant mathematical product Key 1. Unit of measurement 2. Standards of measurement 3. Fundamental unit 4. International System Unit 5. mol 6. A 7. m 8. cd 9. kg 10. k 11. s 12. Factor-label method 13. Conversion factor 14. Conversion factor 15. Derived unit 16. Volume 17. Liter 18. Density 19. Temperature 20. Heat or heat energy 21. Degree Celsius 22. Kelvin 23. Joule 24. Calorie 25. Heat capacity 26. Specific heat 27. Accuracy 28. Precision 29. Percent error 30. Significant figures 31. Addition/subtraction 32. Multiplication/division 33. Scientific notation 34. Variable 35. Directly proportional 36. Inversely proportional





![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)
