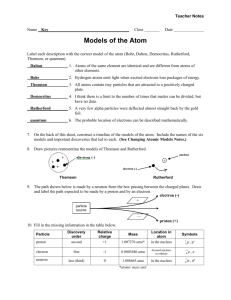
3.1 John Dalton’s (billiard balls) Atomic Theory had five main points: 1- Elements are made of extremely small particles called atoms. 2- Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. 3- atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4- Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. 5- In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated or rearranged. J.J Thomson (blueberry muffin/ plum pudding) discovered the electron using a cathode ray tube experiment. Sealed and removed air from the glass tube High voltage applied to metal electrodes at each end A “ray” was produced that started from the cathode (negative electrode) and streamed across to the anode (positive electrode). Thomson applied an electric field around the tube. Deflected when a negative field was applied, attracted when a positive was applied Concluded that the stream must be composed of negatively charged particles, later named electrons. Ernest Rutherford was J.J Thomson’s student and he is considered as “the father of nuclear chemistry” for his discovery of nucleus/protons in the atom. Rutherford wanted to prove the validity Thomson’s “plum pudding/blueberry muffin” model. He carried out a Gold Foil Experiment to do this. Rutherford shot small, positively charged alpha particles (helium nuclei) at a thin sheet of gold foil. (if Thomson’s model was accurate, the alpha particles would break through the thin foil like bullets through paper, with only minor deflections). This is not what happened! Most alpha particles passed straight through the foil. Some were deflected at various angles; others were reflected straight back toward the source. This did not support Thomson’s model. Only possible explanation to this: the deflection was caused by a concentrated positive charge at the centre of the atom. Since the deflection was backwards when struck directly, this means the positive charge at the centre of the atom must contain most of the atomic mass, and be very strong and stable. Since like charges repel, this also explains the slight deflection when alpha particles pass near it. Rutherford called this the nucleus of the atoms. (must be small, since only a small fraction of alpha particles stuck them – most passed through) therefore, atoms are mostly empty space. Rutherford’s discovery of the nucleus was so unexpected. With the nucleus at the centre, he proposed the electrons orbit around it at a relatively far distance, like planets orbiting the Sun. Rutherford later named the positive charges in the nucleus protons. James Chadwick worked with Rutherford to discover the Neutron. He found it because masses of the nuclei did not match masses of protons – both protons and neutrons have equal mass. Nucleus = very small compared to the overall atom, but very dense. Two atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes.